Advantages and Disadvantages of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
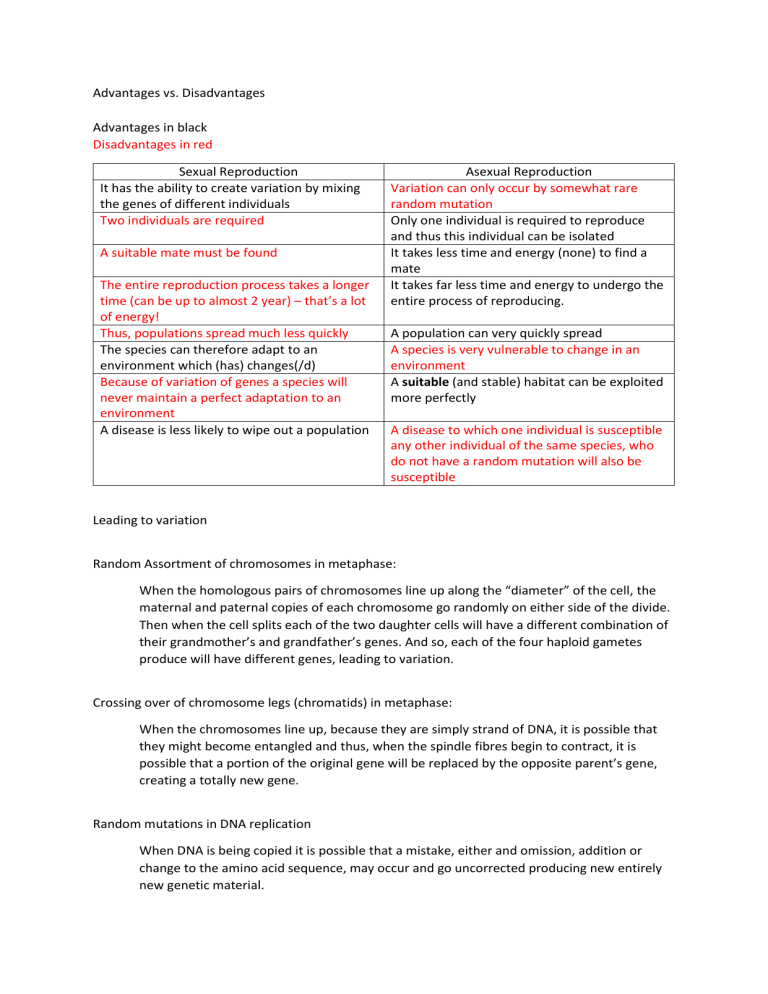
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
Advantages in black
Disadvantages in red
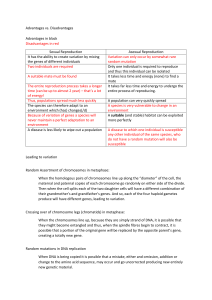
Sexual Reproduction
It has the ability to create variation by mixing the genes of different individuals
Two individuals are required
A suitable mate must be found
Asexual Reproduction
Variation can only occur by somewhat rare random mutation
Only one individual is required to reproduce and thus this individual can be isolated
It takes less time and energy (none) to find a mate
It takes far less time and energy to undergo the entire process of reproducing.
The entire reproduction process takes a longer time (can be up to almost 2 year) – that’s a lot of energy!
Thus, populations spread much less quickly
The species can therefore adapt to an environment which (has) changes(/d)
A population can very quickly spread
A species is very vulnerable to change in an environment
Because of variation of genes a species will never maintain a perfect adaptation to an environment
A suitable (and stable) habitat can be exploited more perfectly
A disease is less likely to wipe out a population A disease to which one individual is susceptible any other individual of the same species, who do not have a random mutation will also be susceptible
Leading to variation
Random Assortment of chromosomes in metaphase:
When the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up along the “diameter” of the cell, the maternal and paternal copies of each chromosome go randomly on either side of the divide.
Then when the cell splits each of the two daughter cells will have a different combination of their grandmother’s and grandfather’s genes. And so, each of the four haploid gametes produce will have different genes, leading to variation.
Crossing over of chromosome legs (chromatids) in metaphase:
When the chromosomes line up, because they are simply strand of DNA, it is possible that they might become entangled and thus, when the spindle fibres begin to contract, it is possible that a portion of the original gene will be replaced by the opposite parent’s gene, creating a totally new gene.
Random mutations in DNA replication
When DNA is being copied it is possible that a mistake, either and omission, addition or change to the amino acid sequence, may occur and go uncorrected producing new entirely new genetic material.
Fertilisation
The fact that any sperm cell can attach to the egg cell to produce a zygote and no gene is biased for or against means that we preserve existing genes and that each offspring has a
unique set of these existing genes.