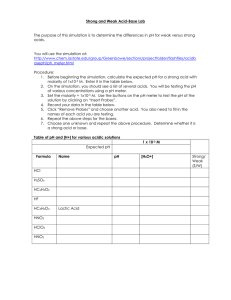
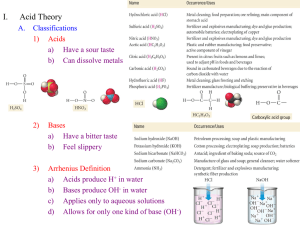
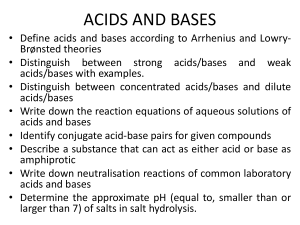
Acid/Base Study Guide Unit 11 Arrhenius pOH = - log[OH ]
advertisement
![Acid/Base Study Guide Unit 11 Arrhenius pOH = - log[OH ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/017612661_1-9dac3d919856aa6dfb79c8f84ce638fb-768x994.png)
Acid/Base Study Guide Unit 11 Key terms and Concepts Arrhenius o Arrhenius acid H3O+ o Arrhenius base OHBronsted-Lowry o Bronsted- Lowry acid o Bronsted- Lowry base o Conjugate acid o Conjugate base Lewis o Acid o Base Amphoteric Polyprotic acid Binary acids Ternary acids [H3O+] > [OH-] [H3O+] = [OH-] pH= -log [H+] Questions you should be able to answer 1. What is the acid ion? 2. What is the base ion? 3. What does pH measure? 4. What does pOH measure? pOH = - log[OH-] [H3O+] < [OH-] 𝐾𝑤 [H3O+] = [OH−] 𝐾𝑤 [OH-] = [𝐻 3𝑂+] Dissociation Properties of Acids Properties of Bases Titrations o Indicator Phenolthalein o Equivalence point Buffer pH pOH Naming o Acids and bases 5. What is the pH scale? a. On the scale, what range is acidic b. What range is basic c. What is neutral Acid/ Base Pairs Identify 1. In the equation below identify what is the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base. H2CO3 + H2O H3O+ + HCO3- H2O + NH3 NH4+ + OHNaming Acids Questions 1. Name the following acids: a) HF b) HBr c) H2S 2. Name the following acids: a) H2SO4 b) H2CO3 3. Name the following acids: b) HNO2 c) H2SO3 4. Name the following bases: a) Mg(OH)2 b) LiOH Math: complete the following Math problems (show all work) pH problems 1. What is the pH of the solution if the concentration is a. [H+] = 0.0056 M b. [OH-] = .000780 M 2. Identify if the solution in problem #1 is an acid or base. a. b. Titration Problems M1V1 = M2V2 3. If it takes 54 mL of 0.1 M NaOH to neutralize 125 mL of an HCl solution, what is the concentration of the HCl? 4. If it takes 25 mL of 0.05 M HCl to neutralize 345 mL of NaOH solution, what is the concentration of the NaOH solution?