Events Leading to the Civil War
advertisement

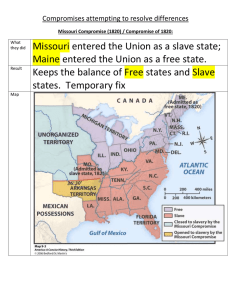
Events Leading to the Civil War Between 1800 and 1850, what region developed an industrial economy based on manufacturing? •The North Which region favored high protective tariffs? •The North Define protective tariffs. • Taxes on imports which are so high that Americans cannot afford to buy foreign goods What was the basis of the South’s economy? • Agriculture (Farming) • Plantations that used slave labor Did the South support or oppose high tariffs? •Opposed Why did the South oppose high tariffs? •Made manufactured goods more expensive As the U.S. expanded westward, what conflict threatened to tear the country apart? •Slavery Define abolitionists. • People who wanted to abolish (end) slavery immediately Who was one of the most important abolitionist leaders? •William Lloyd Garrison What was the name of the antislavery newspaper in Boston? •The Liberator Who published The Liberator? •William Lloyd Garrison Who wrote Uncle Tom’s Cabin? •Harriet Beecher Stowe Describe Uncle Tom’s Cabin. •An antislavery novel •Told the cruelties of slavery How did Uncle Tom’s Cabin affect the North? • Made Northern abolitionists mad • Caused many more Northerners to support the Abolitionist movement How did the Abolitionist movement affect Southerners? •Frightened them What kind of rebellions did Southerners fear? •Slave Rebellions Who was Gabriel Prosser? • African-American slave • Planned a slave revolt in Richmond, Va. • Revolt crushed by Va. militia • Prosser and 35 slaves were executed Who was Nat Turner? • An African-American slave • Led a slave revolt in Southampton County, Va. • Killed 55 whites • 100+ blacks were killed • Turner was captured and executed What were two effects of Nat Turner’s Rebellion? • Increased Southern fears of Slave Rebellions • Southern states passed stricter slave codes Who proposed the Missouri Compromise? •Henry Clay What were the 3 parts of the Missouri Compromise? • Missouri became a slave state • Maine became a free state • Louisiana Territory was divided at the 36 degree, 30 minute parallel; north of the line must be free territory; south of the line could be slave territory How many U.S. senators does each state have? •Two What balance did the Missouri Compromise maintain? • Balance of power in Senate between the North and the South Who proposed the Compromise of 1850? •Henry Clay Who have historians called the “Great Compromiser”? •Henry Clay What were the key points of the Compromise of 1850? • California became a free state • Stronger fugitive slave law • Abolished the slave trade, but not slavery itself, in the District of Columbia • Created the Utah and New Mexico territories; decide slavery by popular sovereignty What did the new Fugitive Slave Act do? • Made it easier for slave catchers to capture and return runaway slaves • Required escaped slaves to be forcibly returned to their owners in the South Who hated the Fugitive Slave Act? •Northerners What was popular sovereignty? • The people of a territory would decide whether they wanted slavery Who proposed the Kansas-Nebraska Act? •Stephen Douglas, Democrat (Illinois) What is a bill? •A proposed law What is an act? •A Law Identify the KansasNebraska Act. • Created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska • Said popular sovereignty would decide slavery in both Kansas and Nebraska • Since both Kansas and Nebraska were north of the Missouri Compromise line, the KansasNebraska Act repealed the Missouri Compromise What effect did the KansasNebraska Act have on the Missouri Compromise? • The Kansas-Nebraska Act repealed the Missouri Compromise. What broke out in the Kansas Territory? • Civil war between proslavery and anti-slavery settlers What adjective was used to describe Kansas in the mid-1850s? • Bleeding Kansas What political party was formed in opposition to the Kansas-Nebraska Act? • The Republican Party What were the two major results of the Kansas-Nebraska Act? •Bleeding Kansas •Republican Party What was the Supreme Court’s decision in the Dred Scott case? • Since Dred Scott was a slave, he could not sue in federal court • African-Americans were not citizens of the United States • Since Congress had no power to prohibit slavery in the territories, the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional What did the Dred Scott decision say about the Missouri Compromise? • The Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional. What power did the Supreme Court use in Dred Scott v. Sandford? • The power of judicial review In Dred Scott v. Sandford did the Supreme Court rule that Scott should remain a slave or gain his freedom? •Remain a slave Which section liked the Dred Scott decision, the North or the South? •The South Which group(s) liked the Dred Scott decision? • Abolitionists? • Republicans? • Slaves? • Slaveholders? Slaveholders Who ran for the U.S. Senate against Stephen Douglas in 1858? •Abraham Lincoln In the Lincoln-Douglas debates who supported popular sovereignty? •Stephen Douglas In the Lincoln-Douglas debates who said, “A house divided against itself cannot stand”? •Abraham Lincoln In the Lincoln-Douglas debates who said the U.S. could not continue half-free and half-slave? •Abraham Lincoln Who won the 1858 Senate election in Illinois? •Stephen Douglas In the 1850s what was the North increasingly against? •The Spread of Slavery to the West By the end of the 1850s, what did Southerners argue states could do? • States could nullify laws passed by Congress • States could secede from the Union What did it mean for a state to nullify a law? • Void it • Do Away with it What did it mean for a state to secede? •Leave the Union Who gave the “House Divided” speech in the 1858 Illinois Senate election campaign? •Abraham Lincoln