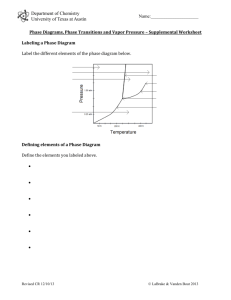
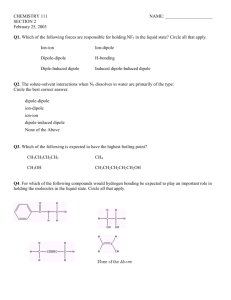
S = J/mol-K
advertisement

HW 12 1. The equilibrium constant of a reaction is 2.48e+02 at 369 K and 4.96e+03 at 491 K. Determine the value of Ho for this reaction: Ho= 3.699e+01 kJ/mol 𝐾𝐾2 1 𝑅𝑅 8.31 4.69𝑒𝑒3 ∆𝐻𝐻 𝑜𝑜 1 � − � → ∆𝐻𝐻 𝑜𝑜 = � � ln � � � ln � � = � 1 1 1 1 𝑅𝑅 𝑇𝑇1 𝑇𝑇2 𝐾𝐾1 2.48𝑒𝑒2 − − 𝑇𝑇1 𝑇𝑇2 369 491 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 = 36 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 ln(𝐾𝐾2 ) = ln(𝐾𝐾1 ) + Based on the higher temperature equilibrium constant, determine the value of So= 1.461e+02 So for this reaction: J/mol-K ∆S o ∆𝐻𝐻 𝑜𝑜 − 𝑅𝑅 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 ∆𝐻𝐻 𝑜𝑜 36.99𝑒𝑒3 𝐽𝐽 ∆𝑆𝑆 𝑜𝑜 = 𝑅𝑅 ln 𝐾𝐾 + = 8.31 ln(4.96𝑒𝑒3) + = 146 𝑇𝑇 8.31 ∗ 491 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 𝐾𝐾 lnK = 2. The heat of vaporization of a compound at 300. K is 36.4 kJ/mol and its vapor pressure is 9.6 torr. Determine the following thermodynamic properties of the vaporization at 300K: 10.90 Go = kJ/mol Hint : The vaporization reaction of material A is A(l) A(g). Think about the expression for the equilibrium constant for this reaction, and what its value would be based on its vapor pressure given above. 9.6 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 ∆𝐺𝐺 𝑜𝑜 = −𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 ln 𝐾𝐾 = −8.31(300) ln � � = 10.9 760 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 So = 85.0 J/mol-K ∆𝐺𝐺𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 = ∆𝐻𝐻𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 − 𝑇𝑇∆𝑆𝑆𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 → ∆𝑆𝑆𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 = ∆𝐺𝐺𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 − ∆𝐻𝐻𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 10.9 − 36.4 𝐽𝐽 = = 85.0 𝑇𝑇 300 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 𝐾𝐾 Assume that Ho and So are temperature independent and estimate the normal boiling point of the compound to the nearest degree Celsius. t= 155 𝑇𝑇𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 = o C ∆𝐻𝐻𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 36400 = = 428 𝐾𝐾 = 155𝑜𝑜 𝐶𝐶 ∆𝑆𝑆𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 85 Hint: At the normal boiling point, the vapor pressure equals 1 atm. Given the value of K at 1 atm pressure, what do you know about Go at the normal boiling point?