COURSE OUTCOMES
advertisement

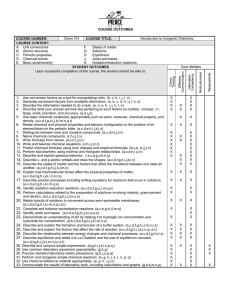
COURSE OUTCOMES Page 2 of 3 COURSE NUMBER: COURSE CONTENT: Chem 140 General Chemistry COURSE TITLE: Measurements, significant figures, dimensional analysis, periodic properties, atomic structure, stoichiometry, thermochemistry and quantum theory Core Abilities STUDENT OUTCOMES Upon successful completion of this course, the student should be able to: 1. Use conversion factors as a tool for manipulating units. (b,c,h,i,j,l,n) 2. Generate conversion factors from available information. (a,b,c,d,h,i,j,l,n) 3. Describe the information needed to do a task. (a,d,e,h,i,j,k,n,s) 4. Describe what your answer will look like pertaining to such factors as number, concept, +/-, large, small, precision and accuracy. (a,d,i,j,l) 5. Use basic chemical vocabulary appropriately such as atom, molecule, chemical property, and density. (a,c,d,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n,q,s) 6. Describe the historical development of atomic theory from Dalton up to the present. (d,i,j,k,l,n) 7. Relate chemical and physical preperties and electron configurations to the positions of an element/atom on the periodic table. (a,c,d,e,h,i,j,k,l,n) 8. Distinguish between ionic and covalent compounds. (a,c,d,h,i,j,l,n) 9. Name chemical compounds. (c,h,i,j,l,n) 10. Write formulas from names. (a,c,h,i,j,l,n) 11. Write and balance chemical equations. (c,h,i,j,l,n,r) 12. Predict chemical formulas using ionic charges and empirical formulas. (a,c,e,h,i,j,l,n) 13. Perform stoichiometric calculations including limiting reactant, percent yield and solution stoichiometry. (b,c,e,h,i,j,l,n) 14. Use the kinetic molecular theory to describe gaseous behavior and the gas laws. (a,b,c,d,h,i,j,k,l,n) 15. Apply the gas laws in calculations. (b,c,e,h,i,j,l,n) 16. Explain the limitations of the ideal gas law and the usefulness of van der Waal’s equation. (a,d,h,i,j,k,l,n) 17. Recognize when a reaction is exothermic or endothermic with respect to enthalpy and to the direction of heat flow. (a,c,g,h,i,j,l,n) 18. Recognize and describe the difference between a state function and a non-state function. (a,c,d,h,i,j,l,n) 19. Perform calculations based on Hess’s law. (b,c,e,g,h,i,j,l,n) 20. Measure heats of reaction. (g,h,q) 21. Describe atomic orbitals and draw the shapes. (a,c,d,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,n) 22. Describe the wave nature of an electron. (a,c,d,i,j,k,l,n) 23. Use quantum numbers to describe electron energies. (a,c,i,j,l,n) 24. Appreciate the incongruance of the wave particle theory. (u) 25. Design and carryout simple experiments. (e,g,h,i,,j,k,l,n,p,q) 26. Demonstrate the appropriate use of common laboratory equipment. (g,h,q) 27. Practice standard laboratory safety precautions. (g,h,i,j,l,p,q) 28. Perform and recognize simple chemical reactions. (e,g,h,j,k,i,n,p,q) 29. Use chemical reference materials appropriately. (e,g,h,i,j,l,n) 30. Use computers to gather and analyze data. (g,h,k,i,m,n,s) 31. Communicate the results of laboratory work. (g,h,k,m,n,p) X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X CHEM 140 General Chemistry METHODS AND TOOLS FOR ASSESSMENT: a. conceptual questions b. computational questions c. multiple choice questions d. essay questions e. identifying unknowns f. classroom observations g. laboratory observation h. lab reports i. in-class group assignments j. extended group assignments. k. oral presentations l. individual assignments m. classroom participation n. written reports o. self-evaluation p. peer-evaluation q. demonstrations r. one minute paper s. concept maps t. role playing u. no formal assessment page 3 of 3