Mechanics of Breathing Lesson
advertisement

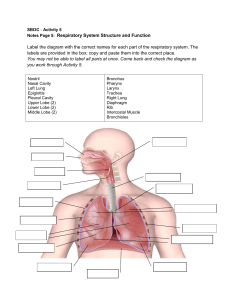
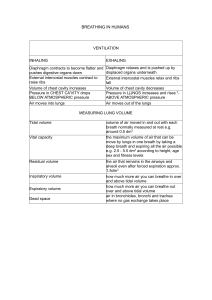
The Mechanics of Breathing Outline for Today’s Class 1. Air is a Gas 2. Polio and the Last of the Iron Lungs 3. The Mechanics of Breathing 4. Model Building 5. Exit Slip Air is a gas Gases move from areas of higher pressure to lower pressure or from high concentration to low concentration. The Iron Lung What Structures are involved in breathing? Review of the Lungs Pleura The pleura includes two thin layers of tissue that protect and cushion the lungs. The very thin space between the layers is called the pleural cavity. A liquid, called pleural fluid, lubricates the pleural cavity so that the two layers of pleural tissue can slide against each other. Intercostal Muscles and Ribs The intercostal muscles and ribs allow the ribcage and chest cavity it expand. The lungs expand to fill this increased space. This also helps to create negative pressure in the intrapleural space. Diaphragm The diaphragm is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle and tendon that serves as the main muscle of respiration and plays a vital role in the breathing process. How do these structures allow us to breathe? Exit Slip 1. Lowering the pressure in the pleural cavity causes the lungs to __________. 2. Contrary to popular belief lungs are not actually like large balloons, they are instead similar to________. 3. Did your model work? If not what do you think went wrong?

![The Breathing System Key Terms [PDF Document]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008697551_1-df641dd95795d55944410476388f877c-300x300.png)