ECEN - 3 2 5
advertisement

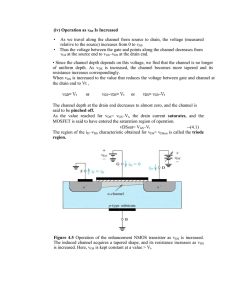
TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez Jose Silva-Martinez Texas A&M University Department of Electrical Engineering College Station, TX jsilva@ece.tamu.edu -1- TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez P-MOS Transistor: 4 terminal device Bulk Source P-type transistor Polysilicon S G B Gate N-Well P+ Diffusion Thin oxide B N+ substrate DIODE Drain Thick oxide G S P+ D D P+ N P-channel Polysilicon (heavily doped) -2- Basic elements: Diffusions + Oxidations + Polysilicon TAMU-ELEN-325 BASIC SCNA CMOS LAYERS J. Silva-Martinez P-channel MOSFET Physical Layer N-well Drain Silicon Nitride CVD Oxide Metal 1 Source Poly Gate Polysilicon Layer 1 p+ Polysilicon Layer 2 Gate Oxide n-well Bulk p+ p substrate P+ Ion Implant Bulk N+ Ion Implant Contact cut to n+/p_ N-channel MOSFET Metal 1 Source Via Oxide Cuts CVD Oxide Metal 1 Drain Poly Gate Metal 2 n+ Pad Contact (Overglass) Gate Oxide p substrate -3- Bulk n+ TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez N-MOS Transistor N-type transistor Inversion: channel is created D-S current is zero B VG>0 VS=0 D VD=0 G B P+ ---------- N+ P substrate N+ N+ S Inversion: Channel connects D and S Inversion channel means that a he number of D-S current is possible B VS=0 VG>0 quasi-free carriers are available and can VD>0 move from drain to source if a proper voltage P+ substrate N+ P ---------- is applied N+ IDS -4- TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez MOS Transistor Subthreshold (weak inversion) B P+ VT >VG>0 VS=0 N+ substrate N-type transistor VD>0 IDS Linear region Saturation -------- N+ P (NA) Subthreshold Mobile carriers concentration< NA VDS Saturation (Strong inversion) B P+ substrate VS=0 N+ VG>VT -------- VD>0 Subthreshold (extremely low-voltage lowpower applications) Linear region (voltage controlled resistor, linear OTA’s, multipliers) N+ P (NA) Saturation region (Amplifiers) Mobile carriers concentration< NA -5- TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez MOS Transistor STRONG INVERSION : BODY EFFECTS Thin oxide B Thick oxide VG=VT S D [ VT = VT0 + γ φ j0 − γ φ j0 − φ j0 − VChannel− B P+ substrate N+ N+ NA n=NA Polysilicon (heavily doped) γ= 2qε si N Bulk C OX γ = BODY FACTOR Threshold voltage: Voltage needed at the gate to create an inversion layer such that the number of carriers in the channel equals the bulk concentration (~1017-1018 electrons /cm3) -6- ] TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez MOS Transistor Two control capacitors: CG-channel and CB-channel Thin oxide B S Thick oxide VG=VT D CG-channel Voltage independent P+ N+ substrate N+ Its value depends of the gate area P depletion region Gate-channel resistance is extremely large CG-channel Channel substrate capacitance: Voltage dependent (εεsi/tsi) and non-linear Depends of the gate area Depends of the square root of the bulk doping -7- TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez MOS Equations in Linear Region VGS GND Drain current: Expression used in SPICE level 1 VDS ID = tox N+ W N+ ID L GND VGS VDS W µ n C OX (VGS −VT −0.5VDS )VDS L Linear approximation IDSAT VGS > VT tox N+ N+ W VDS VDSAT Non-linear channel -8- TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez MOS Equations in Saturation and Linear Region VGS GND - VT + VDS = VGS -VT - + Under these conditions ID = N+ W µ n C OX (VGS −VT )2 2L N+ Strong channel Weak channel VGS GND current is highest - VDS > VGS -VT + + - SATURATION REGION (VDS > VGS –VT ) Carriers are attracted to the drain, and swept in the region where channel is incomplete Current is till given by ID = W µ n C OX (VGS −VT )2 2L or N+ Strong channel N+ I DSAT = no channel -9- W µ n C OX (VDSAT )2 2L TAMU-ELEN-325 MOS MODEL: •Drain current, Triode region •Drain Current, Saturation region •Threshold voltage (zero bias) •Threshold voltage •KP (Spice Model) J. Silva-Martinez Fundamental equations i D = µCOX iD = W [VGS − VT − 0.5VDS ]VDS Leff µCOX 2 W Leff [VGS − VT ]2 [1+ λVDS ] VT 0 [ VT = VT 0 + γ 2φF + VSB − 2φF KP = µCOX - 10 - ] TAMU-ELEN-325 J. Silva-Martinez MOS MODEL: •KP Some values frequently used •N-MOS 10-4 A/V •P-MOS 0.3*10-4 A/V •VT0 N-MOS 0.7V P-MOS -0.9V •Vearly N-MOS 10 V/um P-MOS 15 V/um - 11 -