Organic Molecules
advertisement

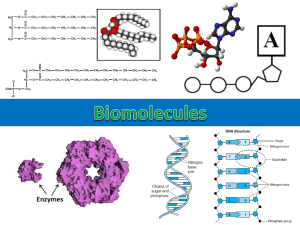
Organic Molecules Carbon Compounds • Organic Compounds – Must have Carbon (C) Four Groups of Organic Molecules • 1. Carbohydrates • 2. Proteins • 3. Lipids • 4. Nucleic Acids What are they made of? Molecule Monomer Carbohydrate monosaccharide Protein Amino acid Lipid Fatty acid chain Nucleic Acid nucleotide 1) Carbohydrates • Has carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO) – Ratio 1C:2H:1O • Made up of simple sugars (monosaccharide) – Glucose common simple sugar (C6H12O6 ) – Fructose – Galactose • Two simple sugars put together makes a disaccharide – Double sugar – Sucrose (table sugar) • Many simple sugars put together makes a polysaccharide Types of Carbohydrates Polysaccharides Function • 1) glycogen: animals store glucose • 2) starch: sugar in plants (store glucose) –Pastas, potatoes, breads • 3) cellulose: gives plants strength 2) Lipids • Have carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O) – More carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) than carbohydrates • Nonpolar molecules – Do NOT mix with water (insoluble) • Made up of fatty acid chains – Head (hydrophilic) – Tail (hydrophobic) Types of Lipids • 1) Triglycerides – Saturated fats (solids)—shortening and animal fats – Unsaturated (liquids)--oils • 2) Steroids – Testosterone – cholesterol • 3) Phospholipids – Form the membranes in cells • 4) Waxes – Highly waterproof 3) Proteins Have the elements C, H, O, and Nitrogen (N) • Made up of amino acids – There are 20 amino acids • Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds • A very long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. • The shape of a protein determines its function • Proteins perform a lot of different tasks – Movement: muscles and skin Types of Proteins • Hormones –Insulin • Enzymes –Function to speed up reactions –Words end in “-ase” –Lipase, lactase, kinase, etc • Hemoglobin –The part of a blood cell that carries oxygen 4) Nucleic Acids Made up of nucleotides Nucleotides have three parts –Sugar –Phosphate –Nitrogen base Function of nucleic acids is to store genetic information. Types of Nucleic Acids DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Nucleotide sugar is deoxyribose RNA Ribonucleic Acid Nucleotide sugar is ribose The pH Scale • Measurement of how acidic or basic a solution is. • Measures concentration of hydrogen ions H+ • pH number of 0-6 means its an acid • pH number of 8-14 means it’s a base (alkaline) • pH of 7 means it’s a neutral Buffers • Chemical substances that neutralize small amounts of either an acid or base • Prevents great fluctuations in pH • Maintains proper pH levels • Example: antacids Properties of Water (H2O) • Water is a polar molecule – Means uneven distribution of electrons – Positive (+) charge on hydrogen, negative (-) charge on oxygen Strange Water Properties 1) High Cohesion and High Adhesion Cohesion: water “sticks” to itself (beads up on surfaces) Adhesion: water is attracted to other substances (runs down the side of a glass) 2) High Specific Heat It takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of water 3) Water Expands When it Freezes – Ice is less dense than liquid (ice floats) Solutions and Mixtures • Mixture: made of two or more elements physically mixed together – Example: Mixing Skittles and M&Ms together Solution type of mixture where one substance is dissolved in another (Kool-Aid) • Solute: what gets dissolved (flavor pack) • Solvent: what does the dissolving (water) • Water is the universal solvent!