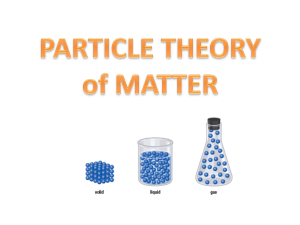
Chapter 4.1 (Textbook pg.139-148) ● Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space ● Classification of Matter: ● Particle Theory of Matter: Matter can be classified according to the particle theory of matter. a. All matter is made up of tiny particles. b. Each pure substance has its own kind of particle, which is different from the particles of other pure substances. c. Particles attract each other. d. Particles are always moving. e. Particles at high temperature move faster, on average, then particles at a lower temperature. ● Pure Substance: Matter that contains only one kind of particle. Can be divided further /classified into Elements and Compounds. a. Water (Distilled) b. Oxygen gas ● Mixture: Matter that contains more than one kind of particle. a. Ex: Salt Water (Mixture of Dissolved salt and Water) b. Ex: Air we Breathe (Mixture of Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, etc.) ● Element: A pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler parts by physical or chemical methods (example: heating, crushing, or grinding an element will not change it into a simpler form). a. Ex: Helium (He) used for balloons, Silicone (S) used to make electronic devices, Gold (Au) used to make jewellery and some electronics, etc. ● Compound: a pure substance made of two or more different elements that are chemically combined. a. Ex: Water is a compound made of the elements Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O). Because they are chemically combined, they can only be separated into their individual elements by a chemical method ● Methods of Separating Mixtures a. Mixtures are made of more than one kind of particle. b. Mixtures are physically combined, and as a result, can be separated by physical methods ■ Filter/ Filtration - Can separate Solids from Liquids or Gases ● Coffee grounds being separated from brewed coffee as the liquid passes through it. ■ Distillation - Can be used to separate liquids in a mixture (based on the desired liquids boiling point) ■ Magnet /Magnetic separation - the magnet will attract Iron and Steel ● Can be used to sort through scrap metal Chemistry, Society, and the Environment: ● Advantages: It allows for… making our lives healthier and safer. a. Industrial Production - Production of energy and materials b. Fertilizer and Pesticide Uses - Improvement in Crop yields c. Consumer Products - Increased variety of available products ● Disadvantages: It often causes… the release of toxic chemicals that are used or produced in manufacturing or isolation of elements or compounds, and are released into the environment. These can accumulate or react with other substances creating harmful byproducts. a. Industrial Production - Pollutants released into the atmosphere (air) and the waterways (water) b. Fertilizer and Pesticide Uses - Toxic accumulation of chemicals in soil and on food products c. Consumer Products - Direct exposure of toxic chemicals to humans