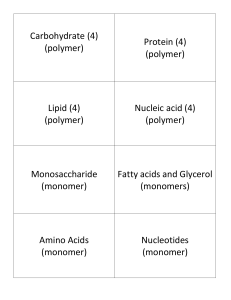
Organic Molecule Review Guide 1. What element do ALL organic life forms contain? 2. Make sure you know the following and can apply to questions: Carbohydrates Monomer & Polymer: Function/s: Lipid Made of: Function/s: Nucleic Acid Monomer & Polymer: Function/s: Protein Monomer & Polymer: Function/s: 3. What is the function and where do you find each of the following examples of organic molecules? a. Glucose b. Starch: c. Glycogen: d. Cellulose: e. Chitin 4. Label the following with carbohydrate/monosaccharide, lipid, protein/amino acid, and nucleic acid/nucleotide: 5. Hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen. It does so faster in the presence of catalase. i. What is the reactant? ii. What is the product/s? iii. What is the enzyme? 6. The pH scale is 1-14, what is an acid?___________what is a base?___________neutral?_______ 7. What is activation energy? 8. What does it mean that an enzyme is specific (lock & key)? 9. Define catalyst: 10. What type of an organic molecule is an enzyme? 11. Why is it important that an enzyme is reusable? 12. Label the following with catalyst (enzyme), substrate, active site and product: 13. What does it mean for an enzyme to be denatured? What happens to that enzyme? 14. What 2 things can denature an enzyme? 15. Looking at the graph of enzyme activity on the right, at what temperature does the following enzyme work the best? What is the optimum temperature for this enzyme? Explain your answer. 16. At what temperature does that enzyme begin to denature? How do you know? 17. Explain what the graph to the right is showing us about enzymes. Make sure to use important vocabulary like catalyst and activation energy when explaining.