Unit 2 BioChemistry Section 3 Carbon Compounds
advertisement

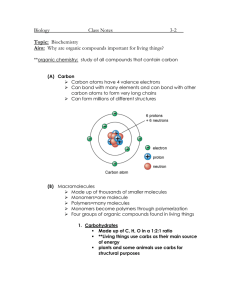
Unit 2 BioChemistry Section 3 Carbon Compounds Organic Compounds : compounds that contain Carbon and usually come from living organisms Why Carbon is so interesting that the whole branch of chemistry is set aside for it? Versatility 4 valence electrons, which make covalent bonds with H, O, P, S, N forms chains or rings between Carbon atoms they can form single, double, or triple bonds page 44 Macromolecules “Giant molecules” made of 100’s-1000’s of small molecules Macromolecules are formed by process -polymerization (small molecules join -> large compounds Monomers are joined to form polymers in a process called Dehydration synthesis ; water is removed to join the monomers Polymers are broken down into monomers by a process called hydration; water is added. There are 4 different groups of organic compound 1. Carbohydrates : made of C, H, O in a 1:2:1 ratio Carbohydrates are a main source of Energy and Structure in plants include sugar and starch Monosaccharide (monomers) - monomer - simple sugar (ex: glucose, fructose) Disaccharide - 2 monosaccharides bonded (ex:maltose, lactose, sucrose) Polysaccharide - giant polymers of linked monosaccharides (monomers) (ex: Starch – energy stored in plants, glycogen - energy stored in animals, Chitin & Cellulose – structural purposes), names usually end in -ose Monosaccharide is a monomer 2. Lipids : made of C, H, O and sometimes P Lipids are used for Energy storage and are part of biological membrane & water proof covering. include fat, oil, wax, steroids (chemical messengers) not soluble in water formed by bonding Glycerol with a Fatty acid chain 1. Saturated - C’s are bonded by single bonds, Maximum number of Hydrogen atoms, usually solid. 2. Unsaturated – one pair of C’s bonded by a double bond, Liquid 3. Polyunsaturated - more than one pair of C’s bonded by a double bond * Cell membrane mainly composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which controls chemical movement into and out of the cell and separates the cell contents from the outside world. 3. Nucleic Acids : made of C, H, O, N, P Consist of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) & Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Store or Transmit heredity or genetic information. Nucleotide (monomers) join to form a nucleic acid (polymers) Nucleotide is a monomer 4. Proteins : made of C, H, O, N, S Amino acids (a.a.) monomers join to form protein polymers 20 different types of amino acids like different combinations of letters make up words, different combinations of a.a.’s make up proteins. a.a.’s consist of an amine group (NH2) and a carboxyl group (COOH) and R group (which makes them different) amino acids are linked by peptide bonds to form proteins. Amino acid is a Monomer Functions: Each protein has specific function that depends on its conformation (shape) Form structure - hair nail (keratin), storage, transport – (hemoglobin), control movement muscle/skeletal (actin myocin, collagen), defense – antibodies, regulation of cell functions – (hormone, enzymes) The function of the protein depends on its shape (depends on organization of amino acids/ how they fold in protein) Primary structure – linear chain of amino acids in specific order joined by peptide bonds. Secondary structure: turns and folds of the primary structure due to hydrogen bonding Tertiary structure: chain of amino acids is twisted or folded to form globular (3D) protein Quaternary structure: two or more polypeptide chains joined together