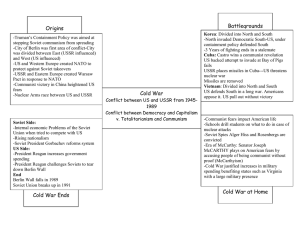
Name: ________________________________________ Date: __________________ Per: _________ The Cold War
advertisement

Name: ________________________________________ Date: __________________ Per: _________ The Cold War AP World History II “A Marriage of Convenience” The Cold War _______________________________________________________________________________ _____________ •Conferences –_______________ (11/43) –________________ (2/45) –________________ (7/45) Goals of the Conferences •USSR wanted Britain and France to open second front on the east to defeat __________________ •Deal with Japan…Stalin agrees to fight Japan only once _____________ was defeated •Division and _________________________ of Germany and Austria •United __________________ •Fate of _________________________________ Bretton Woods •Conference held in Bretton Woods, ____________________________ –Creation of the International Bank (_________________) –International _____________________Fund (IMF) •Goal: TO PROMOTE ___________________________ STABILITY •The ________________ refuses to join Cold War 1945-1949 •After WWII, Soviet Union installs _________________________ governments in E. Germany, Poland, and many other E. European nations. •In response to the rise of Communism in the _______________ that Churchill declares “an ____________________ has descended upon Europe.” •All of this violates promises Stalin made at ________________ Cold War 1945-1949 •Stalin’s Policy: TO GAIN AS MUCH _______________________AS POSSIBLE without a fight. –Wants a ________________________ between USSR and the West –The ______________________: Soviets cut off highway and railroad traffic between West Berlin and W. Germany. •The US engages in the ____________________, where we fly goods in and out of Berlin. Stalin backs down. Cold War 1945-1949 •US policy: __________________________ –Communist threats in ______________and ____________ worsened. –Truman Doctrine: “moral and material aid to any and all countries whose ___________________________ is threatened by ___________.” –____________________ Plan (economic recovery plan)-economic assistance to wartorn nations threatened by ____________________ –________________ (North Atlantic _____________ Organization)-Military commitment which bound the US, Canada, Britain and 9 other Western European States into a _________________________. Cold War 1945-1949 •________________________did not equal war –It did give the Soviets the __________________ •USSR formed its own alliances as well –______________________-Council for Mutual Economic Assistance –____________________-military alliance designed to combat NATO •After 1949, the Cold War goes_________________________! 1949 •Europe joins ________________ •Soviets test their first ___________________ •China’s Civil War comes to end with a victory for ____________________ and his _______________________forces –Nationalist forces flee to ____________________ Korean War •1950-1_______ •After WWII, the Korean Peninsula was divided into ___________________ –North-________________ –South-_________________ •Aided by the victorious Mao, ____________________ invades __________. •US intervenes on behalf of the _______, and the ____________________ are pushed back to the original line of division. STALIN DIES! •1953-_____________________ •Nikita ________________ (1943-1964) •Leonid Brezhnev (__________________) Nuclear Arms Race •By 1949, both sides were armed with ________________ weaponry •ICBMs: ______________________ Ballistic Missiles •MAD: Mutually Assured _____________________ •ABM: Anti-Ballistic ____________________ System The Third World •Europe was “___________________” •Many nations is Africa, Asia, and ____________________, however, were –Freeing themselves of their ______________ bonds –Giving birth to _______________ economies –Had weak ___________________ structures –Were ______________________ in the Cold War •The developing world was commonly referred to as the “____________________” •_______________________ Theory: if one nation falls to communism, an entire region would fall to communism •America supports _________________ leaders often simply because they are anti_______________________ 1950s •1956-__________________ tries to leave the Soviet bloc: Khrushchev _______________ •1956-______________ nationalization of ____________ Canal –Embarrasses ____________ and ___________________ –US and Soviet Union are in control as the “______________________” •1957-_____________________ Cuban Revolution of 1959 •USSR supported Fidel _______ overthrows right wing dictator Fulgencio _______________. •Goals: __________, industrialize, increase literacy rates, and eliminate economic _________ •He and Ernesto _______ Guevara combated what they believed to be US ________________ in __________________ America 1960s-The Hottest it gets! •1961-JFK authorizes the _____________________ invasion of Cuba –Tried to ______________ Castro (fails) –Castro (Khrushchev) installs _______________ missiles in Cuba (uh-oh!) –Building of the _______________ Wall •1962-__________________ Missile Crisis –____________ blockades Cuba –Soviets back down with promise not to invade Cuba and remove missiles from _______________________ Mid-Late 60s •1963-Nuclear ______________________________ –____________________, or _________________ was installed, and directly connected the __________________ to the White House •1964-______________________ overthrown –___________________ assumes power •Space Race ends with ____________ dominance and our land on the ______________. •Growing rift between ___________________ “brothers” China and ____________ Vietnam War •______________________ never fought each other directly…they intervened in the many conflicts going on in the _________________ World. •________________________ helps allies during WWII to defeat the Japanese –In exchange for assistance in getting rid of the French in __________ after the war. –Instead, the allies help the French attempt to get rid of Ho Chi Minh which fails by _______________ Vietnam War •South Vietnam was _____________________, unpopular, but had _______ support. •To prevent the ______________ theory, the US sends over __________ troops by the late 60s •Early 70s-fighting spreads to Laos