Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Worksheet
advertisement

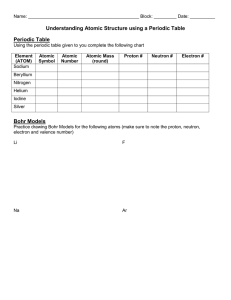
BLOCK: DATE: NAME: ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND THE PERIODIC TABLE ALCHEMY Picture Theory/Discovery Democritus (460 BC) This man came up with the theory that if you took a stone and cut it in half you would have two pieces with the same properties. If you continued to do this you would eventually reach the smallest particle, which he named “atomos”, which means indivisible. Dalton (1808) This scientist came up with the first atomic theory. That all matter is made of atoms, that all atoms of a given element are identical and that chemical reactions involve the combination (rather than the destruction) of atoms. He envisioned the atom as a solid, hard ball and grouped elements according to their atomic weight. J.J. Thomson (1897) This man discovered the electron. He imagined that an atom had chunks of negative particles scattered throughout a fluid smear of positive charge. This is early atomic theory is called the “plum pudding model”. Rutherford (1908) He came up with a revolutionary view of atomic structure thanks to his experiments with radioactive alpha particles. He suggested that the atom had a densely packed nucleus of positive charges surrounded by a ring of electrons (negative charges). Bohr (1913) This physicist studied light spectra which allowed him to come up with the theory that electrons can exist in different energy levels. This is shown with different sized rings (energy levels) of electrons orbiting an atom’s nucleus. Chadwick (1932) This man discovered the third type of subatomic particle: the neutron. Neutrons help to reduce the repulsion of protons, which helps keep the nucleus stable. Unlike protons and electrons, neutrons have no electrical charge. The Atom! Summary Dalton’s Original Theory of Matter: 1. 2. 3. 4. Current model of the atom: Summary of Subatomic Particles Charge weight symbol Location electrons protons neutrons Remember… # p+ = Atomic Number # e- = # p+ (assuming that most atoms are neutral: equal number of + and - ) 3 since… Atomic Mass = # p+ (Atomic Number) # n = Atomic Mass - Atomic Number + #n Atomic Number Atomic Mass Li Lithium 6.99 Observe the pictures of the following atoms, elements and compounds. Describe the difference between each of those pictures that you see. 1. What is/are the difference(s) between atoms and molecules? 2. What is/are the difference(s) between elements and compounds? 3. Describe the difference(s) between the molecules of an element vs. molecules of a compound. BOHR’S MODEL OF ATOMIC STRUCTURE Niels Bohr proposed that _______________ move around the _____________ of an atom in ___________ that are __________________ Bohr created a way to ________________ the structure of atoms(now called _____________________) RULES FOR DRAWING BOHR DIAGRAMS: e- orbit # + (a) Draw nucleus containing p and n (b) Fill e- orbits in order from inside to outside (c) Each e- orbit must be filled before starting to fill the next orbit (d) Each e- orbit can only hold a specific # of e- EXAMPLES Lithium (Li) Oxygen (O) # of e- the orbit can hold THE PERIODIC TABLE Examine a periodic table…What patterns (or trends) can you identify? Dimitri Mendeleev was one the first scientists to study the _______________ of elements Mendeleev organized the elements on the periodic table according to ______________ &_____________ that he observed in their properties (published his first book in the late 1860’s) today, many __________ of elements can be identified on the periodic table: (1) Metals and Non-Metals divided by the ____________________ line on the periodic table Metals to the _____________, Non-Metals to the ______________ the properties of metals and non-metal are very different: METALS NON-METALS (2) Semi-Metals (also called Metalloids) located along the line between the ______________ and _____________________ includes ______, ______, ______, ______, ______, ______, and sometimes _______ usually show both metal and non-metal characteristics Ex) Silicon - has a ________ lustre, yet it is an inefficient _______________ and is __________ (3) Transition Metals found in the ______________ of the periodic table have typical metal properties, but also have the following properties: (a) very ___________ (b) very high _______________ and _____________ points (c) have _______________ combining capacities (ion charges) (4) Periods PERIOD the _________________ rows of the periodic table lists elements in order of increasing ______________________ and ______________________ (5) Families contain elements that share similar ___________________________ Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals FAMILY the _____________________ columns of the periodic table Halogens Noble Gases (6) Diatomic (2-atom) Molecules there are certain ______________ that have elements that don’t like to N O F be by themselves ()…so they find one __________________ () ex) includes _____, _____, _____, _____, _____, _____, _____, and ______ called the “magic 7” + hydrogen. These elements form an imaginary figure 7 on the periodic table Cl Br I At