Solid Figures: 3D Shapes, Prisms, Pyramids Worksheet
advertisement
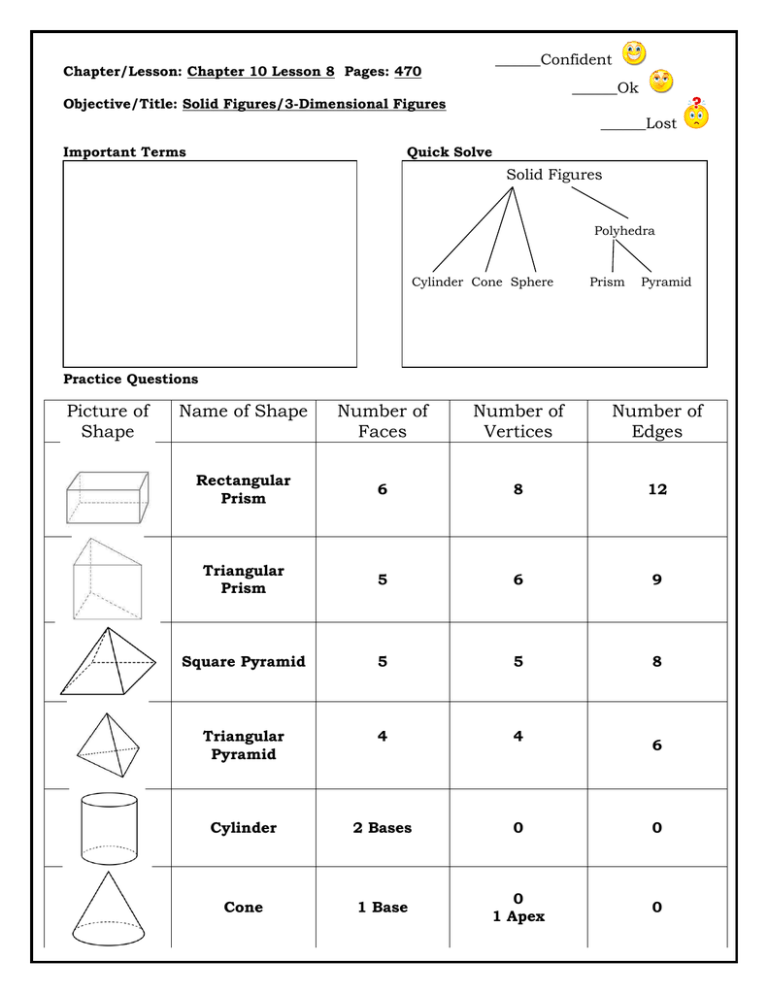
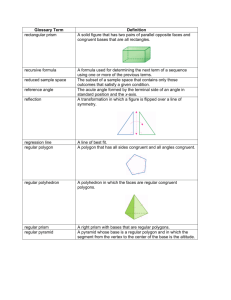
______Confident Chapter/Lesson: Chapter 10 Lesson 8 Pages: 470 ______Ok Objective/Title: Solid Figures/3-Dimensional Figures ______Lost Important Terms Quick Solve Solid Figures Polyhedra Cylinder Cone Sphere Prism Pyramid Practice Questions Picture of Shape Name of Shape Number of Faces Number of Vertices Number of Edges Rectangular Prism 6 8 12 Triangular Prism 5 6 9 Square Pyramid 5 5 8 Triangular Pyramid 4 4 Cylinder 2 Bases 0 0 Cone 1 Base 0 1 Apex 0 6 Notes and Examples Parts of a Solid Figure Vertex: point where 3 or more faces meet Face: polygon shape; also a flat surface Edge: segment formed where two faces meet Base: face the solid appears to rest on Solid Figures are 3-Dimensional figures that occupy a portion of space. Cylinder Cone A cone is a solid figure, but is not considered a polyhedron. It has only one circular base. It does not have any faces because faces are regular polygons, meaning they have straight sides. The point at the top is called the apex, it is NOT a vertex. Sphere A sphere is a solid figure, but is not considered a polyhedron. It has no bases and no faces. A cylinder is a solid figure, but is not considered a polyhedron. It has two congruent, circular bases. It also has one rectangular face that is curved around the circular bases. A polyhedron is a solid figure with faces that are polygons (triangles, rectangles, ...) Triangular Prism Pentagonal Prism Rectangular Prism Hexagonal Prism A prism is a polyhedron with two congruent, parallel bases. The shapes of the bases give each prism their specific names. The bases are always connected by rectangular faces. A cube is a special prism which has bases and faces that are all squares. Triangular Pyramid Square Pyramid Pentagonal Pyramid Hexagonal Pyramid A pyramid is a polyhedron with only one base. The shape of the base determines the specific name of each pyramid. The faces are always triangles that meet at a common vertex.