2.Transducer main characteristics exercises 5AT
advertisement

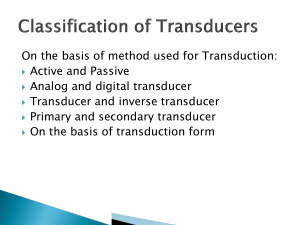
2.Transducer main characteristics exercises 5AT Join: 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. the difference between the real and the apparent value the detection of the smallest input reliability during time the calibration slope the amplitude and phase spectra the time required to reach the 69% of the final value threshold frequency the difference between the real and the theoretical value divided by the full scale value a. repeatibility b. accuracy c. resolution d. linearity error e. sensibility f. frequency response g. cut off frequency h. time constant Fill in the gaps: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. You can say something about the response speed of a transducer if you know its …................ The dynamic range is the interval of the …................ where the relation is linear. The …........... is the highest value of the output signal. The amplitude and phase spectra are the …................ When the temperature rises , the voltage output rises, when it goes down the output voltage goes down, but the value is smaller; there is............. When the threshold ...........is high , the transducer could ........... a fast signal. If ,when the input in zero, there is an output value, you have a........... ............ The ............. curve is the relationship between the input ............ and the output ................. True or false. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The linearity error is the ratio between the output and the input variation. The sensibility is the ratio between the input and the output variation. The time constant is the time in which the transducer output reaches the final value. The time constant is the time in which the transducer input reaches the final value. The cut off frequency is inversely proportional to the time constant. The resolution is the smallest change in the signal output. The cut off frequency is the highest frequency you can find into the signal. When you have a zero offset the calibration curve formula is y mx Answer the following questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is a calibration curve? Define the dynamical parameters. Definition of sensibility ( draw the calibration curve and the sensibility on it too). Define the time constant. What are the amplitude and phase spectra? What is the linearity error? Read and fill in the gaps Sensors and Actuators There are many different types of transducers, but at their most basic, they can be divided into two groups: input ( .............) and ..........(actuator). Input transducers take some sort of ...........energy — such as sound waves, temperature, or pressure — and convert it into a signal that can be read. A..................., for example, converts sound waves that strike its ..............into an electrical signal that can be transmitted over wires. A ................. turns the physical force being exerted on it into a number or reading that can be easily................. Actuators take an .....................and convert it ..........physical energy. A stereo speaker works by ...................the electronic signal of a recording into physical sound waves. ..............motors are another common form of electromechanical transducer, converting ............... into mechanical energy to ................a task. 1. Combining Transducers Many devices work by ......................sensors and actuators to convert energy from one form to another and then back ............... Audio cassettes, for example, are created by using a transducer to turn the ............................from the microphone pick-up — which converted the .............waves into an electrical signal — into ....................fluctuations on the tape head. These magnetic fluctuations are then ..........and ............by another transducer — in this case, the stereo system — to be turned back into an electrical signal. This signal is then fed by .........to speakers, which turn the electrical signal back into audio............. Ultrasound imaging also ........... by converting energy many times. A piezoelectric ................ is used to convert electricity into high frequency .....................(ultrasound), which are focused by the machine and aimed at body tissues. These waves bounce back to the machine, where a transducer converts ........ into electrical signals again. The signals are processed and ......... to a monitor to produce an ............ of the body ............. Other everyday tasks are .............. through the use of energy that is ........... multiple times. Turning on an electric light .............. electrical energy to be converted into visible ........... That electrical energy first had to be generated, however; an electrical ............ is a type of transducer that turns .................(or kinetic) energy into electricity that can then be .................other devices.