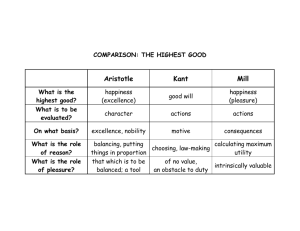
The end may justify the means as long as there is something that justifies the end. Jeremy bentham Brief discussion about utilitarianism “Utilitarianism seeks to promote the greatest good for the greatest number “ Now let’s move on the origins and nature of this theory of utilitarianism. These are the portraits of the two philosophers who are responsible in the concept of utilitarianism. Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart mill in which Jeremy Bentham is named as the father or the founder of utilitarianism and John Stuart mill contributed to utilitarianism by developing the htheory. They have different perceptions regarding utilitarianism and let’s start with Bentham’s Utilitiarianism. 2nd slide Actions are approved when they are such as to promote happiness, or pleasure, and disapproved of when they have a tendency to cause unhappiness, or pain Principle of utility- The principle tells us that an action is right or wrong according to whether it promotes happiness. Utility – usefulness or it is basically wellness or happiness Ex: There are three people drowning and you have the chance to save them. But the thing is The two are close to each other and the other person is separated to them which means either of them were only to be saved. In Utilitarianism, the right thing to do is to save the two persons rather than saving the only one because it will produce greater happiness or greater pleasure. Killing that one person is right because it produces more pleasure. 3rd slide He is claiming that we are ruled by this 2 sovereign masters- pleasure and pain. From what Bentham said that we are ruled by pain and pleasure, he means that whatever we do or act or say and think, our decisions is based on the pleasure and pain it will give to us. We are motivated by pain and pleasure. Since we are governed by these 2 sovereign masters, he means that we are seekers of pleasure and avoiders of pain. People act based on our own interest, Bentham said. And this interest of us is to look for pleasure and keep away the pain. 4th slide- but he said that the physical source of pleasure is the most fundamental or the basis of all others. In utilitarianism, how do we know what act produces the greatest happiness? Bentham created the hedonic calculus. 5th slide This hedonic calculus is like a calculator in calculating or quantifying the pleasure an act will give. It is a way of determining how great the pleasure will be from the action that you will make He was dubbed as the quantitative hedonist or quantitative utilitarian because of his standpoint that an act should be quantified by how much pleasure it will create. So he wrote down 7 criteria in quantifying pleasure Intensity – how intense the pleasure. Will the act you’re going to make will produce strong or high pleasure Duration- how long the pleasure will last. Certainty- Is this guaranteed or is it uncertain. The assurance that it will produce pleasure Propinquity- (when is the time that the pleasure will be achieved?) how far in the future is this pleasure going to occur, is this right now or maybe after a year. (do you want the pleasure of your act to occur right now or for the next month or a year) Well in bentham’s theory, pleasure should be achieved immediately Fecundity- how much further pleasure is going to be generated (may susunod ba may kasunod na pleasure or yun lang ba and that’s it ?) is it just a onetime pleasure or will the act produce more pleasures Purity- The purity of the pleasure. This is similar to certainty but this purity is where the pleasure do not have a mix of pain. The act should result to pure pleasure. Extent – the number of people affected by the pleasure 6th slide Actions are approved when they are such as to promote happiness, or pleasure, and disapproved of when they have a tendency to cause unhappiness, or pain 7th slide The retributive theory seeks to punish offenders (wrong doers, sinner ) because they deserve to be punished. Maybe some of you may agree that those who commit mistakes or the sinners deserves to be punished. The utilitarian theory of punishment seeks to punish offenders to discourage, or "deter," future wrongdoing Bentham’s utilitarnism is an ACT utiltiarianims Because in every situation you are choosing how to ACT. Your actions are important. You can act differently in every situation depending on the calculator . Mill’s Utilitarianism 1st slide But his version of utilitarianism disagrees with what Jeremy Bentham stated. Jeremy bentham believed that physical pleasure is the most fundamental source of pleasure but Mill disagrees with it as he is claiming that intellectual pleasures are higher than physical pleasures These physical pleasures are sensual pleasures, like eating or sleeping. And this intellectual pleasure which mill considered as higher pleasures are in terms of emotion, listening to music, enjoying meditating and more. 3rd slide Rule- you need to make general rules in order to maximize happiness: Ex: In a hospital, there are people in need of organ transplants and there is one healthy person at the hospital too. The organs of the healthy person can be harvested in order to save the four people’s lives. If that is the situation, utilitarianism would kill that one person in order to save the 4 people because it produces the greatest number of pleasure. In rule utilitarianism, it is wrong to kill people and therefore even if you can maximize the happiness in the situation by saving those five people’s lives, the rule says do not kill so therefore that person’s life is save. Another example is lying. In act utilitarianism, if making a lie gives more happiness or pleasure then you go and consider lying for the sake of many people. But in rule utilitarianism, and the general rule is lying is bad, sicne it is a general rule, and can maximize the general people’s happiness then we do not choose to lie. Business Fascination with Utilitarianism Utilitarianism gives us a sense of direction for what we should do and what decisions we should make namely the decision that produces the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people- Business fascination Normally in business context, we think and make decisions that will give us the best benefit or happiness or pleasure. That is how utilitarianism apply to business. For example in a pharmaceutical company, they are to release an approved drug that have side effects but can treat a disease. if the number on the problems of side effects is lesser than the benefits that the cure can give then it is that the act is right or the act is justified. The The end may justify the means as long as there is something that justifies the end. Who is the quantitave hedonist? Jeremy Bentham * John Stuart Mill Aristotle Immanuel kant Who is the qualitative hedonist? Jeremy Bentham John Stuart Mill * Aristotle Immanuel kant Utilitarianism dictates that actions are morally good when they promote the actor's interests and well-being. when they promote general happiness. when they are performed by a virtuous person. when they reflect the following of a just principle, regardless of the consequences Which of the following actions would Mill judge as morally the best? Saving a person from drowning out of a sense of moral duty. Saving a person from drowning out of a desire for celebrity. Saving a person from drowning out of a desire for reward money. All three actions are equally good. Who is associated with Act Utilitarianism? John Stuart Mill Jeremy Bentham Which one uses the Hedonic calculus ? Act Utilitarianism Rule utilitarianism How many elements are there to the Hedonic calculus? 4 6 5 7 Who said that pleasures of the mind are greater than the ones of the body? John Stuart Mill Jeremy Bentham WD Ross hat are higher order pleasures? Intellectual pleasures eg. reading Physical pleasures eg. eating What did Bentham say were the “two sovereign masters” that govern humans? Pleasure and Pain Happiness and Sadness Legalism and Antinomianism Evil and Suffering Which one of the following is NOT part of the Hedonic Calculus? Extent Duration Clarity Purity What does ‘propinquity’ mean? How much pleasure? How certain is the pleasure? How long will the pleasure last? How close or far away is the pleasure? Mill said, “It is better to be ---dissatisfied than a fool satisfied”. Plato Socrates A pig A human being