WORLD HISTORY I SOL STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

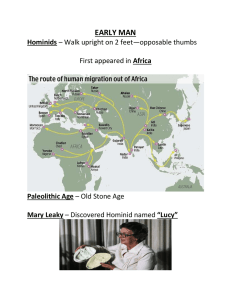
WORLD HISTORY I SOL STUDY GUIDE EARLY MAN Hominids – Walk upright on 2 feet First appeared in Africa Paleolithic Age – Old Stone Age Mary Leaky – Discovered Hominid named “Lucy” Australopithecines – first known hominid Homo Habilis – first to make stone tools Homo Erectus – first to discover fire Neanderthals – first to have burials and migrated to Europe Homo Sapiens – name for modern humans No written language but did have cave art Nomads – moved from place to place, followed the food Hunters and gathers – how they got their food Neolithic revolution – developed agriculture Egypt Located along the Nile River Cataracts – churning rapids along the Nile Delta – broad, marshy, triangular area of land formed by silt Menes – united upper and lower Egypt Pharaoh – name for Egyptian God-Kings Pyramids – used as a tomb for the pharaohs Theocracy – belief that rulers are seen as gods Mummification – process of preserving the dead Hieroglyphics – Egyptian form of writing, written on papyrus Huge influence on the Kush Indus River Valley/Hindu religion India is known as the subcontinent of Asia Monsoons – seasonal winds and rain Indus River is found in modern day Pakistan Mohenjo-Darro and Harappa - major cities of the Indus River Valley Planned cities on a grid system Plumbing was used for first time in a civilization Invented the first ancient toilet No explanation for how the civilization ended Caste System – class structure of Hinduism: Brahmins(priest), warriors, and peasants. Untouchables lowest of the low in the caste system Vedas and Upanishads – sacred writings of Hinduism Mahabharata – great Epic of the Hindu people Moksha – reaching enlightenment in Hinduism Golden Age – height of culture under Gupta. Developed math and the number system (zero) Buddhism Founded by Siddhartha Gautama also known as Buddha Nirvana – the idea of reaching full enlightenment Reincarnation – Individual’s sole or spirit is reborn Karma – what you do in this life affects your next Dharma – an individual’s moral duties Four Noble truths – deal with suffering and overcoming your desires in life Eightfold Path – a Buddhist stairway to enlightenment Phoenicians Located on eastern shore of Med. Sea, Skilled sailors Created the beginnings of the alphabet (phonetic symbols) used today. Developed purple dye called murex from snails Minoans Located on island of Crete in Mediterranean sea. Traders and skilled sailors, made pottery. Women held high rank. King Minos – ruler of Minoans. Knossos – Major city Minotaur – half man half bull monster of the Labyrinth Early Civilizations 5 Characteristics of civilization: 1) Advanced City – people living together 2) Specialized worker – skilled at 1 thing 3) Complex institution – form a government 4) Record keeping – keep track of city info 5) Advanced Technology – new tools Scribes – professional record keepers Cuneiform – first form of writing in Sumer “wedge shaped” Bronze Age – time when people began using bronze instead of copper and stone Artisan – skilled workers Ur – one of the earliest cities in Sumer Ziggurat – Sumerian temple, used for priests to live, grain to be stored, ritual sacrifices Early River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia – “Land between the Rivers” area between the Tigris and Euphrates Located in modern day Iraq Fertile Crescent – Curved shaped area of the world from the edge of the Med. Sea to Sumer. Silt- rich, new soil that made soil perfect for farming Irrigation – new technology for watering agriculture Dynasty – series of rulers by a single family City-State – a city and its surrounding lands Cultural diffusion – process of spreading new ideas from one culture to another Polytheism – belief in many gods Sargon of Akkad – conquered the land of Mesopotamia Hammurabi – created a code of laws, Babylonian Ancient China Located along the Huang He (yellow) River and the Yangtze River Geographically isolated and protected by Himalayas, deserts and Pacific Loess – yellowish silt used for farming Chinese Writing – even though not everyone spoke the same dialect they could still read it Oracle bones – used by priests to talk to the gods Mandate of Heaven – way to justify taking over and become ruler, divine right Dynastic Cycle – the rise, decline, and replacement of dynasties Qin Shi – dynasty that built the Great Wall of China to keep out the Mongols Emperor Wudi – developed a civil service code for how government should work Silk Road- trade route connecting china to Roman Empire Chinese were known for silk, the compass, gun powder, porcelain and paper Daoism/Taoism – individuals relationship with nature, ying-yang: opposing forces Confucianism – respect for your elders and thrive from education Worship of ancestors Persian Empire Controlled land from central Asia to Mediterranean Sea Cyrus – king who showed tolerance toward people, created an imperial bureaucracy where satraps (governors) would control parts of the empire for the king Zoroastrianism – religion emphasized good over evil. Zoroaster was the founder of the religion Royal Road – main road throughout empire for king to travel around to his vast lands Darius and Xerxes – father and son who both fought against the Greeks and lost during the Persian Wars Judaism Located between Jordan River and Mediterranean Sea 1st monotheistic religion belief in ONE god. Hebrews – name for those who follow the Jewish faith Abraham – founder of Judaism led his people from Mesopotamia Moses – led Hebrews from Egypt (Exodus) received