The Utilitarian Approach130M
advertisement

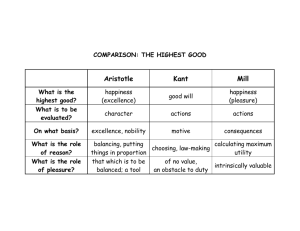
THE UTILITARIAN APPROACH Marcie Neils, Brandon Capelle, Aaron Zimbelman, & Nate Martin Monday 1:30-4:30 LP 5: Ethical Theory Presentation November 10, 2008 PRINCIPLE OF UTILITY The rightness or wrongness of an action is determined by the goodness (utility) or badness (disutility) of its consequences not its intentions. THREE BASIC INSIGHTS The purpose of morality is to make the world a better place. • Morality is about producing good consequences, not having good intentions THREE BASIC INSIGHTS We should do whatever will bring the most benefit (i.e., intrinsic value) to all of humanity. • JEREMY BENTHAM (1748 – 1832) • Bentham believed that we should try to increase the overall amount of pleasure in the world. PLEASURE Definition: The enjoyable feeling we experience when a state of deprivation is replaced by fulfillment. Advantages: Easy to quantify Short duration Bodily “HAPPINESS-MAKING” CALCULUS A method of working out the sum total of pleasure and pain produced by an act in respect of their intensity, duration, certainty, proximity, productiveness, purity, and extent. Measuring Pleasure or Utility • Units of measurement: •Positive = “hedons” •Negative = “dolors” • What must be measured for every action: • How people will be affected (positively or negatively). • The intensity of the reaction. • Calculations for alternatives. • Choose the action with the greatest amount of utility. EXAMPLE: DEBATING THE SCHOOL LUNCH PROGRAM Benefits Increased nutrition for x number of children Increased performance, greater long-range chances of success Incidental benefits to contractors, etc Costs Cost to each taxpayer Contrast with other programs that could have been funded and with lower taxes (no program) Act Utilitarianism Looks at the consequences of each individual act and calculate utility each time the act is performed. Rule Utilitarianism Looks at the consequences of having everyone follow a particular rule and calculates the overall utility of accepting or rejecting the rule. JOHN STUART MILL 1806-1873 Believed that happiness, not pleasure, should be the standard of utility. • HAPPINESS Advantages: A higher standard, more specific to humans About realization of goals Disadvantages: More difficult to measure Competing conceptions of happiness JOHN STUART MILL Qualitative Intellectual separation of pleasures and moral pleasures are superior to more physical forms of pleasure HEDONISTIC ETHICAL THEORY Teaches the end of human conduct is happiness. “the greatest happiness of the greatest number” Pleasure and pain distinguish the conduct of right and wrong. UTILITARIAN CRITICISM o Impossible to apply happiness cannot be quantified or measured o no way of calculating a trade off between intensity and extent. o UTILITARIAN CRITICISM o It is not proven by science or logic to be correct or ethical o - Suppose something bad will happen regardless of whether or not you do it. Then it seems that if you are a utilitarian you should be indifferent to whether you did it or not; after all, the same consequences will come about. UTILITARIAN VIEW ON MUSIC PIRACY The Utilitarian perspective seems to support the piracy of music. To their thinking, they feel as if whatever promotes the most happiness is therefore the right thing to do. Even though this supports piracy, it is still against the law. REVIEW QUESTIONS: Is an action good because you had good intentions? Or is it good depending on the consequences? Should our decisions only be made on what brings us the most happiness or pleasure?