Free Trade Accounts (FTAs)
Background
The Circular on the Implementation Rules on Separate Accounting Business in the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade
Zone (Interim) and the Rules for the Prudential Management of Risks Relating to Separate Accounting Business in the
China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone (Interim) (Circular 46) was released on May 21, 2014. The circular stated that
companies operating in the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone (hereinafter referred to as the “Shanghai FTZ”) would
be allowed to open free trade accounts (hereinafter referred to as “FTAs”) within the Shanghai FTZ to facilitate the free
movement of funds with outside mainland China.
Outline
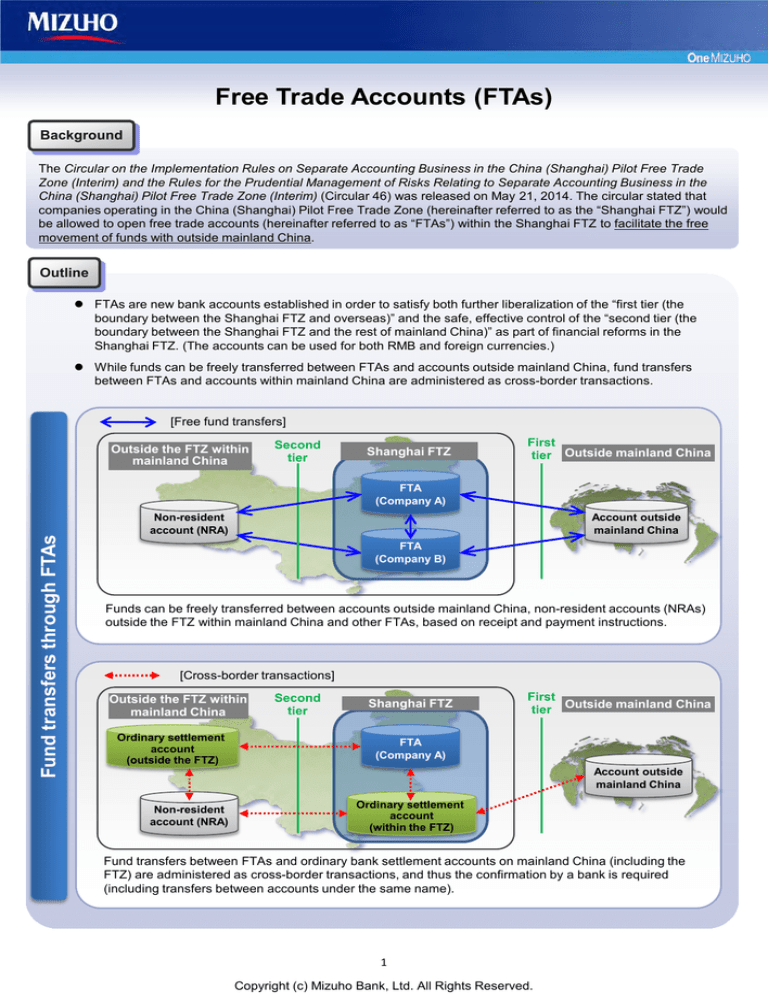
FTAs are new bank accounts established in order to satisfy both further liberalization of the “first tier (the
boundary between the Shanghai FTZ and overseas)” and the safe, effective control of the “second tier (the
boundary between the Shanghai FTZ and the rest of mainland China)” as part of financial reforms in the
Shanghai FTZ. (The accounts can be used for both RMB and foreign currencies.)
While funds can be freely transferred between FTAs and accounts outside mainland China, fund transfers
between FTAs and accounts within mainland China are administered as cross-border transactions.
[Free fund transfers]
Outside the FTZ within
mainland China
Second
tier
Shanghai FTZ
First
tier Outside mainland China
Fund transfers through FTAs
FTA
(Company A)
Non-resident
account (NRA)
Account outside
mainland China
FTA
(Company B)
Funds can be freely transferred between accounts outside mainland China, non-resident accounts (NRAs)
outside the FTZ within mainland China and other FTAs, based on receipt and payment instructions.
[Cross-border transactions]
Outside the FTZ within
mainland China
Ordinary settlement
account
(outside the FTZ)
Second
tier
Shanghai FTZ
First
tier Outside mainland China
FTA
(Company A)
Account outside
mainland China
Non-resident
account (NRA)
Ordinary settlement
account
(within the FTZ)
Fund transfers between FTAs and ordinary bank settlement accounts on mainland China (including the
FTZ) are administered as cross-border transactions, and thus the confirmation by a bank is required
(including transfers between accounts under the same name).
