THE FIRST THREE MONTHS

THE FIRST THREE MONTHS
UTI in 40 to 70% of transplant patients within first 3 months
Increased risk of Klebsiella, enterococcus, pseudomonas
Gram positive organisms up to 40%
Prophylaxis of little benefit
15% of transplant recipients have reflux
Increased risk of pyelonephritis with or without reflux
Aggressive monitoring of U/A, C&S
Minimum 2 week course of treatment
Hospital outpatient POD 2-4
Weekly clinic visit for 6 weeks
Biweekly clinic visit for 6 weeks
Routine visit labs: CBC, CMP, Mg, PO4, Prograf level, U/A
Assessment of renal function
Assessment of patient understanding of medical regimen
Assessment of drug level
Assessment of drug toxicity
Assessment of UTI
Assessment of transplant site
Assessment of volume status
Assessment of blood glucose
Assessment of Mg, PO4
Assessment of serum K
Assessment of blood pressure
Assessment of everything else
Volume depletion ( approx. 10% with Na wasting)
Calcineurin inhibitor toxicity
Acute cellular mediated rejection (highest risk within first 3 months)
3-7% incidence
Delayed appearing antibody mediated rejection
Acute tubular necrosis
Urine leak/urinoma (with or without obstruction)
Obstruction (hematoma, distal ureteral stricture. Prostate dz.)
Neurogenic bladder
Thrombotic microangiopathy related to calcineurin inhibitor
Drugs (NSAID’s, ACEI, ARB, contrast, AIN)
Recurrence of original disease
Post transplant lymphoproliferative disease (we actually had one at 2 months
Calcineurin inhibitor history (drug level may be artificially low if not a true trough)
Drug intake history
Ultrasound
Renal Scan
Polyoma virus titers
Biopsy
Make sure a true trough
Drugs that increase levels
Calcium channel blockers
Ketoconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole
Erythromycin
HAART drugs
Metoclopramide
Grapefruit juice
Make sure patient taking right dose
Rifampin, rifabutin
Barbiturates
Phenytoin
Carbamazepine
Not a true trough
Quit taking fluconazole
Severe gastroparesis
Hair loss
Headache
Memory changes
Tremors
Nausea
Elevated Cr
Type IV RTA
Hypomagnesemia
Hypophosphatemia
Neutropenia
Anemia
Thrombocytopenia
Nausea, vomiting
Diarrhea
Hyperglycemia
Myopathy
Weight gain
Hypertension
Avascular necrosis
Calcineurin inhibitor
Type IV RTA (obstruction, CNI, post transplant tubulopathy)
Renal insufficiency
TMP/SMX
Diet
Other meds
40-60% of post transplant patients with HTN (seems like
90% in our population)
Steroids
Calcineurin inhibitor ( Na retention, renal and peripheral vasoconstriction)
Improved diet, increased Na intake
Renal insufficiency
Mycophenelate mofetil
Azathioprine
CMV disease
TMP/SMX
Other viral infections
Valcyte
Renal insufficiency
Gastrointestinal blood loss
Menorrhagia
Mycophenelate mofetil
B12 deficiency
Hypothyroidism
Folate deficiency
Iron deficiency
Parvovirus B19
Thrombotic microangiopathy
Exacerbation of Hepatitis C
CMV
Drugs (fluconazole, MMF,Valcyte, other)
Proton pump inhibitors
Angiotensin receptor blockers
Routine labs
CMV PCR
BK PCR
EBV PCR
Lipid panel
Parathyroid hormone
Vitamin D studies
D/C Valcyte if CMV D+/- R+
D/C Acyclovir if CMV D-/R-
D/C fluconazole
Adjust CNI upwards
PAN T CELL DEPLETING ANTIBODIES
Alemtuzumab
Thymoglobulin
B CELL DEPLETING ANTIBODIES
Rituximab
NON DEPLETING ANTIBODIES
Basiliximab
Daclizumab
COSTIMULATION BLOCKADE
Belatacept
Solumedrol 500mg IV in OR
250mg IV POD 1
100 mgIV POD2
Prednisone 50 mg po POD3
20mg po POD4 – 7
Thymoglobulin 1.5mg/kg IV in OR before revascularization
1.5 mg/kg IV POD 1-6 depending on graft function ( 3 doses for IGF, 5 doses for SGF, 7 doses for DGF)
Mycophenelate mofetil 500mg po bid (target 1000mg bid)
Prednisone 15 mg po POD 7-14
10 mg po POD14-30
5mg po POD 31, thereafter
Tacrolimus 0.05 mg/kg every 12 hours starting POD3 or when
Thymoglobulin complete. Target blood level 8-10.
Mycophenelate mofetil 1000mg po every 12 hours.
Renal dysfunction requiring dialysis
Differential Diagnosis
Acute tubular necrosis
Technical issues (urine leak, vascular thromboses from anastamotic misadventures, etc…)
Antibody mediated rejection, cellular rejection (rare)
Cortical necrosis
Transplant ultrasound with doppler interrogation
Exclude obstruction, assess for urine leak
Doppler’s assess flow, resistive indices
Renal Scan
Assess radioisotope uptake and excretion
Good uptake, no excretion….ATN
Delayed uptake, no excretion…Rejection, Severe ATN
Percutaneous transplant renal biopsy
<30% decline of Cr over 3 days
Differential diagnosis and evaluation basically the same as delayed graft function
Mid 1990’s, infections exceeded rejection as leading cause for hospital readmission.
Transplant recipients at increased risk for postoperative bacterial infections
Lymphocyte depleting induction regimens increased dramatically risk of CMV
Though uncommon, pneumocystis, other fungal infections potentially catastrophic
30-60% risk of infection/disease within first 3 months if no prophylaxis
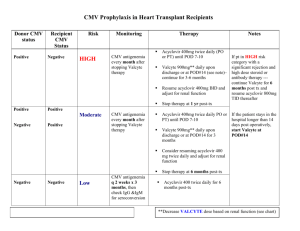
Valcyte 450mg qod to daily for D+/R- for 6 months
Valcyte 450mg qod to daily for D+/- to R+ for 3 months
Acyclovir 400mg tid for D-/R- for 3 months
If R+ gets infected, 30% comes from recipient, 70% comes from donor
Valcyte qod dosing for GFR <30, daily dosing for GFR>30
58%Reduction in CMV disease
39% Reduction in CMV infection
37% Reduction in all cause mortality
Decreased risk of herpes simplex, herpes zoster, bacterial infection and protozoal infections
RR 1.6 for acute rejection with CMV infection
RR2.5 for acute rejection with CMV disease
OR 1.5 for arrythmia, CHF, coronary occlusion with CMV disease
OR 4.0 for post transplant diabetes with CMV infection
Low risk of fungal infection within first 3 months
Candida, Histoplasmosis, Aspergillosis, Toxoplasmosis most common in this area
Fluconazole 100mg daily until GFR>30, then 200mg daily
Give for 3 months
Adjust calcineurin inhibitor with discontinuation
Some centers do not provide
Low risk
TMP/SMX SS daily for 6 months, then Tu/Th until 1 year
Dapsone 25mg daily for one year if sulfa allergic