The Civil War
advertisement

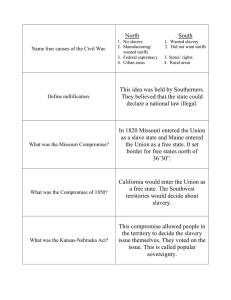
The Civil War Civil War Basics What is a Civil War? • A Civil War is a war between two or more groups inside the same country. • The American Civil War was the North versus the South. When was the Civil War Fought? • The Civil War was fought from 18611865. Who was the Confederacy? • The Confederacy was the South. • Pro Slavery • Anti Tariffs • Anti Federal Power Confederacy Flag and Uniform Who was the Union? • The Union was the North. • Anti Slavery (mostly) • Pro Tariffs • Pro Federal Power Union Flag and Uniform What were the main causes of the Civil War? • The North/Union and the South/ Confederacy disagreed about: 1. Slavery 2. Tariffs 3. The power of the Federal Government Why is the Civil War Important? • The Civil War: 1. Ended slavery. 2. Established the superiority of the Federal Government. 3. The bloodiest war in American history (600,000+ Casualties). Causes of the American Civil War What is Sectionalism? • Loyalty or support to a region or state instead of the Nation. • Northerners and Southerners were loyal to their regions, not the United States. Example of Southern and Northern Sectionalism. Southern Senator attacks Northern Senator. What are Tariffs? • Taxes and goods from other nations. • The purpose of tariffs is to make products from other nations more expensive, so that customers will buy home made products. What was the impact of tariffs on the North? • Tariffs helped Northern Businesses. • Tariffs made European goods more expensive and Northern goods more affordable by comparison. What was the impact of tariffs on the South? • The Southern Economy did not benefit from tariffs. • Southerners had a harder time exporting their cotton and had to pay extra for goods because of the tariff. What was the impact of tariffs on the West? • The West benefit from tariffs. • The money from tariffs went toward building railroads, bridges, roads, dams, and canals in the West which allowed people to move westward. What was the impact of slavery on the North? • Northerners felt violated when Southern slave catchers went to Northern homes and businesses looking for slaves. • Northerners were also against the expansion of slavery to the West. What was the impact of slavery on the South? • Over 75% of the South’s crops were made in large scale plantations with 20 or more slaves. • Cotton was seen as King Cotton because of its value. What was the impact of slavery on the West? • As Western territories became states, Northerners and Southerners battled in the West to ensure their side would win control of the new governments. What was Dred Scott v. Sanford? • Dred Scott sued for his freedom. • The Supreme Court stated that African-Americans were not citizens and the only way to end slavery would be an amendment. The North was angered by the decision. Congressional Conflicts and Compromises Before the Civil War What were the effects of the 3/5’s Compromise? • Southern States received extra representation because their slaves counted as 3/5’s a person. • Most Presidents were Southern, The Supreme Court and Congress were also controlled by the South. What was the Missouri Compromise (1820)? • Missouri was allowed to have slavery. • Maine became a free state. • Slavery was only allowed below the 36’30’ latitude line. What were the effects of the Missouri Compromise? • The purpose of the Missouri Compromise was to keep an even number of slave and free states to keep them from fighting each other. What was the Compromise of 1850? 1. California is allowed as a free state. 2. Ends the Missouri Compromise and allows states to decide about slavery (popular sovereignty). 3. Stronger Fugitive Slave Act which made the North angry. What were the effects of the Compromise of 1850? • The Fugitive Slave Act turned many Northerners into Abolitionists. What was the Kansas-Nebraska Act? (1854) • The Kansas-Nebraska act allowed Citizens in Kansas and Nebraska to chose for themselves whether or not to allow slavery in their territories. What were the effects of the Kansas-Nebraska Act? (1854) • Abolitionist and Pro Slavery groups fought for control of the governments. • Kansas actually turned into a war zone as each group attacked the other. The Battles, People, and Events of the Civil War What was the importance of the Election of 1860? • Abraham Lincoln wins the election despite not even being in most Southern ballots. • The South is worried that the North now has too many people for them to win elections. Southern States decide to secede (leave). Who was Abraham Lincoln? • 16th President of the United States. • Republican • Against the expansion of slavery. • Union must be Preserved. What was the Significance of the Battle of Ft. Sumter? • The first of battle of the Civil War was in Ft. Sumter, South Carolina. • The South wins as Northern troops abandon the fort. What is Secession? • The act of a state leaving a nation. Which States seceded? • South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee . Who was Jefferson Davis? • Mississippi Senator • President of the Confederate States of America (South/Confederacy). Who was Robert E. Lee? • Virginian • America’s best and most famous General. • The General of the Confederacy. Who was Ulysses S. Grant? • The Final General of the Union/North. What was the Significance of the Battle of Antietam? • September 17, 1862. • The bloodiest day in American History. • Over 22,000 dead or wounded. What was the Significance of the Emancipation Proclamation? • Slaves in the Confederacy were now free. What was the Significance of the Battle of Gettysburg? • July 1-3, 1863. • The turning point of the Civil War. • The South’s invasion of the North is ended. What was the Significance of the Gettysburg Address? • “For the People, by the People”. • Lincoln inspires the nation by saying the Civil War’s purpose was to save Democracy. What was the Significance of the Siege at Vicksburg? • May-July 1863. • The Union took control of the Mississippi River. What was the Significance of the Surrender at Appomattox Court House? • Robert E. Lee surrenders officially to Ulysses S. Grant on April 9, 1865. • Unfortunately, President Lincoln was shot 2 days later.