LOCAL CONTROL ACCOUNTABILITY PLANS Mickey
advertisement

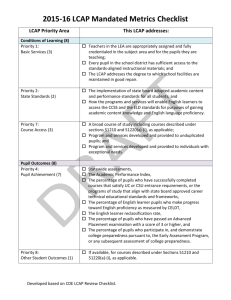
LOCAL CONTROL ACCOUNTABILITY PLANS INITIAL OVERVIEW December 19, 2013 Presentation prepared with templates and resources from Shasta County Office of Education, in conjunction with the CISC Accountability Subcommittee Presented By: Mickey Porter Asst. Supt. WHAT’S IN A NAME?? •L •C •A •P • Language and Cultural Access Program • Licking County Aging Program • Lawn Care Association of Pennsylvania • Leaving Certificate Applied Programme • Lung Cancer Associated Protein • Loosely Coupled Array of Processors • London Coalition Against Pesticides • Literacy Curriculum Alignment Project • Library Cache Auditing Protocol • Landfill Closure Assistance Program • Low Combat Air Patrol • Land Conservation in Asia and the Pacific • Libraries Cooperative Automated Project • Lilac Crowned Amazon Parrot • Logistics Civil Augmentation Program SUGGESTED NORMS FOR TODAY 1. Interrogate Reality 2. Provoke Learning 3. Tackle Tough Challenges 4. Enrich Relationships Source: Fierce Conversations by Susan Scott RULES OF ENGAGEMENT • Engage with electronics • Engage with each other when “group talk” • Engage with the content when “information dump” • Engage as a learner PLAN FOR TODAY 1. Brief Overview of DRAFT LCAP • Section 1: Stakeholder Engagement • Stakeholder Engagement Ideas • Section 2: Goals and Progress Indicators • Classification of Students • Review the 8 State Priorities 2. Ties to Other Plans 3. LCAP Adoption Process 4. Suggested Actions WHAT DOES THIS INTERACTION LOOK LIKE IN YOUR DISTRICT?? Plans Outcomes for Students Funds C-4 MODEL To EMPOWERMENT Act Differently We Must Think Differently © 2013 School Services of California, Inc. Old System State of California New System Community Involvement Policy Funding Program Rules Local Board Implementation Local Board Sets Policy State Provides Funding Local Board Empowers Schools Results Reported to Public Board Revises Policy Focus on Students School Site Performance Audits and Compliance Reviews Compliance Model Student Achievement Empowerment Model LCAP ELEMENTS STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT GOALS AND PROGRESS INDICATORS ACTIONS, SERVICES, AND EXPENDITURES LCAP TIMELINE 01.31.14 03.31.14 06.30.14 10.01.15 SBE Regulations SBE Template LEAs Adopt LCAP (intro to SBE in Jan) SBE Rubrics 3 year plan, updated annually, effective 2014-15 AB 1200 & LCAP Time Frames AB 1200 January15-16, 2014 March 2014 March – April 2014 LCAP SBE Approves EL/LI/FY Guidelines 3/15: 2nd Interim Report LCFF does not change timelines under the AB 1200 fiscal oversight process. 3/12-3/13: SBE Approves LCAP Template SCOE Business & Instructional Staff available for individual district appointments April – May 2014 • Update projected enrollments & ADA • Project revenues and expenses of subsequent fiscal year May – June 2014 Public Hearing for Budget District Public Hearing for LCAP prior to adoption May – June 2014 District Approves Budget District Adopts LCAP TIMELINE COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT PROCESS AND TIMELINE TO REVIEW AND APPROVE DISTRICT BUDGETS AND LCAPS (no later than) July 1 Budget Action LCAP Action Transmit adopted budget to county superintendent Adopt LCAP July 6 August 15 August 30 (or within 15 days of receiving written response) Transmit adopted LCAP to county superintendent County superintendent approves or disapproves budget (conditional approval or disapproval must be accompanied by written recommendations to revise budget) County superintendent may seek written clarification on LCAP from LEA LEA shall provide written response to county superintendent September 15 (or within 15 days of receiving LEA response) County superintendent may submit written recommendations to amend the LCAP September 30 (or within 15 days of receiving written recommendations) LEA must consider county superintendents recommendations at a public hearing October 8 County superintendent shall approve LCAP if conditions for approval are met LEA PLANS • The LCAP template will be developed in a manner that meets both the LCAP requirements and the federal requirements. • The SBE will take steps to minimize duplication of effort at the local level to the greatest extent possible. [EC Section 52064] • LEAs in Program Improvement must continue to meet current LEA Plan requirements. [EC Section 1116(c)(7)] SCHOOL SITE PLANS • Specific actions included in the LCAP, or the annual update of the LCAP, must be consistent with the strategies included in school plans. [EC Section 64001] • Districts are responsible for reviewing school site plans to ensure this consistency. SECTION 1 STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT ADOPTING AND UPDATING THE LCAP 1 Consultation with: • Teachers • Principals • Other School personnel • Bargaining Units • Pupils • Parents 2 Present for