1
Copyright (c) Mizuho Bank, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Offshore financing through FTAs
Background
The Circular on the Implementation Rules for Macro-prudential Management of Offshore Financing and
Cross-border Capital Flows for Separate Accounting Business in the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade
Zone (Interim) (Circular 8) was released on February 12, 2015. The circular stated that companies
operating in the Shanghai FTZ would be allowed to use FTAs to borrow offshore loans (foreign debt) of
up to twice the company’s capital (paid-in capital + capital reserves) from outside mainland China.
Outline
In addition to the traditional methods of obtaining offshore financing, companies in the Shanghai FTZ can
choose one of the following three options.
(1) Foreign debt administration based on the borrowing gap (traditional method)
(2) Administration of offshore RMB-denominated loans based on paid-in capital
(launched in February 2014)
(3) Administration using FTAs (this example)
In principle, no changes are admissible after a company has selected which of (1) to (3) to use. If the
company has to change the selection for a rational reason, they need to file an application, via their
settlement bank, to the PBOC Shanghai Head Office. Only one change is permitted.
Within mainland China
Outside mainland China
Financing scheme
Account outside
mainland China
FTA
Shanghai FTZ
Financing
Repayments
2
Copyright (c) Mizuho Bank, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Foreign debt financing models: A comparison
(1) Borrowing gap* model
(traditional method)
Foreign companies located on
Target companies mainland China (including both
within and outside the FTZ)
(2) Paid-in capital model
(3) Macro-prudential management
model
Companies within the FTZ
(Chinese or foreign)
Companies within the FTZ with an
FTA (Chinese or foreign)
Target currency
RMB/foreign currencies
RMB
RMB/foreign currencies
Financing account
Special account
(RMB/foreign currency)
Special RMB account
(a financial institution in the
Shanghai area)
FTA
(opened at a financial institution
located within the Shanghai FTZ)
Fund usage
Usage based on actual demand
Usage based on actual demand
Usage based on actual demand
Loan period
Unrestricted
One year and longer
(including one year)
Unrestricted
Within the borrowing gap
Paid-in capital × 1 × macroprudential adjustment parameter*3
Capital*1 × offshore borrowing
leverage ratio*2 × macro-prudential
adjustment parameter*3
Upper limit to
financing
Balance management by multiplying
the amount by the following risk
factors*4
<RMB>
Accrual management for shortterm and medium/long-term
(quota not restored)
Management of
debt quota
<Foreign currencies>
Short-term: Balance
management (quota restored
after repayment)
Medium/long-term: Accrual
management
[Balance within the credit limit] =
Offshore financing balance × (1) period
risk conversion factor × (2) currency
type risk conversion factor × (3)
categorization risk conversion factor
• Foreign currency trade finance (×
20%)
• Including off balance financing
Balance management
*1: Capital = [paid-in capital + capital reserves]
*2: The leverage ratio differs for each company. For companies within the Shanghai FTZ, the ratio is “2.”
*3: The parameter is initially set at “1.”
*4: Type of risk and factor
Type of risk
(1) Period risk
(2) Currency type risk
(3) Categorization risk
Risk category
Medium/long-term loans
Short-term loans
RMB-denominated
Foreign currency-denominated
On balance financing
Off balance financing
Factor
1
1.5
1
1.5
1
0.2, 0.5
(* For details about the borrowing gap, please consult the separately listed “RMB-denominated Investment & Capital Increases.”)
If you have any inquiries, please contact the branch in charge of your account or any local Mizuho branch.
Disclaimer & Confidentiality
1. Purpose:
This publication is compiled solely for the purpose of providing readers with information and is in no way meant to
encourage readers to buy or sell financial instruments.
2. Legal, accounting and tax advice:
The information contained herein does not incorporate advice on legal, accounting or tax issues. You should obtain your
own independent professional advice on the legal, accounting and tax aspects of this information.
3. Copyright:
The information contained herein is, as a general rule, the intellectual property of MHBK, and may not be copied,
duplicated, quoted, reproduced, translated, or lent, in whole or in part, in any form or by any means for any purpose
whatsoever without prior consent.
4. Limitation of liability:
The information contained herein was obtained from information sources deemed reliable by MHBK but in no way is the
accuracy, reliability or integrity of such information guaranteed. The contents of this publication may be changed without
prior notice. MHBK disclaims any liability whatsoever for any damage arising out of or relating to this information.
3
Copyright (c) Mizuho Bank, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.





