COURSE OUTLINE
advertisement

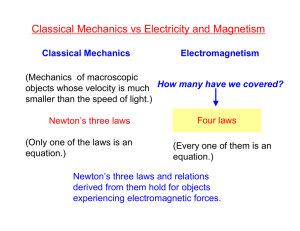
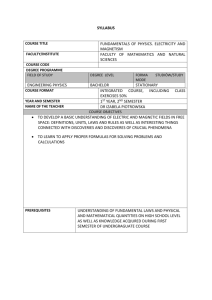
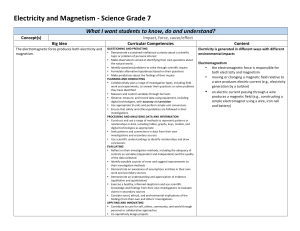
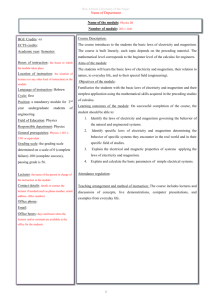
COURSE OUTLINE Central Arizona College 8470 N. Overfield Road Coolidge, AZ 85228 Phone: (520) 494-5206 Fax: (520) 494-5212 Prefix/Number: PHY262 Course Title: University Physics II: Electricity and Magnetism Course Description: Calculus-based treatment of the principles of physics covering electricity and magnetism, light, and thermodynamics. Semester Hours: 4 Times for Credit: 1 Lecture/Lab Ratio: 3 Lectures, 3 Labs Pre-requisites: PHY261, MAT221; RDG100A or RDG100B Co-requisites: MAT 231 Cross Listed: None Grading Options: A/F Approved Modalities: F2F Central Arizona College PHY262 - University Physics II: Electricity and Magnetism Page 2 of 2 Learning Outcome Statements: Standards: Upon completion of this course the student will be able to: The student will meet the learning outcomes at the following level, degree or measurement: 1. Demonstrate knowledge of principles, methods and applications of physics in the areas of electricity and magnetism and themodynamics. • Use Coulombs law to calculate the net force and electric field on a charged particle due to other charged particles located nearby. 2. Define the basic properties of electrical charge, the electrostatic force and the electric field. • Determine the motion of a charged particle moving in a magnetic field. • Use Ohms and Kirchhoff’s laws to find the current in DC circuits. 4. Define capacitance and inductance in an electrical circuit. • Measure capacitance and inductance in an electrical circuit. 5. Outline the relationship between electric and magnetic fields and their interdependence. • Calculate the impedance and current flow in an RLC series AC circuit. • State two ways to produce a magnetic field. • Define the characteristics of an electromagnetic wave, give examples, and contrast this with the characteristics of a sound wave. • Explain which basic property of matter temperature measures. • Define the calorie and relate this to specific heat. • Utilize basic laboratory equipment to measure quantities such as current, voltage, resistance and impedance, and temperature, heat capacity, and specific heat. 3. Apply Ohms Law and Kirchhoffs Laws. 6. Explain the concepts of temperature and heat in terms of kinetic theory. 7. Explain the concepts of specific heat and latent heat. 8. Using the method of observation and scientific inquiry, students will demonstrate their knowledge of concepts and principles by implementing and interpreting the outcome of laboratory experiments. AGEC/Special Awareness Area: Biological & Physical Sciences Revised: 10/2006