Objectives
advertisement

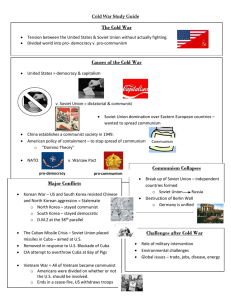
Objectives • Content: Interpret a map on the Marshall Plan and rank the top two countries who received aid. • Learning: List 5 rights guaranteed in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. The Cold War Post WWII and the 1950’s Rebuilding After WWII • United States wanted to prevent economic and political instability in Europe. • Marshall Plan – George C. Marshall’s plan to provide Europe with massive economic aid ($) to help rebuild their economies and to prevent the spread of Communism (Containment) Dresden, Germany Reichstag – Berlin Post War Germany • Germany was partitioned into West and East Germany – West Germany became Democratic and returned to selfrule after occupation. – East Germany became Communist and stayed under Soviet control. Tokyo, Japan Post War Japan • America stayed in Japan for 7 years to re-build • Japan was demilitarized, adopted a democratic government, and returned to self-rule • Japan soon became an ally of the United States United Nations • Formed near the end of WWII to prevent future global wars • First United Nations (UN) meeting in 1946 in California – 50 nations attended and agreed to settle disputes peacefully • Eleanor Roosevelt and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights Universal Declaration of Human Rights • Turn and talk to you neighbor about the right that was most important to you and why it was important. U.S. Economy • Switched from making war materials to consumer goods • The economy was strong –Increased demand for American products –Healthy job market –Increased productivity • Increase in buying on credit U.S. Workforce • Men were able to return to work since economy was booming • Most women returned to caring for the home and children full time. • Labor Unions became more powerful –Workers gain more benefits –Higher salaries Life in Post WWII USA Baby Boom • There was an explosion of baby births following WWII. • 1946-1964 – 79 million babies were born Life in Post WWII USA G.I. Bill of Rights • Gave educational, housing, and employment benefits to WWII veterans. Life in Post WWII USA Women’s Role • Over time, expect women balance household, children, and a job. • Because of prosperity, the next generation of women entered workforce in large numbers Technology in the USA • Explosion of technology • The airline industry grew with the use of the Jet engine • Eisenhower created the interstate highway system Objectives • Content: – Compare the political and economic systems of the U.S. and the U.S.S.R. – Analyze a political cartoon from the Cold War and determine its message. • Learning: – List the characteristics of the two superpowers. Origins of the Cold War U.S.A. VS. U.S.S.R. Cold War • The state of tension and intimidation between the U.S. and the Soviet Union. • There was no actual fighting, but the rest of the world took sides. Two Superpowers United States • Democracy – government where supreme power rests with the people. • Capitalism – private ownership of goods. Two Superpowers Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.) • Dictatorship – absolute power in the hands of one person • Communism – all people own equally U.S. Policy • During the Cold War, the United States pledged to help any country threatened by Communism. – Containment - to stop the spread of Communism Superpower Competition • Competition took place between the two superpowers (U.S. and U.S.S.R.) in many areas. –Influence –Weapons –Technology Influence • After WWII, the U.S.S.R. dominated Eastern European countries and forced them to accept Communism/ Dictatorship. • The U.S. used money to influence countries in Western Europe to be Capitalist/Democratic. “ From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent” -Winston Churchill, 1946 Weapons • Arms Race competition for military supremacy (nuclear weapons) • Both sides want the most powerful weapons and the largest number of them. Duck and Cover Instructional Video What is the political cartoon trying to tell people about the Cold War? Technology • Space Race - competition for space exploration • Soviets launched first satellite into space (Sputnik) • U.S. was first to land on the moon http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oDtWnCSsBSQ&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1 Objectives • Content: – Compare the Butter Battle Book and the Cold War and explain its symbolism. • Learning: – List facts about telegrams from McCarthy and a draft from Truman. Berlin • First serious Cold War conflict • Blockade • Soviet Union blocked cars and trains in and out of West Berlin. This was an attempt to rid West Berlin of Democracy • Airlift • U.S. responded by airlifting food and supplies to the people of West Berlin http://viewpure.com/cH-GVf9floo?start=0&end=0 Berlin Wall: built by Soviets in 1961 and stood until November 1989 to keep the two sides separate. http://www.history.com/topics/cold-war/berlin-wall/videos/deconstructing-history-berlin-w NATO vs. Warsaw Pact • U.S. and other free countries signed an agreement called the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Promise to defend each other against