Nicole Pongratz Allisen Jacques Shannon Griese Amber Teichmiller
advertisement

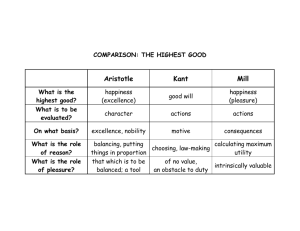
Nicole Pongratz Allisen Jacques Shannon Griese Amber Teichmiller 4/13/2010 It’s the idea that the moral worth of an action is determined solely by its effectiveness in providing happiness or pleasure as summed among all beings. Based on the simple view of human nature. Acting ethically means making decisions & taking actions that benefit people by maximizing “good” and minimizing “bad.” Outcomes, results, or goals are the focus—not the action taken to achieve them. “What is my goal? What outcome should I aim for?” Increase the good that is done & reduce the harm done. 1806-1873 At a young age he spent time learning from utilitarian philosopher Jeremy Bentham. His interest was in showing difference between what economics measured and what human beings really valued. His writing Utilitarianism 1861 defends the view that “we ought to aim at maximizing the welfare of all sentient creatures, and that the welfare consists of their happiness”. Happiness should not only be assessed by quantity, but quality. 1748 – 1832 “Good” for him meant pleasure. Pleasures could be quantified & tried devising a criteria for weighing pleasures against each other His philosophy shows how the convention of law, politics and ethics could all be recast in a simple language of utility "Nature has placed mankind under the governance of two sovereign masters, pain and pleasure…" Moral rule: what one needs to do is to maximize pleasure and minimize pain Believed that education should be made more widely available Spent most of his life critiquing the existing law & advocating legal reform • Never practiced law himself Differences between people # of variables in any situation No time to calculate Consequences Regards all happiness as equally good, regardless of who gets it Problem of personal loyalties Makes choices that are difficult seem as though they should be easy. Happiness and utility are vague terms that we can’t measure or weigh the relative utilities of different courses of action Supreme duties are irrelevant The theory demands too much Require to commit morally reprehensible acts Utilitarianism vs. Capital Punishment • By utilitarian standards, if punishment will bring about more good than bad to society, and that good cannot be brought about in a more advantageous way, then it can be justified. • Although punishment causes one to suffer, in many ways it still benefits society. What is the main point of Utilitarianism?? Answer: It’s the idea that the moral worth of an action is determined solely by its effectiveness in providing happiness or pleasure as summed among all beings. Who were the influential men that we discussed? Answer: Bentham John Stewart Mill and Jeremy “Pleasure, and freedom from pain, are the only things desirable as ends; all desirable things…are desirable either for the pleasure inherent in themselves, or a means to the promotion of pleasure and the prevention of pain…” “The deeply rooted conception which every individual even now has of himself as a social being , tends to make him feel it one if his natural wants that there should be harmony between his feelings and those of his fellow creatures…” THE END