Voltage Regulation:
advertisement

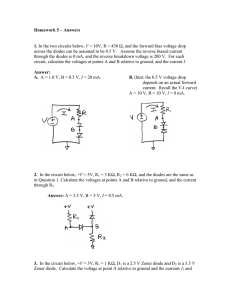
To calculate the value of RS V − Vout RS = in , where IS = IZ+IL, using an average value of IL. IS • Effect of input voltage variation • Effect of load variation Example 1: A 5.0V stabilised power supply is required to be produced from a 12V DC power supply input source. The maximum power rating PZ of the zener diode is 2W. Using the zener regulator circuit above calculate: a) The maximum current flowing through the zener diode. b) The minimum value of the series resistor, RS c) The load current IL if a load resistor of 1kΩ is connected across the Zener diode. d) The zener current IZ at full load. Voltage Regulation: a) Line Regulation In this type of regulation, series resistance and load resistance are fixed, only input voltage is changing. Output voltage remains the same as long as the input voltage is maintained above a minimum value. Percentage of line regulation can be calculated by = ∆Vout × 100 ∆Vin where Vout is the output voltage and Vin is the input voltage and ∆Vout is the change in output voltage for a particular change in input voltage ∆Vin b) Load Regulation In this type of regulation, input voltage is fixed and the load resistance is varying. Output volt remains same, as long as the load resistance is maintained above a minimum value. V − VFL Percentage of load regulation = NL × 100 VNL where VNL is the mini. load resistor voltage and VFL is the full load resistor voltage. Example 2: Say Vin =20V, Vout required is 15V over a load current range from 10mA to 20mA. Design the regulator circuit. Solution: Average load current =(10+20)/2 = 15mA. Let the diode has IZT = 6mA. Therefore, zener must be able to handle maximum IL(average)+6mA = 15+6=2mA. Therefore, PZ = 15Vx21mA =315mWatt. You need a Zener diode having power rating more than 315mW. RS = (Vin – Vout)/Iin(max) = (20-15)/21 = 238 ohms Resistor power rating = V2/RS = 52/238 = 0.1W ** Calculate load regulation (home work)