Electrical Conductivity
advertisement

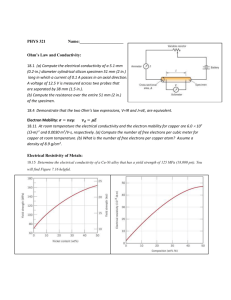
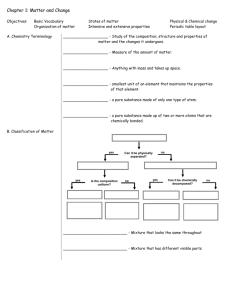
Share with Your Students Conductivity 1. Explain that conductivity is another property of matter. Point out that materials that conduct electricity or heat well have high conductivity and are called conductors. Materials that conduct electricity or heat poorly have low conductivity and are called insulators. Electrical conductivity is the measure of how well a material conducts electricity. Thermal conductivity is the measure of how well a material conducts heat. 2. Ask: Do you think the coating on an electrical wire is a conductor or an insulator? (an insulator) Point out that the different properties of materials, including conductivity, often determine what kinds of jobs they are used for. Electrical Conductivity Name Date Electrical Conductivity STUDENT RESOURCE 1.4 ACTIVITY SHEET 20 minutes Small Groups 1 Build an electrical conductivity tester like the one shown below. Objectives • Students build and use a device for testing electrical conductivity. + – • Students rate the electrical conductivity of different common materials. 2 Use the conductivity tester to test the different materials for Materials For each group electrical conductivity. 3 Record your data in the table below. Sample data Electrical Conductivity Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All Rights Reserved. Best insulators No light plastic spoon Best conductors Dim light Bright light Very bright light pencil “lead” copper disk glass dropper jewelry tongue depressor aluminum foil aluminum foil 1 plastic spoon 1 battery, D-cell 1 tongue depressor 1 battery holder 3 wires, stripped 1 bulb *Not provided in kit 1 bulb holder 1 copper disk 1 dropper, glass paper clip CHEMISTRY • SECTION 1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER • 15 Student Resource 1.4 (p. 15) 1 pc. 1 pc. *jewelry, metal 1 1 Student Resource • 1.4 Electrical Conductivity Inquiry Focus • Infer paper clip *pencil 1. Distribute the Student Resource. Make copies of Student Resource 1.4, Electrical Conductivity, and distribute to students. SECTION 1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER • 9 Electrical Conductivity (continued) + – A Testing for electrical conductivity Teaching Tip Step 2: Save the conductivity testers for use in the Section Assessment. Teaching Tip Step 3: Instruct students to touch each wire of the circuit to the glass part of the droppers, not the rubber part. 2. Students make conductivity tester. Have students make a conductivity tester, as shown. The picture shows a paper clip in the position of the material to be tested. Explain that materials that conduct electricity will allow electric current to move through the circuit and light the bulb. The better the conductor, the brighter the bulb will be. 3. Students test the materials. Have students test each material in the conductivity tester. Have them record their observations on the Resource page. 4.Discuss the Resource page. When students have completed the Resource page, discuss the answers. Ask: What kind of materials were good conductors of electricity? (metals) Point out that other materials might also conduct electricity, but metals are the best conductors. Assessment Ask: In which column of the table would you expect an iron nail to be? Explain. (It would be in the right column because it is a metal and, therefore, a good conductor of electricity.) Extension Thermal Conductivity Safety Step 1: Use water that is hot but will not burn. Test the water on your own hand before distributing to students. 1. To each student group, pass out a tongue depressor, a plastic ruler, a zinc strip, a copper strip, and a plastic cup. 2. Pour hot water into each cup until the cup is half full. Have students place each item into the hot water. 3. Every 30 seconds for three minutes, have students touch each material above the cup edge with the tips of their little fingers, as shown. Have them note which object feels hottest. 4.Ask: What conclusions can you draw about the thermal conductivity of the materials you tested? (Plastic and wood are poor conductors of heat. Copper and zinc are good conductors, but copper is better.) A Testing for thermal conductivity 10 • EXPERIENCE SCIENCE Section Assessment Name Materials For each station Date STUDENT RESOURCE 1.5 ASSESSMENT SHEET Section 1 Assessment 1 Vocabulary Fill in each blank with the correct vocabulary term. 1 Table salt changes from a solid to a liquid at 800ºC and from a liquid to a gas at 1465ºC. The salt is 800ºC, and its melting point boiling point 1 *pencil sharpened at each end with eraser 1 *pencil move through silver easily. Silver has high solubility and low conductivity tester (from Investigate 3) of table is 1465ºC. 2 Silver does not dissolve in water, but electricity and heat conductivity Student Resource • 1.5 Section 1 Assessment . Properties of Matter *Not provided in kit 3 Draw lines to match each picture to the property it is used to determine. – + ˚F 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 conductivity solubility boiling point Conductivity 4 Predict the electrical conductivity of the different parts of a wooden pencil. Use the conductivity tester to determine the electrical conductivity of the eraser, wood, pencil “lead,” and metal band of the pencil. Record your results in the table, using the terms none, low, medium, and high. Eraser Wood Pencil “lead” Metal band Prediction Answers will vary. Answers will vary. Answers will vary. Answers will vary. Conductivity none none medium high 16 • CHEMISTRY • SECTION 1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER Student Resource 1.5 (p. 16) Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All Rights Reserved. 0 1. Set up enough materials stations around the room to allow one-third of the class to work alone at a station during the hands-on portion of the assessment. 2. Make copies of Student Resource 1.5, Section 1 Assessment, and distribute to students. 3. Divide the class into three groups. While one group is working at the stations to complete the hands-on portion of the assessment, the other two groups can be completing the top part of the assessment. Rotate the groups through the stations until each has completed the hands-on portion of the assessment. 4.Discuss the answers as a whole-class activity. SECTION 1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER • 11