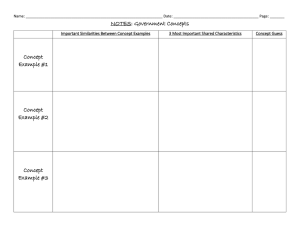
Greece’s Golden Age
advertisement

Greece’s Golden Age Pericles’ Goals 1. _______________________________________ A. _____________________________ people speak for themselves (no representatives) B. _________________government officials – poor men could now serve in the government 2. _______________________________________ - money from the Delian League (alliance of Greek citystates led by Athens) to build up Athens' ___________ 3. ________________________________________ - use money from the Delian League to purchase gold, ivory, and marble and beautify Athens rebuilt acropolis, built new temples for the gods, built the Parthenon, etc… Athens _____________________________ of Greece Greek Art Architecture – _________________ (dedicated to Athena), Design (reflect the order and harmony of the universe), Greek columns (____________, ___________, & __________________________) Sculpture – emphasized natural poses (athletes in motion), realistic (lifelike), and idealistic (gods, goddesses, athletes, etc…) Sculpture: ___________________ 1. Sculptor 2. Statue of Zeus Vases and Pottery Images of ________________ on vases and pottery Greek Drama __________________________ 1. Playwright 2. Tragedies 3. Pride could bring misfortune/the gods could bring down even the greatest hero 4. The Oresteia (The Trojan Wars) ___________________________ 1. Playwright 2. People, not gods, were the cause of human misfortune 3. The Trojan Women (showed suffering of women during the Peloponnesian War) Greek Philosophy _________________________________ 1. Examine one’s beliefs and ideas 2. ___________________________Method question and answer technique to lead pupils to see things for themselves by using their own reason 3. Believed all real knowledge is within each person – “the unexamined life is not worth living” ____________________________________ 1. Student of Socrates 2. Use reason to create the ideal society 3. State should regulate all aspects of a person’s life – did not trust democracy 4. Wrote The Republic (ideal state) a. Philosopher-king (rulers) b. Soldiers (protectors) c. Workers (producers) _______________________________ 1. Student of Plato 2. Did not trust democracy 3. Rule by a virtuous leader (moral example) 4. Reason guided force for learning Herodotus Herodotus 1. Father of ___________________ 2. Stressed the importance of research and bias 3. Wrote _______________________________ Thucydides 1. History of the _____________________________ 2. Placed a lot of emphasis on accuracy and Precision of facts Hippocrates Hippocrates 1. Doctor 2. __________________________________ do no harm (rule of ethics for doctors) Phidias Sculpture: Phidias 1. ___________________ 2. Statue of Zeus Homer 1. Writer 2. _____________________________ Math & Science _____________________________ 1. Physicist 2. Lever and pulley for moving heavy and large objects _____________________________ 1. Mathematician 2. The Elements – basis for modern geometry _____________________________ 1. Mathematician 2. Pythagorean Theorem