review and comment to: • Parent advisory committee • English learner parent advisory committee • Superintendent must respond in writing to comments received 3 4 Adoption of Plan: Opportunity for • Adopted public input: concurrent with • Notice of the the LEA’s opportunity to budget submit written • Submitted to comment COE for • Public hearing approval • Superintendent • Posted on must respond in district website writing to • COE posts comments LCAP for each received district/school or a link to the LCAP ED CODE FOR STAKEHOLDER INVOLVEMENT Stakeholder Engagement Guiding Questions • How have parents, community members, students, and other stakeholders been engaged and involved in developing, reviewing, and supporting implementation of the LCAP? • How has the involvement of stakeholders supported improved performance and outcomes for students? • “A governing board of a school district shall consult with teachers, principals, administrators, other school personnel, local bargaining units of the school district, parents, and pupils in developing a local control and accountability plan.” [EC 52060(g)] PARENT ADVISORY Must include parents/guardians that meet one or more of these criteria Parent Advisory Low Income rep EL Parent Advisory 15% ELs AND Foster Youth rep English Learner rep At least 50 EL pupils Pre-existing committees can be used if requirements are met: Parent Advisory Committee ELAC/DELAC WHAT IS STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT? “An ongoing system through which education leaders meaningfully connect with, learn from and communicate with individuals and groups.” Source: Thoughtstream “Five Criteria For Effective Stakeholder Engagement in Education” 2013 “ Engagement must be deliberate and systematic, and stakeholders should have an influence throughout the decision making process, not just at the end.” Source: Thoughtstream “Five Criteria For Effective Stakeholder Engagement in Education” 2013 How does this differ from Shared Decision Making and/or Information Sharing? FOUR PHASES OF ENGAGEMENT 1. Planning – determining what decisions will be affected, who the participants are, settling on the right questions to ask. 2. Participation – learning from each other and setting priorities. 3. Analysis – consolidating all the input. 4. Sharing – encapsulating and distributing results. Source: Thoughtstream “Five Criteria For Effective Stakeholder Engagement in Education” 2013 FIVE CRITERIA FOR A SUCCESSFUL ENGAGEMENT SYSTEM • Fast – Quick to set up and deploy • Flexible – Easy to use at a reasonable cost • Accessible – To users and stakeholders • Controlled – You manage the what, when, how • Transparent – Feedback to stakeholders throughout the engagement cycle Source: Thoughtstream “Five Criteria For Effective Stakeholder Engagement in Education” 2013 Source: Thoughtstream “Five Criteria For Effective Stakeholder Engagement in Education” 2013 STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT PLAN Plan for Stakeholder Engagement Conditions of Learning Questions Priority 1: Basic Services Priority 2: Implementation of CCSS Standards Priority 7: Course Access Stakeholder to Ask Subgroup Format SECTION 2 GOALS AND PROGRESS INDICATORS CLASSIFICATION OF STUDENTS English Learners (EL) • Based on Home language survey and California English Language Development Test (CELDT) • Reclassified students (Fluent English Proficient) will no longer generate additional funding Low Income (LI) • Qualify based on free and reduced price meals • Foster Youth are automatically eligible SUBGROUPS Racial/Ethnic Subgroups* • Black or African American • American Indian or Alaska Native • Asian • Filipino • Hispanic or Latino • Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander • White • Two or more races Other Subgroups • English Learners* • Low Income* • Foster Youth = 15 students • Students with Disabilities* *Numerically significant student subgroups in the district = 30 students CALPADS DATA COLLECTION • EL, LI, & FY Students enrolled on the fall Census Day will be used as the basis for supplemental and concentration grants. • Certification was due: December 17th • Amendment window closes: February 7th • Hint: Check out TBDs…… NEW: COE REVIEW OF STUDENT DATA • SB 97 requires COEs to “review and validate reported English learner, foster youth, and free or reduced-price meal eligible pupil data for school districts and charter schools under its jurisdiction to ensure the data is reported accurately.” THE 8 STATE PRIORITIES 1. Basic Services 6. School Climate 2. Implementation of Content & Performance Standards 7. Course Access 8. Other Student Outcomes 3. Parental Involvement & Input 4. Student Achievement Groupings Key: 5. Student Engagement Pupil Outcomes Conditions of Learning Engagement CONDITIONS OF LEARNING • Priority 1: Basic Services • Priority 2: Implementation of Content & Performance Standards • Priority 7: Course Access PRIORITY 1: BASIC SERVICES WILLIAMS’ ACT REQUIREMENTS FOR ALL SCHOOLS Sufficiency of standards-aligned instructional materials Proper teaching assignments & proper credentials for instructional staff School facilities maintained and in good repair PRIORITY 1: BASIC SERVICES NEEDS ANALYSIS GOALS • What data are we collecting? • Do we already have an implementation plan that we can use to chart progress? