S3 and S4: Geography Course
advertisement

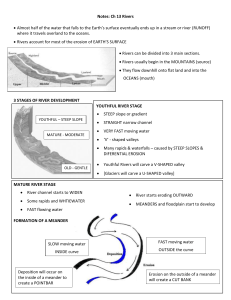
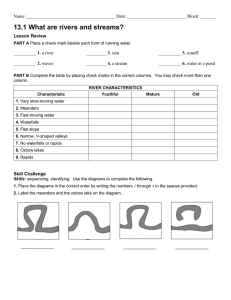
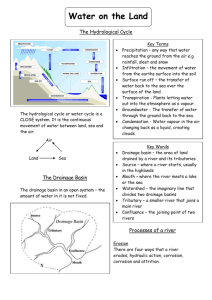
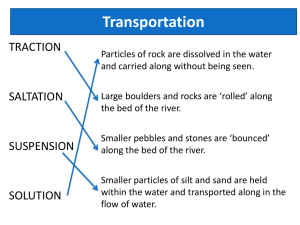
Features of a river: Describe what each of the following landforms are and explain how they are formed. Upper Course: Main processes = Vertical erosion V – shaped valley Interlocking spurs Waterfalls / Rapids / Gorge / Plunge pool Potholes Middle course: Floodplain Meanders Bluff Main processes = Lateral erosion and transportation Lower course: Main processes = transportation and deposition Meanders / Oxbow lakes Slip of slope / Point bar / River cliff Riffles and pools Wide floodplain / Levees Braiding River estuary Delta Important words: Abrasion: Erosion caused by water moving rocks / stones which scrape against the bed and banks of the river Alluvium: Stones, silt and mud deposited by a river, usually on a floodplain Attrition: Process of rocks in the river wearing way by rubbing / banging into one another Braiding: River dividing into separate channels Deposition: Process by which stones, sand and silt is dropped by the river Drainage basin:Area of land drained by one river system Erosion: Process by which the landscape is worn away Estuary: Wide river mouth where it meets the sea. Usually large areas are covered in mud Floodplain: Flat area next to the river in the middle and lower course, formed by silt and mud deposited when the river floods Meander: Bend in the river Oxbow lake: The lake formed by a meander, when the loop of the meander is cut off from the main channel by deposits of mud and silt River cliff: Steep bank of the river formed when erosion happens on the outside of a river bend Source: The start of the river Transportation:The process that moves rock particles down the river Tributary: A small river which joins a larger one Waterfall: A steep break in the course of a river where the water falls vertically. Often as a result of a hard layer of rock