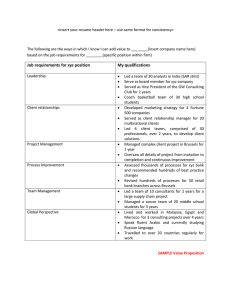
MODQ3M User Guide and Tutorial The following diagram illustrates
advertisement

MODQ3M User Guide and Tutorial The following diagram illustrates the steps of a modQ3M calculation starting from a pdb file. The final product is a Gaussian input file with polarized charges. (Throughout this tutorial symbol > is used to indicate the terminal command prompt) PDB to Tinker XYZ The program pdbxyz from the TINKER package (J. Ponder, Washington University, St. Luis) can be used to convert a pdb file to TINKER xyz format, using the Amber force field. Although this utility does its best to convert a pdb file to an xyz file, sometimes additional work is required to complete the xyz file, in particular for non-standard residues. >pdbxyz test.pdb amber99.prm This command will convert test.pdb to a TINKER xyz file (test.xyz) expressed in force field amber99. XYZ to MIF All the information necessary to perform a MoD-QM/MM calculation is contained in a file called master input file or mif. Two different types of master files can be generated based on different cutting schemes. The program NCcut will generate a master file with partitioning between amide bonds. CCcut generates a master file with partitioning between C-alpha and carbonyl carbon. >NCcut test.xyz Or >CCcut test.xyz will create a file named test.mif. Architecture of the Master File The master file (.mif) contains two sections. Section 1, which starts with the keyword &section1. This section specifies all the keywords. List of keywords, their definitions and default values are given in Table 1.1. Table 1.1 Keyword nparts Definition Number of partitions in the system. The default option for NCcut and CCcut is one residue per partition. natoms Total number of atoms ginput Name of the ONIOM input file nloops Number of self-consistent loops in modQ3M basis Basis set for ONIOM calculations gcommand Command to run Gaussian nproc Number of processors used by Gaussian totalcharge Total charge of the entire system totalmult Multiplicity of the entire system ninit Starting partition number extrafit ESP fitting option 1 = uses the fitting scheme in JCTC, 2, 175 (2006) 0 = Uses ESP charges from g03, but shifts the charges of the link atoms to the atoms in the QM region to which they are attached embed 1 = electronic embedding 0 = mechanical embedding updatecharge Whether to update charges at each iteration theory Level of theory for QM calculation HF, b3lyp, mp2, etc. gscaling Charge scaling for the Gaussian keyword ScaleCharge layer2 Low level theory Amber, AM1 etc. extraparam Whenever ginput has an extra set of parameters after the connectivity section, exxtraparam = 1 Otherwise extraparam = 0 Default Value 1 3-21g* g03 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 HF 555500 Amber 1 opt printframes only deloc Whether to perform optimizations at each step** 1 = with optimization 0 = without optimization If opt = 1, whether to print intermediate steps to a file (movie.xyz) Performs the calculation only on a given partition (i.e: only = 10, will only calculate properties in partition 10 Groups three consecutive partitions (two if partition is at the extremes) and only updates the charge on the central partition (or end partition, if partition is at the extremes) 0 0 0 ** The optimization scheme implemented in modQ3M performs an energy minimization on a given residue at each step leaving entire MM layer frozen. Because of this Gaussian requires at least three atoms of the QM layer frozen. Therefore ONIOM input file should have information about frozen atoms for a given partition. An extra column before the coordinates with a -1 or 0 specifies whether an atom is frozen or not. The list of atoms in each partition and information about QM/MM boundaries are specified in section 2, following the keyword &section2 Each partition starts with a line that looks something like this: 1 & ij.hdr & Qr1 & Qr2 From left to right 1 = partition number ij.hdr = Here i is the charge of the domain and j is the multiplicity. Qr1 = charge of region 1 Qr2 = charge of region 2 (See in JCTC, 2, 175 (2006) for definition of regions) Inside a partition you’ll find lines that look like this: 1 R1 2 R1 link 3=HX 1 R1 means atom 1 belongs to region 1 (Details of these regions are published in JCTC, 2 175 (2006) 2 R1 link 3=HX means atom 2 which belongs to the QM region is linked to atom 3 of MM region for that particular QM/MM setup. It also means that a cut between these atoms is handled with the standard link H scheme. Note: In addition to the master input file, modQ3M needs an ONIOM input file. modQ3M requires the details of connectivity section and any extra parameters defined at the end of this ONIOM input file. This file can be generated using the program t2oniom, starting from the TINKER xyz file. Type the following sequence of commands at the command prompt to generate the ONIOM input file. >setcharges amber99.prm >t2oniom test.xyz Notice that a value is printed on the screen when you run the second command. This is the total charge of the protein. Open the master input file with a text editor. Replace the totalcharge with the value you obtained. t2oniom will create a file called input.com. Rename this file to test.com. This input file should have all extra parameters needed by an ONIOM calculation as implemented in Gaussian. Open the master file with a text editor. Change the nloops from 1 to 3. Save and Exit. Now you are ready to run the calculation. >modQ3M test.mif & You can check the progress of the calculation with the following command: >tail –f test.out Once the calculation is finished the new charges are found in the file test_out.com. Check the test_out.log file in case of an error. Other Utility Programs getcharges Reads the charges in the _out.com file and prints it on the screen. >getcharges test_out.com n1 n2 n1 and n2 are optional command line arguments. Upon specifying these numbers charges in the range n1 to n2 can be printed out. chargescom2com >chargescom2com 1.com 2.com This program creates a file named updated.com by replacing the charges of 2.com file with charges of 1.com file. com2tinker >com2tinker test.com test.xyz This program converts test.com file into a TINKER xyz file using test.xyz as a template. tinkersort This program takes a TINKER xyz file whose atoms are not labeled sequential and sorts it with right order and sequence. coordcom2com This program creates a file named updated.com by replacing the coordinates of 2.com file with coordinates of 1.com file. >coordcom2com 1.com 2.com n1 n2 n1 and n2 are optional command line arguments. Upon specifying these numbers, coordinate replacement can be limited to the range (n1,n2). If not specified all atoms are replaced. coordlog2com This program creates a file named updated.com by replacing the coordinates of 2.com file with the last set of coordinates of an ONIOM output file 1.log. >coordlog2com 1.log 2.com n1 n2 n1 and n2 are optional command line arguments. Jose A. Gascon University of Connecticut 2016