1. What is the Law of Demand?
advertisement

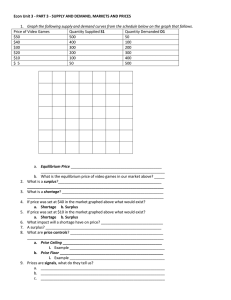
ECONOMICS STUDY GUIDE 1. What is the Law of Demand? 2. What is the Law of Supply? 3. What is a Complementary Good? 4. What is a Substitute Good? 5. List the Demand Shifters: (have these memorized for the test!) T R I B E 6. List the Supply Shifters: (have these memorized for the test!) R O T T E N 7. What is Equilibrium and how do you find it? 8. What is a shortage and what causes you to have one? 9. What is a surplus and what causes you to have one? UNIT 2 (CHAPTERS 5-7) ECONOMICS STUDY GUIDE UNIT 2 (CHAPTERS 5-7) 10. What are the four areas we look at to determine how competitive a market is? 11. What is perfect competition? 12. What is monopolistic competition? 13. What is an oligopoly? 14. What is a monopoly? 15. Give an example of a positive externality and one example of a negative externality. 16. What is a public good? APPLICATION & PRACTICE Chap 5 Supply & Demand Illustrate the Law of Demand Illustrate the Law of Supply If only price changes, then we move ____________________. If TRIBE or ROTTEN happen, then the curve______________. Substitutes : Substitutes Price of A↑ Demand for B ____ Complements Complements: Price of A↑ Demand for B ____ Price of A↓ Demand for B ____ Example: Price of A↓ Demand for B ____ Example: ECONOMICS STUDY GUIDE UNIT 2 (CHAPTERS 5-7) Chap 6 Supply & Demand Shifters Ice Cream KFC Chicken Shift the curve… New discovery: Ice Cream makes you live longer!! Shift the curve… Price of chicken feed rises drastically!! Equilibrium and Disequilibrium* Shortage Surplus Equilibrium- Qd ____Qs Shortage- Qd ____Qs Surplus- Qd ____Qs Government Controls* Price FLOORS go ______________ equilibrium and result in a _________. Price CEILINGS go _____________ equilibrium and result in a _________. Chapter 7 Label the four different market structures on the arrow below. Place the least competitive market structure on the far left and the most competitive market structure on the far right. Level of Competition ECONOMICS STUDY GUIDE UNIT 2 (CHAPTERS 5-7) 1. What is the Law of Demand? The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. As price goes up, quantity demanded goes down. As price goes down, quantity demanded goes up. 2. What is the Law of Supply? The direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. As price goes up, quantity supplied goes up. As price goes down, quantity supplied goes down. 3. What is a Complementary Good? A product that is used or consumed jointly with another product. (ex.: cheeseburgers and buns, tennis rackets and tennis balls) 4. What is a Substitute Good? A product that may be used in place of another product. (ex.: Toms and Bobs shoes, iPod and Zune) 5. List the Demand Shifters: (have these memorized for the test!) Tastes and preferences Related goods (complementary & substitute) Income Buyers (# of) Expectations of consumer 6. List the Supply Shifters: (have these memorized for the test!) Resources (cost & availability) Opportunity cost of alternative production Technology Taxes & subsidies (Government action) Expectations of future profits Number of sellers 7. What is Equilibrium and how do you find it? Equilibrium is the point at which the quantity of a product demanded by consumers in a market equals the quantity supplied by producers. You find it by locating where the supply and demand curves intersect. 8. What is a shortage and what causes you to have one? A shortage is when the quantity demanded is higher than the quantity supplied. This occurs when the price is set too low, such as with a price ceiling. 9. What is a surplus and what causes you to have one? A surplus is when the quantity supplied is higher than the quantity demanded. This occurs when the price is set too high, such as with a price floor. ECONOMICS STUDY GUIDE UNIT 2 (CHAPTERS 5-7) 10. What are the four areas we look at to determine how competitive a market is? Number of producers, similarity of products, ease of entry, control over prices. 11. What is perfect competition? Perfect competition is when there are many producers and consumers, identical products, easy entry into the market, and when producers have no control over prices. 12. What is monopolistic competition? In monopolistic competition there are many producers selling differentiated products (different products that could be substitutes like pizza and tacos), with few barriers to entry and some control over prices. 13. What is an oligopoly? An oligopoly is when there are few producers selling similar products in a market with high barriers to entry where the producers have some control over the prices. 14. What is a monopoly? A monopoly occurs when there is only one producer selling a unique product in a market with high barriers to entry and a producer with substantial control over prices. 15. Give an example of a positive externality and one example of a negative externality. When I get a flu shot I provide a positive externality to people I encounter who won’t be exposed to me with the flu. Pollution from a factory is a negative externality to neighbors of the factory. 16. What is a public good? A public good is a good or service that is not provided by the market system because of the difficulty of getting people who use them to pay for their use. APPLICATION & PRACTICE Chap 5 Supply & Demand Illustrate the Law of Demand Illustrate the Law of Supply If only price changes, then we move along the curve. If TRIBE or ROTTEN happen, then the curve shifts. Substitutes : Substitutes Price of A↑ Demand for B ____ Price of A↓ Demand for B ____ Example: iPod and Zune, McDonald’s or Chic-fil-A, Oreos and Tuxedos Complements Complements: Price of A↑ Demand for B ____ Price of A↓ Demand for B ____ Example: Peanut Butter and Jelly, Hamburgers and Buns, Tennis Rackets and Tennis Balls ECONOMICS STUDY GUIDE UNIT 2 (CHAPTERS 5-7) Chap 6 Supply & Demand Shifters Ice Cream KFC Chicken Shift the curve… New discovery: Ice Cream makes you live longer!! Shift the curve… Price of chicken feed rises drastically!! Equilibrium and Disequilibrium* Shortage Surplus Equilibrium- Qd _=__Qs Shortage- Qd _>__Qs Surplus- Qd _<___Qs Government Controls* Price FLOORS go _ABOVE equilibrium and result in a _SURPLUS_. Price CEILINGS go _BELOW_ equilibrium and result in a _SHORTAGE_. Chapter 7 Label the four different market structures on the arrow below. Place the least competitive market structure on the far left and the most competitive market structure on the far right. Level of Competition