MOS Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)
advertisement

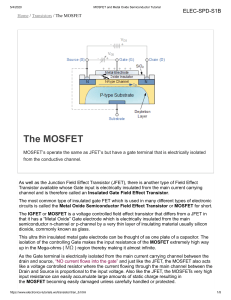
MOS Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) Made By: Group 8 Introduction What does (MOSFET) mean? It is the metal-oxide-semiconductor fieldeffect transistor. The MOSFET has become the most widely used electronic device, especially in the design of integrated circuits(ICs). A semiconductor is made of manufactured material that acts neither like a insulator nor a conductor. MOSFET is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. MOSFET- Basic Structure 3 terminal device: • Source • Drain • Gate VG =0 …. ISD=ID=0 VG <0 …. ID=0 VGS –Vt = v0V Structure and principle of operation We have a top view of MOSFET, the the gate length,L, and gate width, W. The overlap is made as small as possible in order to minimize its parasitic capacitance. Clear that L does not equal the physical dimension of the gate, but rather the distance between the source and drain regions underneath the gate. The overlap between the gate and Top view of an n-type the source/drain region is required to ensure that the inversion layer forms a MOSFET continuous conducting path between the source and drain region. Regions of MOSFET I-V Characteristics of MOSFET References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. http://www.ece.cmu.edu/~ee321/spring99/ LECT/lect20apr2.pdf http://wwwinst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee130/sp06/chp7full .pdf http://www.diodes.com/content_glossary/m osfet_transistor/ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tz62tq_KEc http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp? arnumber=00100256