Magnetism and Electricity Study Guide and Reflection Journal
advertisement

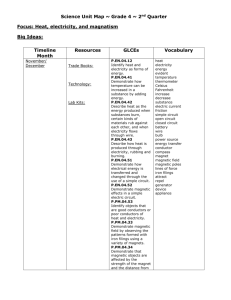
__________________________ # ____ G Se Si Science Big Idea #2: Physical and Chemical Science: The student will produce evidence that demonstrates understanding of: S4C.2.3 Magnetism and Electricity *Magnets attract and repel each other and certain kinds of other materials; electricity in circuits can produce light, heat, sound, and magnetic effects; electric circuits require a complete loop through which an electric current can pass. through scientific connection, scientific thinking, use of scientific tools and technology, conducting scientific investigations, and engaging in scientific communication. In this portfolio you will need to keep: Your investigation worksheets Word bank Any notes from class discussions Essential Question: How does energy change from one form to another as it moves through a system? Big Ideas □ Magnets and electricity produce related forces. □ Electric circuits may produce or use light, heat, sound, mechanical, and magnetic energy. (S4C.2.1.3) □ Electric circuits require a closed pathway through which an electric current can pass. (S4C.2.1.3) □ Materials have different properties. Some materials transfer heat more rapidly than others or some materials conduct electricity better than others. (S4C.1.1.1) □ When electric charges are made to flow through a material they produce an electric current. □ Charges can flow more easily through conductors than insulators. □ The atoms in conductors have loosely held electrons that can move freely. Electrons in insulators cannot move freely among atoms. □ □ □ □ □ □ □ Current flow is affected by the energy of the charges and the properties of the objects that the charges travel through. The four factors that determine the resistance of an object are diameter, length, material, and temperature. If more than one path is available, more current will flow through the path that has the lower resistance. All electric circuits have these basic features: devices that run on electrical energy, sources of electrical energy, and conducting wires. A series circuit has only one path for the current to take. A parallel circuit has more than one path for the current to take. Shocks can be prevented with devices that redirect current or break circuits (examplesthird ground prong, fuses, and circuit breakers). ________________’s ’s Magnetism and Electricity Reflection Journal Date One Two Three Four My reflection of what I learned today. Date Five Six Seven Eight Nine My reflection of what I learned today. Magnetism Vocabulary 1) force: a _________________ or ________________ that can cause an object to move. 2) magnet: is any material that attracts ______________ and materials that contain iron. 3) magnetic pole: the ends of a magnetic object. 4) magnetism: the ___________________ and repulsion of magnetic materials. 5) attract: to _________________ together. 6) repel: to ___________________ apart. 7) magnetic force: the ___________________ or _________________ between magnetic poles. 8) magnetic field: the area of __________________ force around a magnet. 9) magnetic field lines: are lines that map out the ___________________ magnetic field around a magnet. 10) compass: a device that has a magnet on a needle that spins freely 11) electromagnet: a magnet created by wrapping a ________ of wire with a current running through it around a core of material that is easily magnetized. 12) temporary magnet: a piece of _____________ that acts like a _______________ when it is touching a _____________________ magnet. 13) induced magnetism: the power of a _____________________ magnet’s magnetic field on a piece of __________ which makes the iron act like a ___________. Magnetism Content □ Magnets stick to _________________________. □ Magnetic poles that are _________________ attract each other, and magnetic poles that are alike ___________________ each other. □ Magnetism can be _________________ only in iron or steel (and a few other metals). □ The magnetic force acts through space and most ________________________. □ The magnetic force of attraction between two magnets decreases with _____________________________. So, the greater the distance between two magnets the weaker the force of attraction. □ Compasses, iron ______________________, and iron objects can be used to detect magnetic fields and magnetic field lines. □ Magnetic _____________________________________ spread out from one pole, curve around the magnet, and return to the other pole. □ Just like a bar magnet, Earth has a magnetic field around it and _______ magnetic poles. □ An electric current produces a magnetic ___________________. □ The magnetic field produced by a current has __________________________ and a direction, and the field can be turned on or off. Electricity Vocabulary 1) electric force: the _____________ between charged objects. 2) electric energy: the energy of __________________ charges. 3) electric field: a region around a charged object where the object’s electric force is exerted on other charged objects. 4) electricity: the interaction between ____________________ charges. 5) electric current: the continuous flow of electric ________________ through a material. 6) electric circuit: a complete, unbroken or ________________ path through which electric charges can flow. 7) system: a group of interacting ________________ or __________________ components. 