Sponges and Cnidarians
advertisement
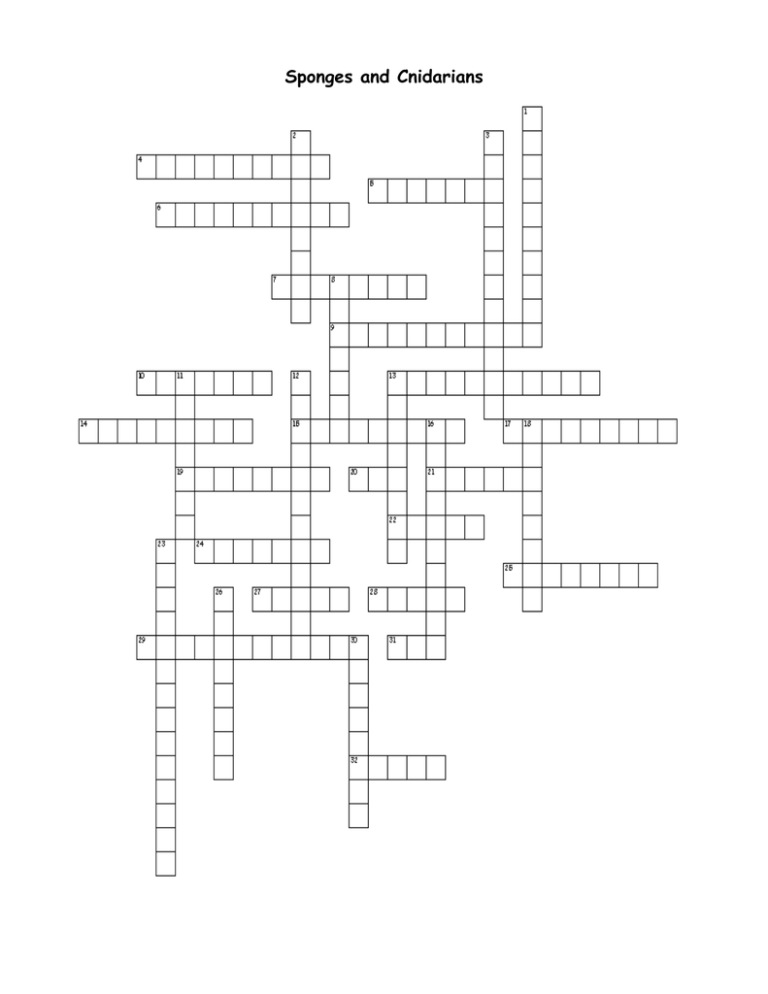
Sponges and Cnidarians Across 4. Released from the base of a hydra to unattach and tumble to another area 5. An asexual reproduction in sponges in which small outgrowths on the sponge break off and become new sponges 6. Marine cnidarian shaped like a flower 7. Jellylike, nonliving layer between the two cell layers of sponges 9. Flagellated collar cells that line the interior of a sponge 10. Attaching to a surface and not moving 13. Mobile cells in sponges that take food to other cells in the sponges body 14. Class containing jellyfish 15. Makes up the case in which corals live 17. Outer cell layer of cnidarians 19. Internal buds made by sponges and released when conditions become too harsh for the adult sponge 20. Number of cell layers in sponges 21. bell-shaped cnidarians with mouth and tentacles on the underside 22. Incurrent pores on sponges 24. Simplest aquatic animal 25. Phylum for sponges 27. Freshwater cnidarian 28. vase-shaped cnidarian with upright tentacles and a mouth on the top 29. Cell layer in cnidarians surrounding the gastrovascular cavity 31. Another name for the gastrovascular cavity 32. Immature, motile sponge stage that is produced from sexual reproduction Down 1. Stinging cells in the tentacles of cnidarians for capturing prey 2. Thick or thin jellylike layer between the cell layers of cnidarians 3. The ability of a sponge to regrow missing parts 8. Large opening at the top of a sponge where excess water leaves 11. Flexible protein fibers making up the skeleton of sponges 12. The type of feeding found in sponges 13. Class containing corals 16. Coiled, harpoonlike structure with a trigger capable of being shot out into prey 18. Microscopic organisms trapped by sponges for food 23. Sponges ability to produce both eggs and sperm but not self-fertilize 26. Web of nerves in cnidarians 30. Tiny hard spike-shaped particles of limestone or silica in a sponge’s skeleton




