Literary Elements

Literary Elements
Fiction: Fiction writing is writing that is created or made up.
Short Story: A short story is a piece of fictional writing with one major plot.
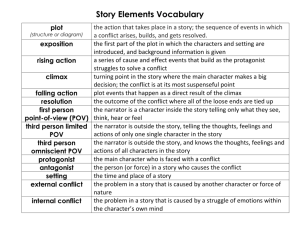
Plot: Plot is the sequence of events of a story.
Exposition: The exposition is the beginning of the story; the reader finds out the setting, characters, and background information of the story.
Initiating Event: The initiating event is the one event in the story that starts the conflict.
Rising Action: The rising action contains all the events that develop the conflict of the story.
Climax: The climax is the turning point of the story.
Falling Action: The falling action contains all the events that lead to the end of the story.
Resolution: The resolution is the ending of the story; the conflict is resolved.
Setting: The setting is the time and place of the story.
Theme: The theme is the central message or insight into life revealed through the story. It may be stated or implied.
Foreshadowing: Foreshadowing is the use of clues and hints that suggest events that have yet to occur.
Flashback: Flashback is a section of a literary work that interrupts the sequence of events to relate an event from an earlier time.
Point of view: The point of view of the story is determined by whom is telling the story.
First person point of view: First person point of view is when a character in the story is telling the story.
Third person limited point of view: Third person limited point of view is when a narrator is telling the story who is not in the story. This narrator follows the events of one of the characters.
Third person omniscient point of view: Third person omniscient point of view is when a narrator is telling the story who is not in the story. This narrator can follow the events of all of the characters.
Irony: Irony is the technique that shows a difference between what is expected and what actually happens.
Symbolism: Symbolism is the use of symbols in a story. A symbol is a concrete object that represents an abstract idea.
Dynamic Character: A dynamic character is one who changes or grows during the course of a story.
Static Character: A static character is a character whose characteristics do not change over the course of the story.
Conflict: A conflict is a struggle between two opposing forces.
External Conflict: An external conflict is created when the main character struggles with an outside force.
Internal Conflict: An internal conflict is created when the main character struggles with a problem inside himself.