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? • Where do we want to be in 3 years? • How do these goals relate to the state priorities and locally identified priorities? PRIORITY 2: IMPLEMENTATION OF CONTENT & PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Common Core State Standards English Language Development Standards PRIORITY 2: IMPLEMENTATION OF CONTENT & PERFORMANCE STANDARDS NEEDS ANALYSIS GOALS • What data are we collecting? • Do we already have an implementation plan that we can use to chart progress? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? • Where do we want to be in 3 years? • How do these goals relate to the state priorities and locally identified priorities? • How are subgroups addressed? PRIORITY 2: IMPLEMENTATION OF CONTENT & PERFORMANCE STANDARDS COMMON CORE IMPLEMENTATION SUPPORTS Common Core Implementation Strategies Areas of Focus in a Common Core Implementation Plan Our Next Steps Common Core Implementation Components Supporting Teachers Common Core Professional Learning SBAC Preparing for Using Technology in Instruction Use of Instructional Time and Strategies Classroom Instruction Formative and Summative Assessment Communication & Stakeholder Outreach Supporting Students Supporting Administrators Curricular Resources and Instructional Materials 09.10.13 Common Core Professional Learning SBAC Observation of High Quality Teaching and Learning What to Expect to See and Hear Providing Effective Feedback Monitoring Student Learning Leading the Work Technology Skills Targeted Interventions Gaps to Address During Transition from former Standards to CCSS Student Teacher Parent & Community School Board 9 LINK: http://www.ccsesa.org/index/attachment s/LeadPlanGuide_WEB.pdf PRIORITY 7: COURSE ACCESS GRADES K-6 Definition Scope for K-6 The extent to which ALL students have access to, and are enrolled in, a broad course of study, including the programs and services developed and provided to unduplicated pupils and individuals with exceptional needs, and the program and services that are provided to benefit these pupils. • English Language Arts • Mathematics • History/Social Sciences • Science • Visual and Performing Arts • Heath • Physical Education PRIORITY 7: COURSE ACCESS GRADES 7-12 Definition The extent to which ALL students have access to, and are enrolled in, a broad course of study, including the programs and services developed and provided to unduplicated pupils and individuals with exceptional needs, and the program and services that are provided to benefit these pupils. Scope for Grades 7-12 • • • • • • • • • English Mathematics History/Social Sciences Science Foreign Language Physical Education Visual and Performing Arts Applied Arts Career Technical Education PRIORITY 7: COURSE ACCESS NEEDS ANALYSIS • What data are we collecting? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? GOALS • Where do we want to be in 3 years for all students and for special populations? PUPIL OUTCOMES • PRIORITY 4 : STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT • PRIORITY 8: OTHER STUDENT OUTCOMES PRIORITY 4: STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT All Districts Districts with High School Statewide assessments The Academic Performance Index English learners who make progress toward English proficiency as measured by the CELDT* English learner reclassification rate A-G completers or CTE sequences/clusters of courses and align with state board-approved CTE standards Students who have passed an AP exam with a score of 3 or higher Students who demonstrate college preparedness on the Early Assessment Program* *or any subsequent assessment PRIORITY 4: STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT NEEDS ANALYSIS • What data are we collecting? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? GOALS • Where do we want to be in 3 years with all students and with special populations? PRIORITY 8: OTHER STUDENT OUTCOMES GRADES K-6 Student Outcomes, if available in: • • • • • • • • English Language Arts Mathematics History/Social Sciences Science Visual and Performing Arts Heath Physical Education Technology Integration PRIORITY 8: OTHER STUDENT OUTCOMES GRADES 7-12 Student Outcomes, if available in: • • • • • • • • • • English Mathematics History/Social Sciences Science Foreign Language Physical Education Visual and Performing Arts Applied Arts Career Technical Education Technology Integration PRIORITY 8: OTHER STUDENT OUTCOMES NEEDS ANALYSIS • What data are we collecting? