Biochemistry Basics: Polymers, Monomers, & Enzymes
advertisement

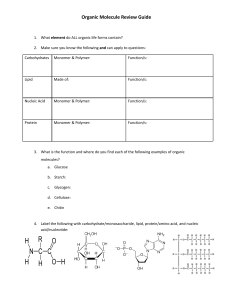
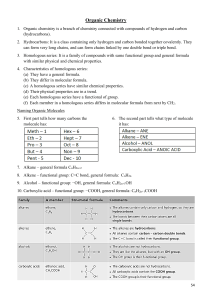
Carbohydrate (4) (polymer) Protein (4) (polymer) Lipid (4) (polymer) Nucleic acid (4) (polymer) Monosaccharide (monomer) Fatty acids and Glycerol (monomers) Amino Acids (monomer) Nucleotides (monomer) Provides quick energy Provides the most energy Regulates most cell function Make up the genetic information of living things Hydrolysis Dehydration synthesis Combines monomers into polymers by removing water Breaks polymers into monomers by adding water Enzyme (3) They are proteins A catalyst (speed up reactions) Lowers activation energy Their names end in -ASE Substrate (3) The substance the enzyme acts on Catalyst Activation Energy The substance that increases the rate of a reaction The minimum energy needed to undergo a chemical reaction Inhibitor Active Site Substance that slows down or stops a chemical reaction The region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate during a chemical reaction Product What the enzyme creates through the chemical reaction