EOQ basic model – Graphical method
advertisement
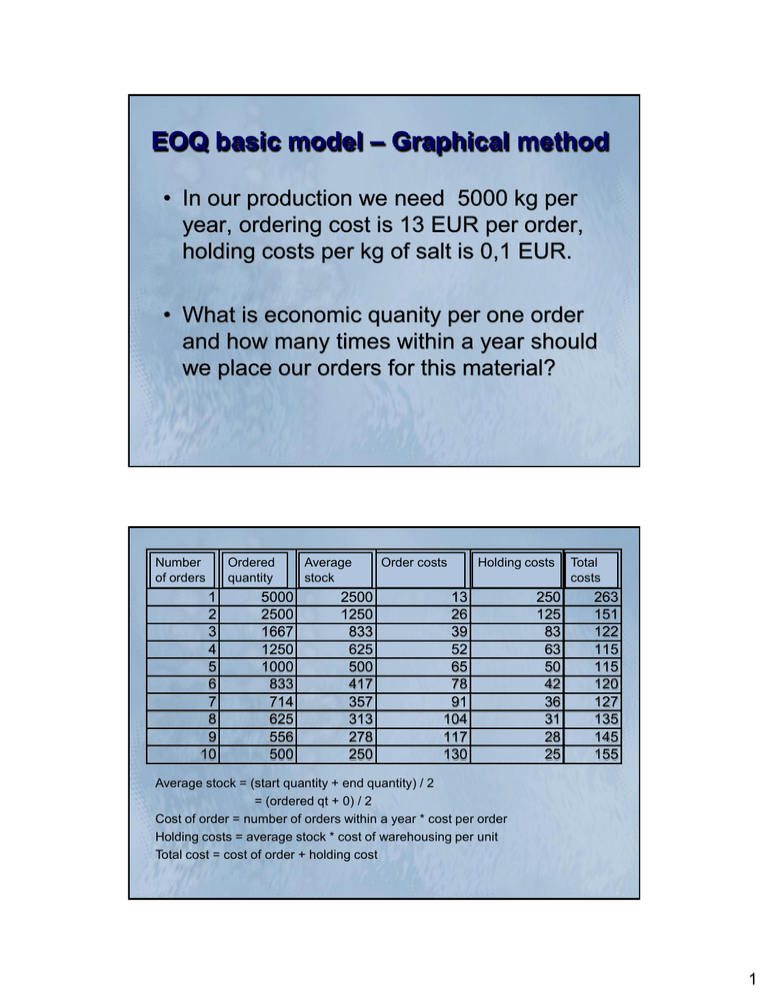
EOQ basic model – Graphical method • In our production we need 5000 kg per year, ordering cost is 13 EUR per order, holding costs per kg of salt is 0,1 EUR. • What is economic quanity per one order and how many times within a year should we place our orders for this material? broj naručena prosječna trošak trošak Number Ordered Average Order costs Holding costs ukupni Total of orders količina quantity stock costs narudžbi zaliha naručivanja skladištenja trošak 1 5000 2500 13 250 263 2 2500 1250 26 125 151 3 1667 833 39 83 122 4 1250 625 52 63 115 5 1000 500 65 50 115 6 833 417 78 42 120 7 714 357 91 36 127 8 625 313 104 31 135 9 556 278 117 28 145 10 500 250 130 25 155 Average stock = (start quantity + end quantity) / 2 = (ordered qt + 0) / 2 Cost of order = number of orders within a year * cost per order Holding costs = average stock * cost of warehousing per unit Total cost = cost of order + holding cost 1 300 250 200 Economic order 150 100 trošak naručivanja trošak skladištenja Ordering cost 50 Holding cost 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Number of orders per year At the example EOQ is achieved if company orders 4 or 5 times per year, which means that order quantity will be higher than 1000, and less than 1250 kg of salt per order. EOQ – basic model - Equation EOQ = 2ca h c – ordering cost per one order a – annual quantity h – holding costs 2 • For our example: EOQ = 2*13*5000 0,1 EOQ = 1140,17 kg of salt With ordering period 5000/1140,17 = 4,38 orders within a year Round up values – your cannot order 4 point 38 times!!! So 4 orders each 1250 kg of salt! EXCERCISE – ZADATAK Company KINDERGARDEN, inc. Produces educative woden toys. For the little train EDI we need annual quanities as follows: a) 15000 of wood pieces b) 1000 kg glue c) 1500 kg colour Calculate optimal order quantity for each material. If ordering costs are 15 EUR per order. And holding costs for wood 0,5 EUR/piece, glue 0,65 EUR/kg, colour 0,9 EUR/kg. For each product show the graphical solution. 3