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? GOALS • Where do we want to be in 3 years with all students and special populations? ENGAGEMENT • Priority 3: Parent Involvement & Input • Priority 5: Student Engagement • Priority 6: School Climate PRIORITY 3: PARENT INVOLVEMENT & INPUT Seek Parent Input for District Decisions Seek Parent Input for School Site Decisions Seek Parent Input for promoting parental participation in programs for: • Low income • English learners • Foster Youth • Students with exceptional needs PRIORITY 3: PARENT INVOLVEMENT & INPUT NEEDS ANALYSIS • What data are we collecting? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? GOALS • Where do we want to be in 3 years? PRIORITY 5: STUDENT ENGAGEMENT All Districts • School Attendance • Chronic Absenteeism Rates Districts with Middle School • Middle School Dropout Rates Districts with High Schools • High School Dropout Rates • High School Graduation Rates PRIORITY 5: STUDENT ENGAGEMENT NEEDS ANALYSIS • What data are we collecting? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? GOALS • Where do we want to be in 3 years with all students and with special populations? PRIORITY 6: SCHOOL CLIMATE • Suspension Rates • Expulsion Rates • Other local measures, including surveys of students, parents and teachers on the sense of safety and school connectedness PRIORITY 6: SCHOOL CLIMATE NEEDS ANALYSIS • What data are we collecting? • What data do we want to begin to use and track to show improvement over time? GOALS • Where do we want to be in 3 years with all students and with special populations? LCAP SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES December – January • Develop LCAP timeline for your district. • Determine LCAP Development Team. • Talk to school board about their responsibilities in regard to LCFF and LCAP. • Correct CALPADS data for English Learners, Foster Youth, and Low Income during amendment window. • Review SARC data and other district data that further clarifies the current state of the district related to each of the 8 State Priorities. • Develop Stakeholder Engagement Plan. • Engage Stakeholders: teachers, principals, other school personnel, bargaining units, parents, and pupils. • Establish or re-establish a Parent Advisory Committee. Be prepared to record how parents, community members, students, and other stakeholders were engaged and involved in developing the LCAP (collect evidence). • Establish or re-establish an English Learner Parent Advisory Committee (if 15% or at least 50 EL students). February – March • Prepare to articulate the core services and program of support for ALL students. • Begin discussing data, needs identified through the data, 3-year goals, within each State Priority area for all students and each student subgroup with teachers, principals, other school personnel, parents, and students - need evidence of these consultations. • Begin discussing services and actions needed to implement goals within each State Priority area for all students and each student subgroup with teachers, principals, other school personnel, parents, and students - need evidence of these consultations. • Engage Stakeholders. April – May • Determine expenditures needed to provide services: to all students and to identified sub-groups. • Amend the LCAP to include input from stakeholder groups, including written comments. • Update local board on LCAP development and incorporate suggestions for revisions. RESOURCES SCOE/COMMUNITY SUPPORT • Investing in Personnel • TBD – hopefully February 2014 SCOE Personnel • CalPads Assistance • Robin Horwinski (IT) | rhorwinski@scoe.org • Two More Sessions: • Thursday, February 13, 2014 8:30am-12:30pm • Monday, March 24, 2014 8:30am12:30pm • College/Career Readiness • Stephen Jackson (Career Dev) | sjackson@scoe.org • Coop • Gail Eagan (ESS) | geagan@scoe.org • Cradle to Career • Dan Blake(ESS) | dblake@scoe.org • Session for Charters and Authorizing Agency – TBD • Customized Support • Mickey Porter (ESS) | mporter@scoe.org • New Position (ESS) | TBA • Denise Calvert (Business) | dcalvert@scoe.org • Judy Thomson (Business) | jthomson@scoe.org • Data Assistance • Rick Phelan (ESS) | rphelan@scoe.org • Foster Youth • Debra Sanders (Alt Ed) | dsanders@scoe.org • BrightBytes Partnership • Kristen Swanson/Mickey Porter • SCOE LCAP Webpage • www.scoe.org/lcap WEST ED AUDIO SEGMENTS • Episode 1 - What is the Local Control Funding Formula? • Episode 2 - What Makes LCFF Different and Better? • Episode 3 - What Should LEAs Do Now? (August 2013) • Episode 4 - Performance Based Budgeting and Planning • Episode 5 - Accounting and LCFF • Episode 6 - Local Control Accountability Plan and LCFF State Priorities LINK: http://lcff.wested.org/lcff-channel/ NEXT STEPS/INPUT • Feedback: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/LCAP121913 QUESTIONS? THANK YOU!