PASSIVE ACTIVE
advertisement

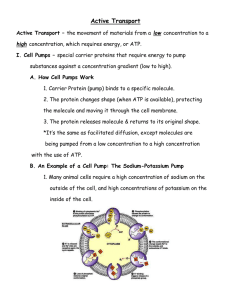
PASSIVE ACTIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION CARRIER PROTEINS FACILITATED DIFFUSION CHANNEL PROTEINS FACILITATED DIFFUSION AQUAPORINS (OSMOSIS) Na+ - K+ PUMP PROTON PUMP COTRANSPORT EXOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS (Phagocytosis) RECEPTOR MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS (Pinocytosis) MEMBRANE MEMBRANE PROTEIN PROTEIN MEMBRANE MEMBRANE PROTEIN PROTEIN MEMBRANE MEMBRANE PROTEIN PROTEIN MEMBRANE MEMBRANE PROTEIN PROTEIN MEMBRANE MEMBRANE PROTEIN PROTEIN VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE VESICLE NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP NO HELP Moves small, uncharged, nonpolar molecules across membranes from [HIGHER]→[LOWER] EX: O2 from lungs to blood; CO2 from blood to lungs Moves glucose into cells with the use of proteins that change conformation & flip to other side Moves water molecules across cell membranes from [HIGHER]→[LOWER] Moves ions such as Ca++, Cl-, Na+, K+ passively from [HIGHER]→[LOWER] Electrogenic pump that moves 3 Na+ out of cells and 2 K+ into cells creating an electrochemical gradient [LOWER]→[HIGHER] Cells engulf solutes or fluids Electrogenic pump that moves H+ across a membrane to create an electrochemical gradient [LOWER]→[HIGHER] EX: Make lysosomal interior acidic Linked to ATP formation in photosynthesis/respiration Moves a molecule into/out of cells by coupling its transport to the movement of another down its gradient EX: Glucose linked to movement of H+ Cells engulf large molecules or whole cells EX: White blood cells/bacteria Specific molecules (ligands) are taken into cells after binding to receptors on the cell surface EX: cholesterol uptake Transport vesicles fuse to cell membranes and release their contents outside cell EX: used by Golgi