the Ten Commandments from god on top of Mt. Sinai Covenant – Promise between god and man Torah – Holy book of Judaism (1st five books of the Bible) Ancient Greece Geography is divided by Mountains which influenced the development of city-states. Athens – life centered on education. Direct Democracy (citizens make laws) Pericles led the Golden Age of Athens. Built the Parthenon to worship gods. Reformers (people who made change) – Draco, Solon, Cleisthenes (democracy) Sparta – life centered on military. Ruled by an oligarchy (group of leaders) led 300 in the Battle of Thermopylae against the Persians Persian Wars – fought against Persia (Darius and Xerxes) Battle of Marathon Peloponnesian War – Athens vs. Sparta (led to downfall of Greece) Trojan War – war fought to expand empire to the Black Sea…….or maybe a chick? Delian League – created to bring all of Greece together to solve problems Homer – wrote epics such as the Iliad and the Odyssey Philosophers- great thinkers of Greece – Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle Greek Columns – great architectural Design (Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian) Alexander the Great- Expanded Greece (Hellenistic Period) Alexandria became the center for Greece and the spread of Hellenistic Culture Islam Originated on the Arabian Peninsula Language spoken was Arabic Religion founded by Muhammad Moved from Mecca to Medina Quran/Koran – Holy book of Islam 5 Pillars of Islam - Declare Faith (no God but Allah) - Pray 5 Times a Day (facing Mecca) - Giving Alms (money to the poor) - Fasting during Ramadan (can’t eat or drink) - Pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) Dome of the Rock – Islamic mosque (Jerusalem) Battle of Tours – stopped Muslim advance in the rest of Europe. Charles Martel led the fights against the Muslims. Saladin – Muslim leader who Reclaimed holy land (2nd crusade) Christianity Origins of the religion are from Judaism Jesus crucified by Romans (Pontius Pilate) Bible – sacred book of the religion Gospels – first four books of the Bible Disciples – followers of Jesus (Peter and Paul) Byzantium and Russia Located in Asia Minor (Turkey) Capital was Constantinople Justinian – Emperor who created code of laws Artwork – mosaics(broken glass) Icons (religious pics) Great Schism – split of the church Eastern Orthodox Church – New religion that didn’t recognize pope’s authority Hagia Sophia – Orthodox church in Constantinople Saint Cyril created the Cyrillic Alphabet to translate the Bible into Russian Ancient Rome Located in the center Italian Peninsula. Tiber and Po River. Alps Mountains to the North Language was Latin Roman Mythology influenced the names of the planets. Patricians – Upper class Citizens Plebeians – Lower class citizens Timeline of Roman Government - Monarchy, Republic, Empire, Decline During the Republic – Consuls (head of Gov.) Senate (most powerful) Assembly (Plebeians) - Representative democracy, used the Forum to discuss making laws Julius Caesar – declared himself absolute ruler, killed by the senate Triumvirate – group of three leaders of Rome (first and second) Augustus Caesar – First Roman Emperor, senate declares absolute power for life! Punic Wars – fought between Rome and Carthage (N. Africa) Hannibal - Led Carthage Scipio – Led Rome Pax Romana – 200 years of peace and prosperity in Rome Twelve Tables - Rome’s written code of laws Pope – head of the Catholic Church, much power in Rome Coliseum – Gladiator fights Circus Maximus - Chariot races Aqueducts – built to bring water into the city (used the arch) Middle Ages Also known as the Dark Ages of Europe Feudal System – Gov. based on land. Structure: Kings, Lords, Vassals, Serfs Germanic Invaders - Vikings (Scandinavia) Anglo-Saxons (England) Magyars (Hungary) Franks – most powerful Germanic Tribe Charlemagne – Holy Roman Emperor ENGLAND William the Conqueror – united England Magna Carta – document which gave some rights and limited King’s power Hundred Year’s War – fought between England and France over land FRANCE Joan of Arc – French peasant girl whose visions helped lead France to victory SPAIN Ferdinand/Isabella –to rid Spain of Muslims (Reconquista) Inquisition – people accused of Heresy(against the Church) RUSSIA Ivan the Great – conquered the Mongols Crusades – started by Pope Urban II to reclaim the holy land of Jerusalem Richard the Lionhearted – led many of the crusades against the Muslims Black death (bubonic plague) – led to population decline across Europe killing millions. Plague brought over by fleas from rats along the trades routes of Asia. Renaissance Machiavelli – wrote “The Prince” about government support of absolute power and how to rule by fear! Humanism – philosophy that believes in worth of a person Petrach – father of Humanism Gutenberg - created the printing press. First printed the Bible ART Leonardo da Vinci - Mona Lisa and Last Supper Michelangelo – the “David” and painted ceiling of Sistine Chapel Japan/Africa/Mesoamerican Civilizations JAPAN (series of Islands – archipelago) -Influenced by China Shinto - state religion Tori – Shinto shrine AFRICA Axum - East Africa (Christian city) Zimbabwe – Southeast Africa Ghana/Mali – traded gold and salt Timbuktu – trade center of Mali MESOAMERICA (worshipped Sun, had calendars, math, sacrifices) Mayans - Central Mexico Chichen Itza – sacred pyramid Life revolved around trade and agriculture Aztecs – Central Mexico, near Mexico City. Tenochtitlan capital city Life focused agriculture and warfare Incans - Andes Mountains of South America (Peru) Machu Picchu – city in the mountains Used terrace farming