Notes: Ch 13 Rivers

Notes: Ch 13 Rivers
Almost half of the water that falls to the Earth’s surface eventually ends up in a stream or river (RUNOFF) where it travels overland to the oceans.
Rivers account for most of the erosion of EARTH’S SURFACE
Rivers can be divided into 3 main sections.
Rivers usually begin in the MOUNTAINS (source)
They flow downhill onto flat land and into the
OCEANS (mouth)
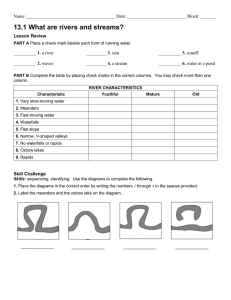
3 STAGES OF RIVER DEVELOPMENT
YOUTHFUL – STEEP SLOPE
MATURE - MODERATE
OLD - GENTLE
YOUTHFUL RIVER STAGE
STEEP slope or gradient
STRAIGHT narrow channel
VERY FAST moving water
‘V’ - shaped valleys
Many rapids & waterfalls – caused by STEEP SLOPES &
DIFERENTIAL EROSION
Youthful Rivers will carve a V-SHAPED valley
[Glaciers will carve a U-SHAPED valley]
MATURE RIVER STAGE
River channel starts to WIDEN
Some rapids and WHTIEWATER
FAST flowing water
FORMATION OF A MEANDER
SLOW moving water
INSIDE curve
Deposition will occur on the inside of a meander to create a POINTBAR
River starts eroding OUTWARD
MEANDERS and floodplain start to develop
FAST moving water
OUTSIDE the curve
Erosion on the outside of a meander will create a CUT BANK
OLD RIVER STAGE
Move very SLOW
Has a nearly FLAT slope
Wide FLOODPLAIN
Lots of MEANDERS
OXBOW lakes
MEANDER & OXBOW LAKE FORMATION
A river wants to find the shortest, straightest way to the ocean, so it will change paths along the floodplain cutting off wide loops leaving behind a curved body of water called an OXBOW LAKE.
FLOODS!
Rivers may overflow its banks as a FLOOD. The floodwater may cover part or the entire valley floor where the river runs eroding and depositing sediments.
This part of the valley floor is called the FLOODPLAIN.
Floods can ERODE or DEPOSIT.
FROM VALLEY TO FLOODPLAIN
Flooding speeds up erosion and deposition creating a broader floodplain on the valley floor.
Elevated ridges along stream banks are called
NATURAL LEVEES.
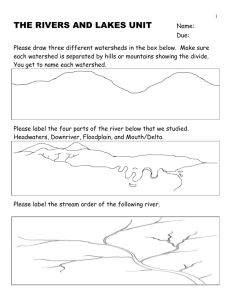
PARTS OF A RIVER SYSTEM
A TRIBUTARY is a stream that runs into a larger stream.
The main river will eventually drain into the OCEAN
A river and all of its tributaries is called a RIVERSYSTEM
The beginning of a river is known as the SOURCE. Begins from a spring or precipitation.
When the mouth of a river finally reaches its destination, be it ocean or lake, the water slows down & deposits its sediment, forming a DELTA.
An ALLUVIAL FAN is similar to a delta, but forms on land where a river emerges from a mountainous area and flows out onto a more gently sloping plain.
Notes: Ch 13 Rivers (page 2)
DRAINAGE BASINS or WATERSHEDS
The drainage basin, or WATERSHED, of a river includes all the land where rain falls that drains into the river directly or through its tributaries.
A watershed is like a PRECIPITATION COLLECTOR!
Every drop of water or POLLUTION that falls into the watershed goes into that river.
There is an INCREASE in storm water RUNOFF with urbanization.
There is a DECREASE in INFILTRATION with urbanization.
DIVIDES
High land (mountains) that separates one drainage basin from another is called a DIVIDE.
The major divide in the U.S. is called the CONTINENTAL.
The MISSISSIPPI Drainage Basin is the largest watershed in the U.S.
DRAINAGE PATTERNS
DENDRITIC is the most common
DENDRITIC RECTANGULAR
RADIAL
3 MAJOR WATERSHEDS OF VIRGINIA:
1. CHESAPEAKE BAY
2. GULF OF MEXICO (via MS River)
3. NORTH CAROLINA SOUND
Largest Localized Watershed in Virginia: JAMES RIVER
TRELLIS