Application note: MCB versus MCCB
advertisement

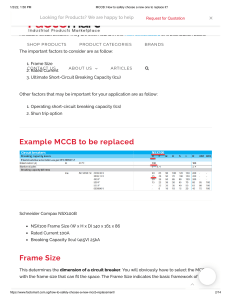
Application note: MCB versus MCCB A circuit breaker is the key to a safe system for the disconnection of the power supply in case of overload or short circuit. There are two types of circuit breakers generally used i.e.: Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) Characteristics of MCB’s: Low price (compared to MCCB’s) Require small space Currents up to 125A Characteristics of MCCB’s: Very high price (compared to MCB’s) Require large space Currents up to 1600 A Maximum current trough the circuit breaker is adjustable Main effects of using MCCB’s instead of MCB’s: More space required The enclosure in which a MCCB will be mounted is larger due to the larger size of the MCCB. This may result in requiring more enclosures and interconnections. Especially for offshore platforms this may cause a problem due to the generally limited available space on a platform. Higher cost More and/or larger enclosures increase the costs substantially. Moreover MCCB’s are much more expensive than MCB’s. As generally currents in solar power systems and to the connected loads are (well) below 125A and the functionality of a MCB is same as or similar to a MCCB. In order to save costs and space Tss4U recommends to use MCB’s where possible. Circuit Breaker comparison table (examples) Output circuit breaker Battery circuit breaker Battery circuit breaker MCB S 202 C25 MCB S802 C125 MCCB Tmax T2S R125 1 5.3 7.4 35x69x88 mm 53x95x88 mm 120x70x130 mm 212 cm³ 443 cm³ 1092 cm³ Rated current max 25A 125A 160A Icu max 20KA 50KA 85KA Electrical life (no. of operations) 10000 10000 8000 Weight 250 g 490 g 1100 g Type Price (factor) Dimensions (WxDxH) Volume Source: ABB Tss4U B.V. The Netherlands Looyenbeemd 3a 5652 BH Eindhoven Tel: Fax: +31 40 235 1702 +31 40 235 1881 info@tss4u.nl www.tss4u.nl 15-11-2013 CoC 17156182 VAT No: NL8120.42.530.B01