4. Cardiovascular System Cont. WEB
advertisement

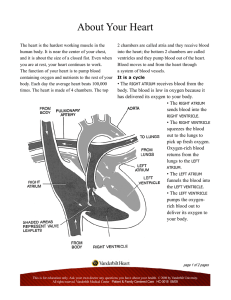
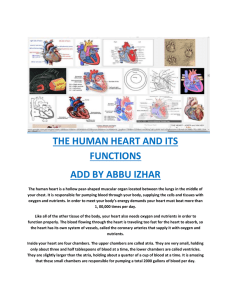
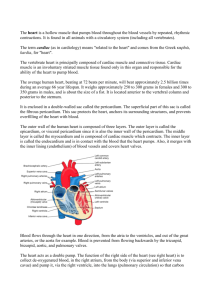
The Cardiovascular System Cont. Chapters 19, 20, 21 III. Heart • • Cardiac muscle tissue Four chambers • Right atrium • Right ventricle • Left atrium • Left ventricle • Atria are upper, less muscular chambers Heart Valves • Prevent blood from flowing back • Atrioventricular – Tricuspid – Bicuspid or mitral • Semilunar – Aortic – Pulmonary Functions of the Heart • • • • Generating blood pressure Routing blood Ensuring one-way blood flow Regulating blood supply – Changes in contraction rate and force respond to changing metabolic needs Cardiac Cycle • Repetitive contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of heart chambers • Normal blood pressure <120/80 • Measured by sphygmomanometer • High blood pressure = hypertension Circuits Pulmonary circuit Between the right side of the heart, to the lungs, and back to the left side of the heart Systemic circuit Between the left and right sides of the heart and the rest of the body Common Disorders of the Circulatory System • Anemia - lack of iron in the blood, low RBC count • Leukemia - cancer; white blood cells proliferate wildly • Hemophilia - bleeder’s disease due to lack of fibrinogen in thrombocytes • Heart murmur - abnormal heart beat caused by valve problems • Heart attack - death of heart muscle; happens when supply of blood to an area of heart muscle is blocked, usually by a clot in a coronary artery