1 Powerful Skeletal muscles are attached to _____________ or _____________, are
advertisement

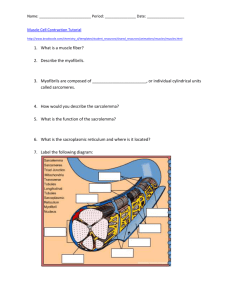
1 BSC 2085, Chapter 9A Class Notes – Fall 2010 Powerful Skeletal muscles are attached to _____________ or _____________, are ___________________, ___________-nucleate, and under ____________________ control. Cardiac muscles found only in the _____________ have _______________ chains of cells, have _______ or _______ nuclei per cell, and are under ______________________ control. Smooth muscles are not ________________, have ___________ nucleus and are under _________________ control. (Slide #6) What are the 4 main characteristics of Muscle Tissue? What are 4 functions of muscles? Each Muscle is served by one __________________, one _____________ and one or more _______________. (Slide #9) Each skeletal muscle _________________ or muscle ________________is supplied with a ________________ that controls its activity. Skeletal muscle has a rich _____________ supply, as contracting muscle fibers use huge amounts of __________ and require almost continuous delivery of _____________. (Slide #10) What are the 3 connective skeletal muscle sheaths and what do they surround? (Slide #12) Please describe 4 types of muscle attachments: (Slide #14) A muscle cell is a cylindrical cell that is ____ to _____ microns in diameter, and up to __________ long. _________________ of embryonic cells have previously fused to produce one mature muscle cell. The plasma membrane of the muscle cell is called the _____________________ and the cytoplasm is called the __________________. The muscle cell has many _________________________ for making ___________ (energy molecules). _____________________ store glycogen in the muscle. _________________ a red pigment, is used for oxygen storage in the muscle. What are three unique elements of the muscle fiber? 80% of the volume of the muscle fiber (cell) is comprised of ______________________. (Slide #18) What comprises the dark A bands and the light I bands of the myofibril? 2 What is the role of elastic titin? Please Label these Figures: Slide #20 Slide # 28 3 (Slide #21) Myofibrils may contain hundreds of _________________ packed end to end. A _____________ is the smallest contractile unit of a muscle fiber (cell) and it is the functional unit of skeletal muscle. The Sacromere consists of one _________ flanked by one half of an ____________. (Slide #22) A Sarcomere is the region of a myofibril that is between two successive ____________. A Sarcomere is composed of __________ and ________ myofilaments made of contractile proteins. (Slide #25) Thick filaments run the entire length of an ____________. Thin filaments run the length of the _____________ and partway into the A band. ___________ is coin-shaped sheet of proteins that anchors the thin filaments and connects myofibrils to one another. The _________________ (stands for “helle” = bright) is the lighter mid-region where filaments do not overlap. The _____________ (stands for middle) is a line of protein myomesin that holds adjacent thick filaments together. The myofilaments are connected to the sarcolemma and held in perfect alignment at the __________ and ___________. Please Label the Figure above (shown on Slide #28). (Slides 29-30) The thick filament called _______________ has a _______________ and two __________________________. Myosin Heads contain 2 smaller, light polypeptide chains that act as ___________________during contraction, and also have these three things: (Slide #31) Actin has a twisted double strand of fibrous protein called _______________ that consists of ___________________ that bear active sites for _________________ head attachment during contraction. ____________________ and ____________________ are regulatory proteins bound to Actin. (Slide #36) The ______________________________ is a network of smooth endoplasmic reticulum surrounding each myofibril. The SR has pairs ______________________ that form perpendicular cross channels. The __________________________ (SR) functions in the regulation of ______________________________________________. (Slid #37) The ___________________ are continuous with the sarcolemma, and penetrate the cell’s interior at each A band–I band junction. The T tubule is associated with one pair of _______________________ of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum; together these form _____________ that encircle each sarcomere. (Slide #39) Muscle contraction is ultimately controlled by _____________________________________ travelling along the sarcolemma. _______________________ conduct impulses deep into muscle fiber. 4 (Slide #40) At the Triad, integral proteins of the _______________________ and the SR __________________ protrude into the space between the T tubule and SR cisternae. These integral proteins interact to play an important role in ____________________________. (Slide #41) T tubule integral proteins are ____________________________. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum integral proteins called _________________________________ are gated channels that regulate _____________________________ from the SR’s cisternae. (Slide #42) The T tubule, SR cisternae and Sarcomeres work together to “couple” electrical impulses and Ca 2+ release to muscle contraction. This is called ____________________________________. (Slide #43) The generation of force does not necessarily cause shortening of the fiber. Shortening occurs when tension generated by cross bridges on the thin filaments ____________ forces opposing shortening. (Slide #44) In the ________________________________ Model of Contraction, in the relaxed state, thin and thick filaments overlap ________________. During contraction, myosin heads bind to ___________________, detach, and ______________________________ to propel the thin filaments toward the M line. (Slide #45) As H zones _________________ and _____________________, sarcomeres shorten, muscle cells shorten, and the whole muscle shortens. 5 6 7