EARTHS SYSTEMS
advertisement

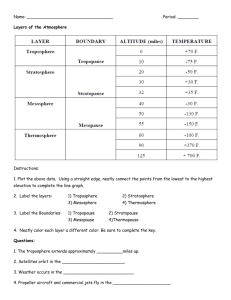
EARTHS SYSTEMS ATMOSPHERE • Invisible layers of air primarily made up of Nitrogen (75%), Oxygen (20.9%), and Argon (.9%) gases GREENHOUSE EFFECT • Radiation from the sun is reflected by earth and then bounced into the atmosphere where the water particles in the air trap the heat; the water particles remain in the troposphere causing the lowest layer of atmosphere to be warmer TROPOSPHERE • Zone where weather occurs; a dense layer of air in which molecules are fueled by sunlight and create energy for weather STRATOSPHERE • Above the troposphere; temperature increases and contains the ozone layer MESOSPHERE • Above the stratosphere; has the same pattern as the troposphere THERMOSPHERE • Above the mesosphere; temperature increases with increasing altitude. This layer is less dense because molecules are widely spaced and have less pressure. CORIOLIS EFFECT • Affects the direction of winds CUMULUS CLOUDS • Moist air collects rapidly over a small area • Cumulonimbus clouds cause thunderstorms STRATUS • Air rising gently over a large area and then cools slowly; makes sunlight seemed filtered; they contain ice crystals that can make the sun or moon appear to have a halo CIRRUS • High in the atmosphere and look wispy; they form when water vapor condenses directly into ice crystals AIR MASSES • Large areas of air with the same temperature and moisture levels of the surface COLD AIR MASS • Produces cold weather WARM AIR MASS • Produces warm weather MARITIME AIR MASS • Moist air that forms over the ocean CONTINENTAL AIR MASS • Dry air that forms over the continents COLD FRONT • Leading edge of a cold air mass; these fronts bring snow, thunderstorms, and heavy rains WARM FRONT • Leading edge of a warm air mass; these bring rainy weather followed by clear weather LOW PRESSURE • Causes cloudy and rainy weather; rapid low pressure changes cause storms BAROMETER • Measures the pressure of air pushing down on the tube of mercury WIND VANE • Measures the direction of the wind ANEMOMETER • Measures wind speed RAIN GAUGE • Measures the amount of rain OCEAN CURRENTS • Large rivers of water flow through the ocean • Cold Currents- run deep below the surface and creep along the bottom of the ocean until they reach the tropics • Warm Currents- water heated by the sun and are pushed along by steady winds from the equator JET STREAM • The jet stream is a fast flowing, river of air found in the atmosphere at around 12 km above the surface of the Earth just under the troposphere. It flows west to east. GULF STREAM The warm current that flows from the equator; it originates in the Gulf of Mexico and runs past the east coast of the United States towards Newfoundland