Doc3
advertisement

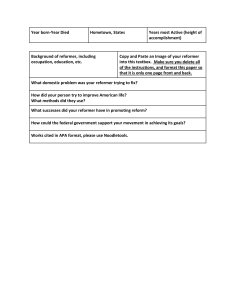
Susan Brownell Anthony is asocial reformer women's rights activist (Februaryand 15, 1820 – March 13, 1906) who played a pivotal role in the women's suffrage movement. Susan B. Anthony as a historical figure is synonymous with women’s political leadership. She is committed to social equality, she collected antislavery petitions at the age of 17. In 1856, she became the New York state agent for the American AntiSlavery Society. Louisa May Alcott was an American novelist and 29, poet best known as the (November 1832 – March 6, 1888) author of the novel Little Women (1868) and its sequels Little Men (1871) and Jo's Boys (1886). Writing her first successful book, Hospital Sketches, a collection of letters home; Little Women which brought her to fame was based on her actual family. She wrote short stories called lurid which usually involved powerful women, murder, suicide, madness, passion, and drug experimentation. Arthur Holly was an American physicist (September 10, 1892 – March 15, 1962) who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton Effect, which demonstrated the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation. It was a sensational discovery at the time: the wave nature of light had been well-demonstrated. He is also known for his leadership of the Manhattan Project's Metallurgical Laboratory. Theodore Roosevelt Jr. was an (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919) American statesman, author, explorer, soldier, naturalist, and reformer who served as the 26th President of the United States from 1901 to 1909. He also served as the 25th Vice President of the United States and as the 33rd Governor of New York. Roosevelt completed the transition to a strong, effective executive. Roosevelt did this through the force of his personality and through aggressive executive action. (August 1, 1779 – January 11, 1843) Francis Scott Key was an American lawyer, author, and amateur poet from Frederick, Maryland and later Georgetown, D.C., near Washington, D.C. who wrote the lyrics for a poem entitled at first "The Defence of Fort McHenry", which when set to an old English gentlemens' society tune, eventually became the United States' national anthem, "The Star-Spangled Banner".