8) components: devices or parts of an electric circuit system that transfer electrical energy to heat, light, sound, or mechanical energy. 9) switch: a device used to ___________ and ____________ circuits. 10) open circuit: an __________________ circuit through which electricity will NOT flow. 11) closed circuit (or pathway): a __________________ circuit through which electricity will flow. 12) conductor: a material through which a charge or electricity can _______ through easily. 13) insulator: a material such as rubber, that do NOT allow _________________ to flow. 14) resistance: the __________________ of how ____________________ it is for charges to flow through an object. 15) series circuit: a circuit with only one ______________ for current to flow. 16) parallel circuit: a circuit with __________ pathways for current to flow. 17) electricity source: provides the _________________ to light a bulb or run a motor. 18) D-Cell: a _________________ of electricity. 19) battery: a set of cells that work together to make ________________________. 20) electricity receiver: a ______________________ that uses electricity from the source to make something happen (ex. light, heat, sound, or movement). 21) transfer: the act, or process of ___________________from one form to another form 22) heat: the transfer of thermal energy from a warmer object to a ___________ object. 23) mechanical energy: energy connected to __________________ or position of an object. 24) static electricity: the buildup of ___________ on an object. 25) protons: a ______________ charged particle. 26) electrons: a _________________ charged particle. 27) static discharge: the loss of static _____________________ as electric charges transfer from one object to another. 28) friction: the force that ______ surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. 29) charging by friction: is the transfer of _________________ from one uncharged object to another by _________________ the objects together. 30) charging by conduction: is the transfer of ____________________ from one object to another by direct ____________________. 31) charging by induction: is the movement of a charge on an object by using the electric field of another without direct _____________________. 32) schematic diagram: a way to _________________ a circuit on a piece of paper. 33) graph: a ______________ aide that shows a relationship of _______________ things. 34) prediction: an educated __________________ based on __________ or prior ______________________. 35) intersection: a point where ______________ lines cross. Electricity Content □ Charges that are the same _______________ each other. Charges that are different _________________each other. □ A few methods by which charges can redistribute themselves to build up static electricity are: by _____________________ , by ____________________ , and by _______________________________. □ Friction increases when surfaces push harder against each other. In general smooth surfaces produce less friction. Friction acts in a direction ______________________ of the direction to the objects motion. Without friction, a moving object will not stop until it strikes another object. □ When electric charges are made to flow through a material they produce an ___________________________________________. □ The atoms in ______________________________ have loosely bound electrons that can move freely. Electrons in insulators cannot move freely among atoms. □ The four factors that determine the resistance of an object are ________________, length, material, and _________________________. □ All electric circuits have the same basic features: devices that are run by electrical energy, __________________________of electrical energy, and conducting wires. □ A _______________________ electrical circuit will transfer chemical energy stored in a battery to light, sound, heat, mechanical, or magnetic energy. □ When an electrical circuit has all the components in one loop so there is only one pathway for the electricity to flow, it is called a __________________ circuit. □ Disadvantages of a series circuit which has only _____ path for electric current to take: o A burned-out bulb is a break in the circuit, and there is no other path for the current to take. So if one light goes out, the other lights go out as well. o The light bulbs in the circuit become dimmer as more bulbs are added because the resistance within the circuit decreases. o In a multi-light circuit, a switch will either turn on or off all of the lights together. □ In a _____________________ electric circuit, the different components or parts are on separate branches. □ Advantages of a parallel circuit which has _______ than one path for electric current to take: o Each bulb (electric receiver) is connected by a separate path from the energy source (battery) and back to the battery. o A burned-out bulb in one branch, will not break the circuit in the other branches, so charges still move through the other branches and the components continue working. So, if one bulb goes out the other remain lit. o Switches can be added to each branch to turn components on and off without affecting the other branches. o The light bulbs in the circuit remain the brightness as more bulbs are added because each bulb is directly connected to the electric source (or battery). □ When two or more batteries are used in a circuit, the batteries must point in the ___________________ direction.