Document 17624694
advertisement
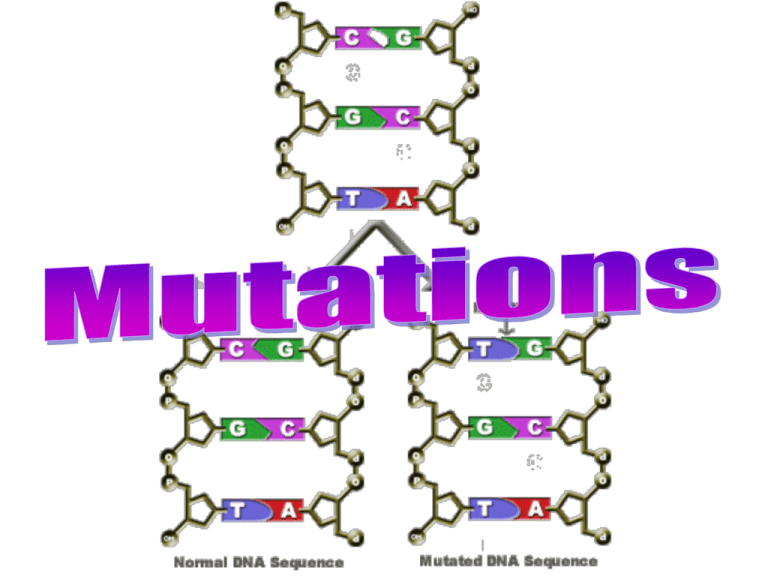
Defined: a change in an organism’s DNA • Where: DNA or Chromosomes • When: During replication, Synapses, or Crossing-Over • Mutations can affect a single gene or an entire chromosome: – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region Gene: Point Mutations DNA mRNA Amino acids Defined: one nucleotide is substituted for another • Often repaired by DNA Polymerase (spellchecker) enzyme • May lead to amino acid change (see animation) • May not lead to any change (Silent Mutation) – Ex: DNA “CCC” is mutated into “CCG” » Same amino acid is created (glycine) Gene: Frame Shift Mutation (deletion) DNA mRNA Amino acids Defined: Insertion/deletion of a nucleotide • Entire sequence of DNA/RNA after the mutation is shifted (see animation) • Much more serious to the structure/function of the final protein – mRNA sequence may have early or late “stop codons” Gene: Frame Shift Mutation (insertion) DNA mRNA Amino acids Defined: Insertion/deletion of a nucleotide • Entire sequence of DNA/RNA after the mutation is shifted (see animation) • Much more serious to the structure/function of the final protein – mRNA sequence may have early or late “stop codons” Impact on Offspring • Somatic cell mutations • Germ cell mutations – Affect only the individual – May be passed to future generations (either – Not passed on to future harmful or beneficial) generations – Ex: Sperm cell mutation – Ex: Muscle cell mutation • Natural selection often removes mutant alleles from a population when they are less adaptive. Mutation Causes • Mutagen: agents in the environment that can change DNA – Speed up replication process – Break apart nucleotides • Ex: UV sunlight breaks hydrogen bond between thymine (T) and adenine (A) REview 1) What is a mutagen and how do they cause problems? 2) How are proteins affected if the DNA code is mutated? Example: ATTCGAGG is mutated to ATTCGTGG 3) What is the difference between a point mutation and frame shift mutations? 4) When are mutations passed on to future generations? 5) Are all mutations considered bad/dangerous? Explain.