7th Grade Geology Review Sheet
advertisement

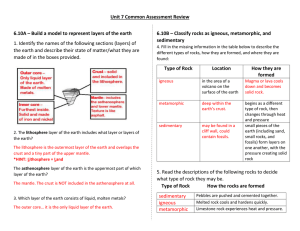
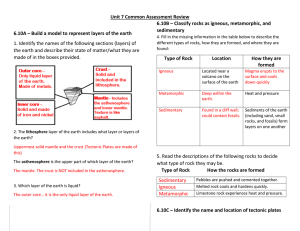
Geology Review Sheet 7th grade Science 2018-19 geological time the measurement of time from the formation of Earth to the present - on a geologic time scale - our lifespan is a blip, an insignificant length of time. You will hear people say things, “on a geologic time scale …” * Earth Structure: * geosphere or lithosphere the hard outer layer of Earth made of crust and hard, upper mantle; broken into tectonic plates * atmosphere the air that surrounds Earth * biosphere all the living things on Earth * hydrosphere Earth’s water, both in the seas and on land * Earth’s Layers: * crust the rigid outer layer of Earth * lithosphere the hard outer layer of Earth made of crust and hard, upper mantle; broken into tectonic plates * asthenosphere the fluid portion of the mantle that has special properties - it moves like silly putty * mantle the layer of Earth below the crust; upper part is solid and lower part is semisolid * inner core the solid layer at the center of the Earth * outer core the molten layer at the center of the Earth convection the heat transfer in a fluid which causes hot fluid to rise and cold fluid to sink, repeating in a cycle convection in the asthenosphere is what moves Earth’s plates Rock cycle the processes by which rocks are constantly being recycled and changed into different kinds of rocks minerals naturally occurring, usually inorganic (fancy word which means not from living things), solids consisting of a single element or compound that has a definite chemical composition and internal arrangement of atoms. Minerals are pure substances - they have an EXACT chemical recipe, or formula. Quartz is an example of a mineral - there is more oxygen in the earth’s crust than in the atmosphere because of the mineral quartz, show below. The chemical formula is SiO2 crystal an orderly arrangement of atoms or molecules. Crystal shape is a physical property that helps to identify a substance. Quartz crystals are shown to the left crystallize to form into crystals Igneous: * igneous rock a rock that forms when melted rock (magma or lava) hardens * lava molten rock on the surface of Earth vs. * magma molten rock under the surface of Earth * volcano an opening in Earth’s crust where lava, cinders, ash, and gases come to the surface dormant in terms of volcanoes, a volcano that is not presently erupting but is likely to in the future extinct in terms of volcanoes, a volcano that is not expected to erupt again Igneous Rock Examples: granite an igneous rock made of mostly quartz, visible as white crystals and feldspar, visible as little black specks obsidian is called volcanic glass because it is a rapidly cooling volcanic rock, shown below Metamorphic: * metamorphic rock a rock that has changed from ANOTHER ROCK because of heat, pressure, or a chemical reaction - think of it as having a parent rock Examples: marble a rock that derives from limestone as a result of pressure, temperature, and time gneiss a coarse-grained rock that has been subjected to extreme heat and pressure. The source rock is often granite, but it can also be from a sedimentary rock or another metamorphic rock. schist a highly metamorphosed rock that can come from different source rocks, including slate slate a metamorphic rock that forms when heat and pressure are applied to shale. Slate looks very similar to shale, but slate is much harder because of the compression. Sedimentary: * sedimentary rock a rock that forms when layers of sediments get stuck together * sediments particles of earth materials that are carried along by wind or water * weathering the process by which larger rocks crack and break apart over time to form smaller rocks * erosion the carrying away of weathered earth materials by water, wind, or ice * deposition the settling of sediments sand is rocks that are smaller than gravel but bigger than silt sandstone a sedimentary rock made of sand particles stuck together shale a sedimentary rock made of clay or silt silt rocks that are smaller than sand but bigger than clay limestone a sedimentary rock made mostly of calcite from deposits of ocean animal shells Plate Boundaries: plate boundaries the edge of a tectonic plate where earthquakes, volcanoes, and other tectonic activity takes place because of the motions of the plates plate a huge, irregularly shaped slab of the Earth’s lithosphere that fits together with all the other slabs to form the surface of the Earth plate tectonics a theory that says Earth’s outer layers are made of moving plates tectonic the movement of Earth’s crust tectonic plate sections of the lithosphere that move on top of the fluid asthenosphere; composed of Earth’s crust and the hard top layer of the mantle convergent boundary a boundary where plates move toward each other hotspot a volcanic area that forms as a tectonic plate moves over a place heated from deep within Earth subduction when one tectonic plate slides under another subduction zone a place along a convergent boundary where one plate moves under another plate divergent boundary a boundary where plates move away from each other transform a fault where two plates slide past each other transform boundary a boundary where plates move past one another earthquake when the ground shakes or moves suddenly due to the release of built up stress convection within the Earth’s crust or upper mantle; occurs along plate boundaries uplift when sections of Earth’s crust rise as tectonic plates move seismology the study of earthquakes fault a break in the earth’s crust either within a plate or between plates folding the deformation of rock layers in Earth’s crust as tectonic plates move hotspot a volcanic area that forms as a tectonic plate moves over a place heated from deep within Earth Landforms: terrain the physical features of land basin a large low area where sediments have been deposited plateau a large area of flat-lying sedimentary rock that has been lifted high above its original elevation terminal moraine an area of glacial sediment that forms at the farthest reaching point of a glacier continental shelf a relatively shallow area of the ocean, usually less than 200 meters deep, that surrounds a continent; the flooded part of a continent trench the deep area where oceanic plates are converging and sinking dome formed when magma pushes up from below Earth’s surface but doesn’t erupt. The rocks above are uplifted and the cooling magma forms an igneous core beneath talus jagged rocks found at the base of cliffs groundwater water that has soaked into the ground and fills up spaces between rocks or deposited materials Lab Vocab: carbonate a substance made of carbon and oxygen Extra Vocab: bedrock the rock that forms Earth’s crust elevation the vertical distance of the land’s surface above sea level