and ___________________ •By 1975, all of Vietnam became ___________________ •The US pulls out in _________, having lost ___________________ lives The 70s-Air Conditioning •____________________-a peaceful period of the cold war (_____________ of tensions) •US gets closer ____________________ to China (_____________ visits China) •Nuclear Non-__________________________ Treaty (1968-69) •________________ Arms ______________ Treaty (SALT)-1972 •Anti-____________________ Missile Treaty (1975) Early-Mid 80s: Call the repairman! •1979-Soviet invasion of ______________________ –Threatened ____________ supplies in the middle east. •Arms control negotiations were __________________ •The _____________ Race heated up again •Moscow (80)/Los Angeles (84) _____________________ Boycotts Third World Battlefield! •_______________________ •1979-____________________ Revolution –Cuba and the USSR consistently tried to export ____________________ ideals throughout Latin America. –The Marxist, Soviet supported _______________________ overthrew the established _______________ dictatorship that had ruled Nicaragua since 1937 –The US threw its support behind the ______________________-a right-wing counterrevolutionary ________________ movement. Gorbachev •Takes over in 1985 and realizes the Soviets could no longer compete with the US in the arms race _______________________. •________________________ is taken down •1991-the Soviet Union _______________________ The Cold War Begins! "A shadow has fallen upon the scenes so lately lighted by Allied victory. . . . From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. . . . Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Bucharest, and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject . . . not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in many cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow. . . . I do not believe that Soviet Russia desires war. What they desire is the fruits of war and the indefinite expansion of their power and doctrines." ----Winston Churchill, speech delivered March 5, 1946 From World War to Cold War • United Nations established to keep _____________ and protect ______________ • Founding countries include _______, _____________, __________, _________, and Republic of _____________ • UN unable to prevent ______________ from growing between USA and USSR Bi-Polar World • The World quickly divides between – Those who support the USA (______________ Bloc) – Those who support the USSR (_________________ Bloc) – Those who hope to stay ____________________ and receive benefits from both (nonaligned nations) Nonaligned Nations •India, most of _____________, the _____________ world, and parts of Central and __________ America Communism in China • 1949 Mao Zedong pushes ______________ into exile in _________, establishes People’s _____________ of China • China becomes worlds largest _____________________ nation • Today Taiwan rejects __________________ attempts at unification Mao’s Great Leap Forward • 19____s • Plan to create a truly communist _________________ ________________ • _______________________ of farming and industry • Miserable failure, some call it the Great Leap ___________________• Caused ________________, millions died More Mao • Focuses on building _________________ • Tests first __________________ bomb in 1964 • Introduces some elements of ________________, then worries about straying from _______________ past The Cultural Revolution • 1960s • Goals: Erase everything ____________ and _____________, create a new society based on communist values • Disaster: Red Guards run amuck, _____________ kill teachers, medical students imprison _______________, many arrested and executed for being “_______________ _________________” I’ll have capitalism, hold the democracy! • Deng ___________________ takes control of China in ________________ • Adds elements of ______________________ into economy • Similar to Lenin’s New __________________ ____________________ • Remains politically communist, limiting __________________________. • 1989 _________________________ Square Massacre • Will democratic reforms ever take place? Change Over Time • Under the communists China has – Moved away from ____________________– Banned _______________________ – Eliminated the __________________ class – Granted political and legal equality to ______________________ – Created laws limiting families to ___________ child only – Added elements of ____________________ into the economy – Begun building one of the world’s strongest _____________________ Berlin • In _________________ Soviets built the Berlin Wall surrounding West Berlin • The fall of the Berlin wall in December 1989 signified the end of the __________ War and the fall of the _______ Germany After the Cold War • Decline of Soviet Bloc leads directly to ___________________ • Berlin Wall torn down in ________________ • Mass exodus of people out of ____________________ Germany • Today Germany struggles with ______________________ and economic issues associated with rejoining the economically poor East Germany into West Germany The End of the Cold War • Living standards in _____________________ Europe improve drastically • Eastern European states begin to _______________ against ___________________ – Demand _________________– ___________________ – Economic ___________________ Poland • Lech Walesa leads _____________________- movement against USSR 1980s • Polish gov’t arrests ______________________ • 1989 Solidarity _________________ • 1989 Berlin Wall torn down • 1990 Collapse of ________________ • 1990 Poland gains ____________________, _____________ _____________ elected President USSR Collapses! • Long history of economic ________________- and a _________________ of consumer goods • 1970s USSR invades __________________ • USA equips the _____________________- (freedom fighters) in a guerilla war against USSR • War is politically and economically costly USSR Collapses! • Mikhail __________________ takes power 1985 • Institutes two new policies – ___________________- (openness) – ____________________ (restructuring) • Plans meet with ___________________________ in Russia • USA continues to push ____________ and ________________ races • Economic and political turmoil lead to USSR’s _____________.