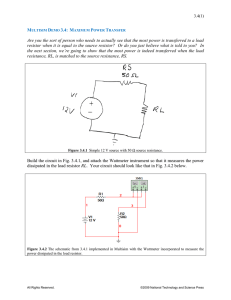
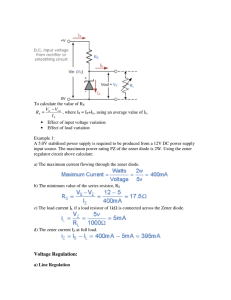
Power dissipation
advertisement

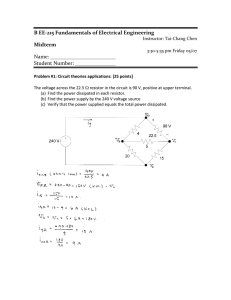
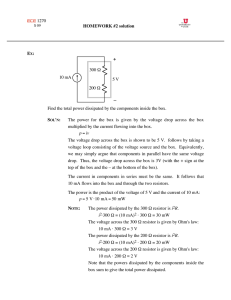
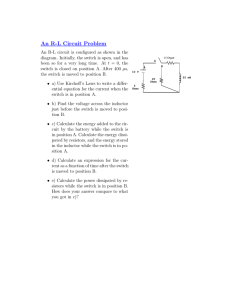
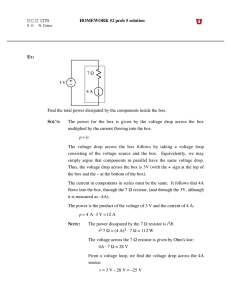
Power dissipation The power dissipated in a circuit element is the rate at which it transforms electrical energy into other forms, usually thermal energy. The power dissipated by a circuit element can be calculated by multiplying the voltage drop across the device by the current flowing through it. P = VI The unit for measuring power is the watt (W). Sample problem What is the power dissipated by a resistor if it has a voltage drop of 5.6V and a current of 550 mA. Solution P = VI P = 5.6 V × 0.55 A P = 3.08 W Rounding to 2 significant figures gives an answer of 3.1 W. Additional question Calculate the power dissipated in the following cases. (a) A heating element has a current of 12 A when connected to a 240 V supply. (2.9 × 103 W) (b) A television set on standby (ready to be activated by a remote control) draws a current of 70 mA when connected to a 240 V supply. (17 W) (c) A diode has a current of 120 mA when forward biased with a DC voltage of 0.70 V. (8.4 × 10–2 W) (d) A zener diode has a current of 400 mA with a reverse bias (breakdown) voltage of 35 V. (14 W) Jacaranda Physics 2, 2nd edition © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 2004 1