an attack by a Communist nation (“to attack one is to attack all”) • In response to NATO, Communist countries signed a similar agreement called the Warsaw Pact. – The U.S.S.R. was the leader U.S. At Home: The Red Scare • Red = Communism • Senator Joe McCarthy began a Communist witch hunt in the early 1950’s. He identified US citizens he believed to be supporters of Communism. (McCarthyism) • Thousands of people were accused of espionage (spying), ruining their lives and careers. http://youtu.be/X_uTbVfDtgI Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were accused of spying for the Soviets and were executed http://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/rosenbergs-executed http://nuclearsecrecy.com/nukemap Warm Up: List reasons why you think these tunnels were built Objectives • Content: – Compare maps from the beginning of the Cold War to 1962. • Learning: – List reasons the Vietnamese tunnels were built – List the events of the Cold War in chronological order. Korean War 1950-1953 • After WWII, Korea was occupied by Soviet Union in the North and the U.S. in the South. • Both became their own states – North Korea led by Kim Il Sung (Communist) – South Korea led by Syngman Rhee (anti Communist) • North Korea invaded South Korea and the U.S. sent troops to help South Korea resist the spread of Communism. • After the United Nations sent troops to help South Korea, China helped North Korea. Korean War 1950-1953 • The war eventually ended in a stalemate • The dividing line between North and South Korea is almost in the same position as before the war. http://korean-war.commemoration.gov.au/cold-war-crisis-in-korea/korean-war-strategic-map.php Rising Tensions • U.S. U2 spy plane shot down over the Soviet Union (1960) • Cuban Revolution (1953-1959) – Overthrow of a pro U.S. government by Fidel Castro – Cuba becomes Communist Cuba • Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) – Failed U.S. sponsored invasion of Cuba to take down the Communist government led by Fidel Castro According to this map: Which countries are now Communist? Is the United States containing communism?. Cuba • Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) – “The closest the world ever came to nuclear war” – U.S. spy plane captures pictures of Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba. – President Kennedy ordered a naval blockade of Cuba and demanded the removal of the missiles. • https://youtu.be/H5ZzL9KsyPY https://youtu.be/-yfIoHXOO9E Cuba • 13 day standoff lead to the agreement: – U.S. will never again invade Cuba – Soviet Union will remove all nuclear weapons from Cuba (U.S. will remove also) http://qz.com/314271/a-timeline-of-us-cuban-relations-since-the-cuban-revolution/ Vietnam • Vietnam was divided after they won independence from France in 1954. • North Vietnam was Communist (leader: Ho Chi Minh) • South Vietnam was not (leader: Diem). • North Vietnam wanted to unify both states to form one country with Ho Chi Minh as its leader. Gulf of Tonkin • Gulf of Tonkin Incident – President Johnson used a reported attack on two U.S. ships to pass the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution – The resolution granted Johnson the authority to militarily assist South Vietnam without Congress’ approval. Vietnam War 1955-1975 • By 1965 U.S. was actively fighting with the South Vietnamese to stop the spread of Communism from North Vietnam. • Remember the Domino Theory: If one country falls to Communism, all the surrounding countries are at risk to fall too! http://www.history.com/topi cs/vietnam-war/cu-chitunnels Rise of Anti-War Protests • Americans were sharply divided over involvement in the Vietnam War • Protests increased because there were not enough volunteers for the war. This caused the U.S. government to draft soldiers for the war. Kent State Massacre May 1970 War Ends in Vietnam • The Vietnam War finally ended for the U.S. with a cease fire agreement. • U.S. troops withdrew in 1973. • By 1975 North Vietnam took Saigon and South Vietnam surrendered. Objectives • Content: Evaluate the evidence and determine who won the Cold War. • Learning: Summarize the events of the Cold War. Communism’s Height in 1980 Red = Pro Soviet Union Yellow = Pro China Black – neutral Problems for the U.S.S.R. • Too many different ethnic groups, languages and cultures to stay united. • Unable to keep the country successful with strict communism (and an arms race with the United States) Berlin Wall • 1987- U.S. President Ronald Reagan tells Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev to “Tear down this wall!” • 1989 – Berlin Wall is taken down • Germany reunited in 1990. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YtYdjbpBk6A&feature=related&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mo de=1&safe=active • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wnYXbJ_bcLc&feature=related End of the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.) • By December 25th, 1991 the Communist government of the USSR Collapses – 15 independent countries – Boris Yeltsin - Russian President Communist countries today (5) Cuba, China, Laos, Vietnam & North Korea Who won the Cold War? Explain.