Cardiac Conditions: Anatomy, Disease, & Treatment
advertisement

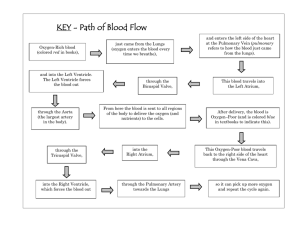
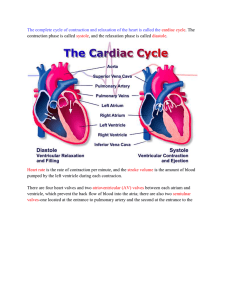
Cardiovascular II Cardiac Conditions Cardiac Anatomy • 4 Chambers • Walls = myocardium • Membranes endocardium = inner liner pericardium = outer sac Valves prevent backflow • tricuspid = Right AtrioVentricular valve • bicuspid/mitral = Left Atrio-Ventricular valve • semilunar= pulmonary @ base of pulmonary a. to lungs • Aortic – between left ventricle & aorta Cardiac valves Cardiac cycle • 1 heart beat: alternate atrial & ventrical contractions • Systole: max contraction of ventricles • Diastole: max relaxation to fill up • Vena Cava --- Rt Atrium----Rt Ventricle--Pulmonary a----Lungs---Pulmonary v-----Lt Atrium---Lt Ventricle----Aorta----Brain & Systemic circulation Conduction System • SA node: initiates beat • AV node: receives & sends impulse • Bundle of HIS: sends impulses to ventricles • Purkinje fibers: terminal branches in ventricles • Vagus n. X= inhibitor; slows HR via acetylcholine (rest) • Sympathetic nerves: accelerate HR via epinephrine (fight/flight) Coronary Artery Disease • S: brief periods of chest pain (CP) due to O2 insufficiency angina may last a few minutes triggers: phys activity, stress, heavy meal • E: coronary thrombosis 2° atherosclerosis • T: Nitroglycerine: dilates coronary arteries (4) immediately - sublingual lifestyle changes CABG if severe (70% +) and multiple blockages & EF 35% or less • R: same as for atherosclerosis CABG Coronay Artery Bypass Graft • Open heart surgery • Median sternotomy • Sternal precautions for 8-12 weeks - see handout • Internal Mammary a. or Saphenous vein graft • 2 – 4 bypasses may be needed Angioplasty • For single artery partial occlusions • Balloon tip catheter inserted into coronary artery • Balloon expands to crush plaque build-up • Stent placement often to keep it patent MI • S: severe, crushing CP, may radiate to neck, jaw, left arm; tight chest band; N & V, diaphoresis; W = SOB, anx, wk, palp, indig • E: occlusion of coronary artery • T: chew aspirin & 911 thrombolytics & anticoag tPA = clotbuster • R: fam Hx, CAD, angina, HTN, obesity, etc. <50% Ejection Fraction; 35% EF needs CABG Dx: CPK & Troponin enzymes, EKG, Hx Cardiac Arrest • • • • • • Sudden cessation of cardiac circulation=0% EF No significant heart pumping = 0% BP No significant electrical heart activity Flat-line EKG = no PQRST wave, no HR Collapse – apparent death – need CPR STAT E: V-fib, severe MI with massive cardiac death, drowning, suffocation, electrocution, drug overdose; vital organs receive no circulation • CPR and defibrillator Congestive Heart Failure • Usually develops slowly: cardiac output unable to meet the demands of the body • S: SOB, enlarged heart, irregular HR, tachy- or bradycardia, poor endurance, fatigue Rt = ankle edema +, distended neck veins, enlarged spleen: Rt ventricle weak Lt = pulmonary edema: Lt ventricle weak • E: Caused by MI, CAD, damaged heart valves, HTN, conduction system failures CHF CHF Medical Treatment • Diuretics – control fluid retention and BP • K+ supplementation & low salt diet • Digitalis – to ↑ pumping force of heart and cardiac output • Will need O2 supplementation eventually • Watch out for digitalis toxicity – lethargy and generalized weakness over a few days – caused by K+ depletion Cor Pulmonale • • • • • Very serious Rt sided failure Due to chronic lung disease Insufficient blood getting to lungs Severe hypoxemia; pulmonary HTN Hypertrophy of R ventricle due to ↑ work of heart • Need bronchodilators, supplemental O2, & eventually respirator Cor Pulmonale Mitral valve • Stenosis: narrowed or rigid, ↓ flow through it • ↑ resistance L atrium L ventricle • Blood backs up into L atrium & lungs • Congested veins in neck & lungs • Pulmonary edema • Poor circulation to body: cyanosis • Often 2 Rheumatic HD Aortic Valve • Stenosis: narrowed valve from L ventricle to aorta limits blood leaving ventricle • Blood backs up into L ventricle • L ventricle hypertrophies due to overwork • ↓ systemic circulation to body • ↓ blood to brain from aorta syncope • Atherosclerosis contributes Valve Insufficiency • Valve opening too large to prevent backflow • Leaking and regurgitation • Mitral V = blood leaks back into L atrium with every L ventricle contraction, causes congestion in lungs • Aortic V = backflow from aorta back into L ventricle overfills & dilates Rheumatic Heart Disease • Strep infection causes Rheumatic Fever & autoimmune reaction in children • Mitral valve inflamed • Vegetations develop on valve flaps • MV stenosis and/or insufficiency results in CHF with pulmonary edema (PE) • Blood stasis in atrium leads to thrombus & PE – need coumadin to prevent Rheumatic HD Endocarditis • • • • • • Strep infection of tooth, skin, UTI, UResp Vegetations filled with bacteria break off Emboli travel through circulation Go to brain, lung, kidney and infect Congenital heart defects often affected Need antibiotics whenever dental work is done Heart Block = BBB • Electrical impulses do not pass from SA node to AV node & bundle of His • Partial block = bradycardia results, decreased ventricle force, and heart failure • Complete block = need pacemaker Pacemaker A-fib and A-flutter • Rapid atrial contractions result in rapid and poor ventricle contractions = ↑ HR • Tachycardia & arrhythmia causes ↓ blood flow to brain @ times dizziness • Due to mitral stenosis, MI, idiopathic, meds, caffeine • Beta Blockers to ↓ ventricular rate • Coumadin to prevent clots & stroke • Cardioversion (shock) may help Normal EKG A-fib Pacemaker V-fib • Most serious arrhythmia • Chaotic electrical impulses cause ventricles to quiver instead of contract • No BP, EF of 0% cardiac arrest • Fatal within 4 minutes without CPR • Need defibrillator to re-start sinus rhythm • 5 PVC’s in a row can trigger V-fib V-fib V-fib Normal rhythm Pre Ventricular Contraction 5 PVC’s in a row can trigger V-fib Diagnostic Procedures • Auscultation – stethoscope for murmurs (valves) • EKG – arrhythmias, MI, CAD, valve disease • Echocardiogram – US record of heart in action: size, EF, shape, motion of heart valves & chambers • Cardiac catheterization – via vein into heart chambers to analyze cardiac output, pressure, etc. • Angiogram/arteriogram – x-ray with dye to show blockages ( may need CABG)