1 The digestive system has two groups of organs: 1) ... _____________________________ or GI tract that ____________________ and _______________________
advertisement

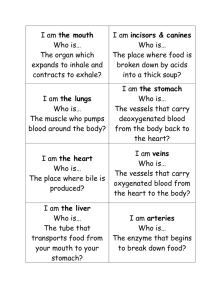
1 Chapter 23 Class Notes BSC 2086 Fall 2010 The digestive system has two groups of organs: 1) the ___________________________, or _____________________________ or GI tract that ____________________ and _______________________ food, and includes the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, _____________________, ___________________________________, and large intestine; 2) ____________________________ digestive organs, that include: teeth, tongue, _________________________ and digestive ________________________: salivary glands, ______________________ and ______________________________. What are the 6 essential activities of Digestion? (Slides 8 – 10) GI Tract Regulatory Mechanisms include: 1) ________________________ and ___________________________ that: respond to ___________________, changes in _______________________ and __________, the presence of ____________________ and _____________________ products of digestion. The mechanisms ________________________ that _______________________ or _________________________ digestive glands, stimulate ________________________ muscle to ______________ and move __________________ contents. 2) __________________________ and ________________________ controls, where ______________________________________ plexuses initiate short-timed reflexes in response to stimuli in the GI tract, and long lasting reflexes in response to stimuli in the GI tract involve the _______________ and _________________________ nerves; _________________________ from cells in the stomach and small intestine stimulate target cells in the same or different organs. The Peritoneum is a serous membrane of abdominal cavity, the ______________________________ peritoneum is on the _________________ surface of digestive organs, and the _____________________ peritoneum lines the body wall. (Slide 14) The __________________________ is a double layer of peritoneum that provides: routes for __________________________, ___________________________________ and ____________________; it holds organs __________________ and stores ___________________. The ____________________________________ circulation drains nutrient-rich _____________________ from ________________________ organs and delivers it to the _________________ for processing. What are the 4 Tunics of the Alimentary Canal? 2 The _______________________________ lines the Lumen. What are its functions? What are the 3 sub-layers of the Mucosa? (Slide 20) Epithelium layer has _____________________________ epithelium and ________________ __________________________ cells. Mucus ________________________ digestive organs from enzymes, and eases food passage. The mucus epithelium may secrete ______________________ and ___________________________. The ___________________________ is ________________________________________ tissue that has ______________________________ for nourishment and absorption, and _______________________________________ (part of MALT). The ___________________________ mucosae is smooth muscle that produces local movements of mucosa. (Slide 22) The submucosa has what 5 things? The ___________________________________ is responsible for __________________________ and ____________________________________ ; it has inner circular and outer longitudinal layer ____________________________________ and ____________________________ in some regions. (Slide 26) The _____________________________________________ is the intrinsic nerve supply of the alimentary canal, with the ______________________________________ plexus that regulates ________________________ and ______________________________ in the mucosa, and the _____________________________________ nerve plexus that controls ______________________________. The _______________________________________ linked to the ___________________ via afferent visceral fibers. Long ______________________________________ fibers synapse with enteric plexuses. Sympathetic impulses __________________________ secretion and motility; ________________________________ impulses _________________________ secretion and motility. (Slide 33) What are 3 functions of the Tongue? (Slide 34) Which 3 types of papillae of the tongue house taste buds? (Slide 38) What are 4 functions of Saliva? 3 (Slide 42) _________________________ is 97–99.5% _____________________, slightly acidic solution that contains what 9 things? (Slide 43) What is Xerostomia? (Slide 44) _______________________ deciduous teeth erupt (6–24 months of age), their roots are ___________________________ and teeth fall out at ___________________ years of age as ______________________________ teeth develop. There are ____________________ permanent teeth. All except ________________ molars (wisdom teeth) erupt by the end of adolescence. (Slides 49-51) The _______________________ of the tooth is the exposed part above the ___________________ (gum); it is covered by ______________________—the hardest substance in the body and is made of calcium salts and ____________________________________crystals). The ____________________ portion is embedded in the jawbone, and is connected to crown by ___________________ of tooth. The ___________________________ is calcified connective tissue that covers root and attaches it to the periodontal ligament Periodontal ligament forms a fibrous joint called a ___________________________. The _________________________ is a groove where gingiva borders the tooth. The ___________________ is bonelike material under enamel that is maintained by _______________________________of pulp cavity. The _____________________ cavity is surrounded by dentin. The ___________________________ connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves Root canal: extends from pulp cavity to the apical foramen of the root. (Slide 53) Dental __________________ (cavities) are the gradual demineralization of enamel and dentin. Dental __________________________ (sugar, bacteria, and debris) adheres to teeth, ________________ from bacteria dissolves calcium salts, ____________________________ enzymes digest organic matter (e.g., your gums and teeth). Prevention is ______________________________________________. (Slide 54) Gingivitis is caused by _____________________ that calcifies to form calculus (tartar), which disrupts the seal between the ________________________ and ___________________; _________________________ bacteria infect gums, but infection reversible if ___________________ is removed. (Slide 55) What is periodontitis and what are the consequences? 4 Chapter 23 B (Slide 2) What is the function of the Oropharynx and the Laryngopharynx? (Slide 7) Describe the 4 Digestive processes that take place in the mouth: (Slide 8) ______________________________ involves the tongue, soft palate, pharynx, esophagus, and ________________________ muscle groups. The _____________________ phase uses _____________________ contraction of the tongue. The _______________________________ phase is ____________________________; its control center is in the _____________________ and lower ________________________. (Slide 12) What process moves food through the esophagus to the stomach? (Slides 13-14) What are 8 gross anatomy features of the stomach? What is omentum (slide 17)? (Slide 20) Describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve supply to the stomach: (Slide 22) What are the 3 layers of muscular externa of the stomach? (Slide 23) What are two unique features of stomach mucosa? (Slide 25) What are the 4 gastric gland types? 5 (Slide 27) What 2 things do Parietal Cells secrete? What do Chief cells secrete? Describe the positive mechanism of Chief Cell secretion: What 4 things do Enteroendocrine glands secrete? (Slide 31) What causes gastritis? What causes peptic ulcers? Describe the 5 digestive processes of the stomach: (Slides 34-35) What are the 3 phases of gastric secretion? (Slide 36) What 3 chemicals stimulate Parietal cells? What do anti-histamines do here? (Slide 39) What is the rate of peristaltic waves? (Slide 42) How long does fatty chime remain in the duodenum? CONTINUE HERE… (Slide 44) The _______________________ is the major organ of digestion and absorption; it is ___________________ long from ___________________ sphincter to ileocecal valve . Its subdivisions include: The bile duct and main pancreatic duct join at the _________________________________ ampulla (enlarged area of duct), and enter the duodenum at the major duodenal ______________________ (bump on duodenum); these are controlled by the hepatopancreatic ___________________________. 6 (Slide 49) What are 4 structural modifications of the small intestine and what is their function? (Slide 50) What is a second function of circular folds? What 2 types of cells are contained in the villus epithelium? (Slide 53) Briefly describe microvilli: (Slide 54) What 5 types of cells are contained in the intestinal crypts? What is intestinal juice and what is its function? What is the largest gland in the body? The ____________________________ ligament separates the (larger) right and (smaller) left lobes, and _________________________ the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall. The round ligament is a remnant of the ____________________________ vein running along the free edge of the falciform ligament. (Slide 62) Briefly describe the hepatic, cystic and bile ducts: (Slide 64) Briefly describe a liver lobule: What 3 things are located in the portal triad of the liver? What can be found in the hepatic sinusoids (Slide 66)? (Slide 68) What are 4 functions of hepatocytes? What are the 3 major ingredients of bile, and what is a function of bile salts? What is a major function of the gall bladder? 7 Chapter 23 Part C Briefly describe the Endocrine and Exocrine Functions of the Pancreas: What are 4 enzymes contained in pancreatic juice? Which enzyme is secreted from pancreas in its inactive form? (Slide 6) Protease activation in duodenum: _______________________________ is activated to trypsin by brush border enzyme __________________________________; ______________________________________ and ________________________________________ are activated by _________________________. (Slide 8) What stimulates bile secretion? (Slide 9) Gallbladder contraction is stimulated by _______________________________________________ from intestinal cells exposed to ___________________ and _____________________ in chyme. (Slide18) Chyme contains what 3 things? (Slide 19) What are 3 requirements for digestion and absorption in the small intestine? (Slide 22) What chemical initiates peristalsis? (Slide 26) Describe 3 unique features of the large intestine: What are 4 regions of the large intestine? (Slide 35) What are 2 positive contributions of intestinal flora? (Slide 36) What are 2 main functions of the large intestine? (Slide 41) What are 3 types of chemical digestion? (Slide 42) What are 7 enzymes that digest carbohydrates? 8 (Slide 43) What are 2 ways carbohydrates are absorbed? (Slide 45) What 7 enzymes digest proteins? (Slide 45) How are amino acids absorbed? (Slide 48) What are the 2 steps for digesting lipids? (Slide 49) Describe the steps involved with the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids: (Slide 52) How are nucleic acids digested and absorbed? (Slide 54) How are vitamins absorbed? (Slide 59) What is celiac disease and how is it treated?