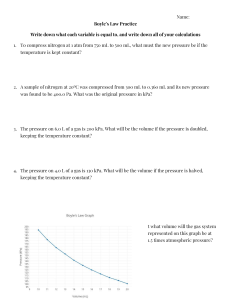
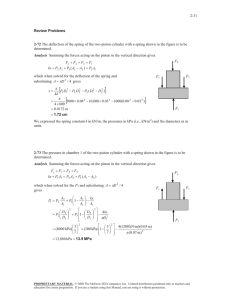
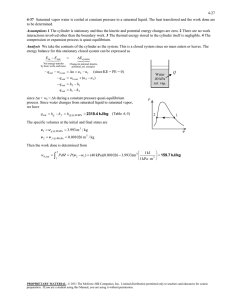
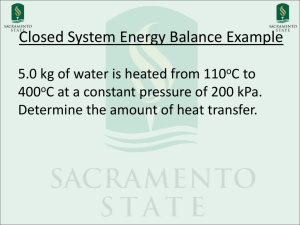
Properties of Pure substances
Air as a mixture of gases is pure. Water and its vapor in a tank is pure, but air and water
vapor in the liquid form in a tank is not pure .
Acetone
5
10
Acetone
250
3
225
2.
1
2. 9
3.
8
kJ
/kg
3000 kPa
-K
200
4
10
175
2. 8
T [°C]
P [kPa]
150
3
180°C
3
10
3. 2
130°C
1100 kPa
125
100
300 kPa
100°C
3. 4
75°C
75
kJ
/kg
2
10
-K
50
50 kPa
25
0.05
0.05
0.1
0.2
0
10-3
0.5
1
10
10-3
-2
10
-1
10
0
10-2
0.2
10-1
0.5
100
3
1
10
0.1
10
v [m /kg]
3
v [m /kg]
Go to plots> property plot and select the fluid to plot any property in EES
Critical point
Saturated liquid line
Saturated vapor line
Quality line
vapor
X= quality=
𝑚𝑣
𝑚𝑣 +𝑚𝑙𝑖𝑞
= dryness fraction
Liquid
For liquid line x=0, for vapor line x=1
101
g
3/k
1
L+v
T [°C]
150
Any two states are needed to describe
the thermodynamic property:
U(p,v), u(p,x) u(h,x) u(p,t)
2. 9
5m
3000 kPa
200
0. 3
4
0.0045
0. 1
1
0. 0
39
Acetone
250
1100 kPa
L
100
But at the saturated liquid or vapor line
Or inside the dome, P and T both can
not be used to determine
any property. Either P or T can be used
along with some other variable, say, x
V, s, h
v
300 kPa
50
50 kPa
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
0
-50
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
s [kJ/kg-K]
3.5
4.0
Acetone
1200
1100
Default unit system:
140 kPa
1000
4200 kPa
30 kPa
4.69 kPa
900
0.85 kPa
h [kJ/kg]
v=volume(water, p=500[kpa], x=.8)
v1=volume(steam, t=500[c], s=5.8[kj/kg-c])
770 kPa
800
0.9
700
0.8
600
0.6
500
0.4
400
300
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
s [kJ/kg-K]
3.5
4.0
4.5
Go to > help > help index> thermo physical property to see the property library in EES
Go to > help > help index> fluid property information to see various fluids for which you
can get the property
Real fluid and ideal gases
If you write the name of the fluid as : ‘methane’ then it is treated as real fluid
If you write that as: ‘ch4’ then it is treated as ideal gas
Internal energy and enthalpy of an ideal gas is a function of temp only, so no
other variable is needed if temp is specified.
h=enthalpy(air, t=400) { t is sufficient to find h}
h1=enthalpy(air, v=.2, s=4){ here two variables are needed since t is not given}
Example problem-1
A vessel having a volume of .4m3
contains 2 kg of liquid water and water
vapor mixture in equilibrium at a
pressure of 600kpa. (a) Find the volume
and mass of liquid , (b) volume and mass
of vapor
Example problem-2
A rigid vessels contains saturated ammonia
vapor at 20C. Heat is transferred to the
system until the temp reaches 40C. What is
the pressure at this point.
Example problem-3
A piston cylinder arrangement contains
air at 250kpa, 300C. The 50kg piston has
a dia of .1m and initially pushes against
the stops. The atmosphere is at 100kpa,
20C. The cylinder now cools as heat is
transferred to the ambient. (a) At what
temp does the piston begin to move
down, (b) How far has the piston
dropped when the temp reaches
ambient.
pf=100+50*g#/area*convert(pa,kpa)
area=pi*d^2/4; d=.1
v1_ac=area*.25; v1=volume(air,p=250,t=300)
m1=v1_ac/v1
t2=temperature(air,p=pf,v=v1) { final temp of air for piston to
come down}
v2=v2_ac/m1
v2=volume(air,p=pf,t=20)
h2=v2_ac/area; ht_fall=.25-h2
• The height of the stops
above the bottom of
cylinder is 0.25m